Эндрю «Сэнди» Ирвин (Andrew «Sandy» Irvine ) и Джордж Мэллори (George Mallory)
История альпинизма полна героических моментов, загадок и противоречий.
Одной из такой крупнейшей загадкой является восхождение на Эверест в 1924 году англичан: Джорджа Мэллори (George Mallory) и Эндрю «Сэнди» Ирвина (Andrew «Sandy» Irvine )..
Успех этого восхождения в не сомнения был бы экстраординарным событием в мире альпинизма, и даже спустя почти 30 лет, когда на вершину Эвереста поднялись непалец-шерпа Тенцинг Норгеей (Tenzing Norgay) и новозеландцец Эдмунд Хиллари (Edmund Hillary) это событие стало мировой сенсацией!
Но тем не менее, до сих пор остается загадкой кто-же на самом деле первым взошел на Эверест, эта тайна по прежнему будоражит умы многих альпинистов и историков, становясь для некоторых из них навязчивой идеей и делом чуть ли не всей жизни.
Ключевой вопрос в этой загадке: были ли Джордж Мэллори и Эндрю «Сэнди» Ирвин на вершине Эвереста в 1924 году все же может быть однозначно решен, несмотря на то что с тех пор прошло практически 90 лет! Дело в том, что хотя и было найдено тело Джорджа Мэллори на склоне Эвереста, но тело Эндрю «Сэнди» Ирвина и что особо важно их походный фотоаппарат так и не были найдены!
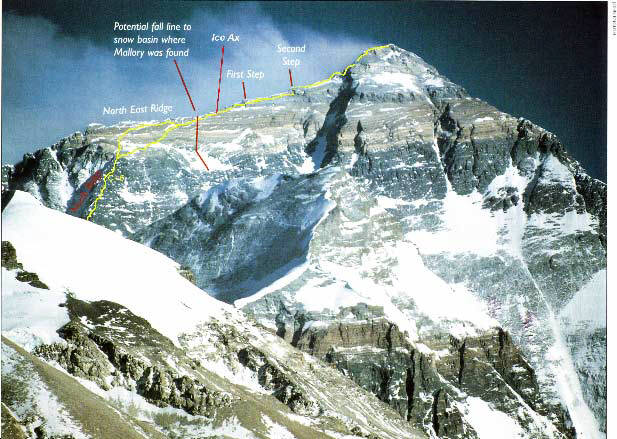
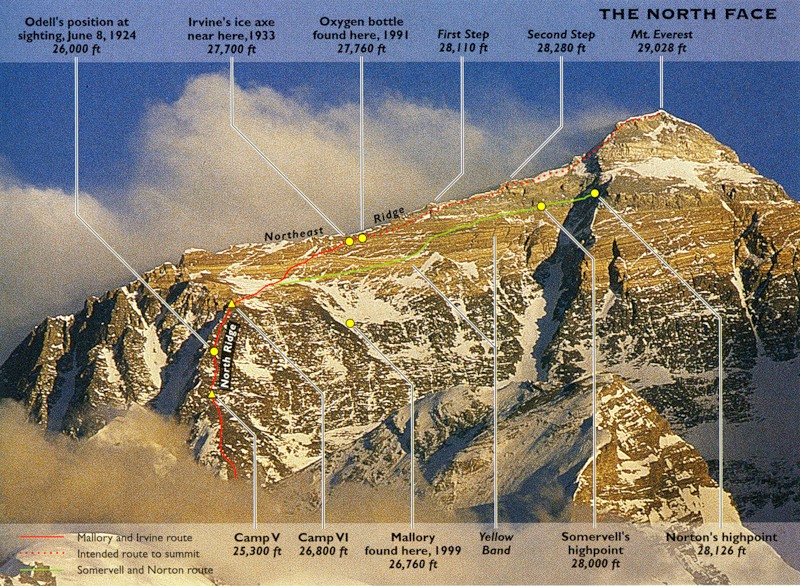
маршрут Мэллори и Ирвина и отметки находок их экспедиции
Конечно, без однозначных весомых доказательств восхождения 1924 года безусловно считается что первыми людьми взошедшими на Эверест были непалец-шерпа Тенцинг Норгеей (Tenzing Norgay) и новозеландцец Эдмунд Хиллари (Edmund Hillary) в 1953 году, спустя 29 лет после Мэллори и Ирвина.
Сегодня, историк альпинизма и исследователь Эвереста Tom Holzel уверен, опираясь на некоторые новые исследования, что ему известно где на склоне Эвереста нужно искать тело Ирвина и их фотоаппарат, что бы навсегда разгадать эту альпинистскую загадку века.
Прежде чем расспросить подробней Тома о его бедующих поисках, давайте немного остановим свое внимание на Северном склоне Эвереста.
Северный склон Эвереста был эпицентром первых попыток восхождения на Эверест на протяжении 1920-х годов.
Первая такая попытка была осуществлена Британской командой в 1921 году, тогда Джордж Мэллори во главе небольшой группы альпинистов стали первыми людьми, ступившими на слоны Эвереста и поднявшимися до высоты Северного Седла (7003 м).
Вторая Британская экспедиция в 1922 году достигла отметки 8320 м, однако из-за трагедии (под лавиной погибли семь шерпов) восхождение было прервано. При этом это была первая в мире экспедиция в которой альпинисты пользовались кислородными баллонами – совершенно инновационный и неизвестный метод в альпинизме в то время..
А следующая экспедиция 1924 года уже стала мировой загадкой тогда, когда Мэллори и Ирвин навсегда исчезли в дымке облака на предвершинном гребне (у второй ступени Эвереста).
Последний раз Джорджа Мэллори и следовавшего с ним молодого альпиниста Эндрю Ирвина, восходящих к вершине по северо-восточному хребту на высоте чуть выше 8500 метров, наблюдал и снимал член экспедиции, кинооператор и геолог Ноэль Оделл. Затем они скрылись за облачностью и тех пор живыми их никто не видел.
Через 75 лет в 1999 году тело Мэллори было найдено американской экспедицией на высоте 8155 метров. Оно было запутано страховочной веревкой и находилось ниже на 300 м от найденного ледоруба Ирвина, что указывает на возможный срыв альпинистов с горы. Тело Ирвина так и не было найдено.
При этом не было никаких однозначных доказательств в какой фазе экспедиции произошла трагедия: при подъеме на Эверест или уже при спуске.
Таким образом, важность поиска фотокамеры, которую брали с собой Мэллори и Ирвин на которой могла остаться фотографии с вершины Эвереста (в том случае если альпинисты все же взошли на вершину) остается на сегодняшний день приоритетной задачей.
Косвенно о покорении Эвереста в 1924 году говорят и те факты (по мнению эксперта Грэхэма Хойлэнда, несколько лет посвятивший изучению восхождения 1924 года), что, Мэллори, учитывая малоопытность своего напарника, мог выбрать более лёгкий путь (третью ступень), где их и видел Оделл. В таком случае достигнуть Эвереста им не составляло существенных проблем, а погибнуть они могли уже при спуске. В кармане одежды Мэллори были найдены солнцезащитные очки, что указывает, что срыв произошел в темноте, но не была найдена фотография его жены Рут, которую он обещал оставить на вершине Эвереста!
25 мая 1960 года было осуществлено первое покорение Эвереста по Северной стене со стороны Тибета, которое было осуществлено китайской экспедицией, ее членами: тибетцем Nawang Gombu и китайцами Chu Yin-Hau и Wang Fu-zhou.
Спустя 5 лет в переполненном актовом зале Географического Общества СССР, в Ленинграде, Ван Фу-чжоу, рассказывая о восхождении, впервые сказал сенсационную фразу:
– На высоте около 8.600 метров мы нашли труп европейца.
Зал загудел, эхо трагедий далеких 20-х годов, ледяным дыханием коснулось сидящих альпинистов.
– Почему Вы думаете, что это был европеец? – Вопрос прозвучал первым после окончания доклада.
Ответ был по восточному мудр и по военному лаконичен:
– Он был в подтяжках…
Более подробней о этой Китайской экспедиции на Эверест читайте в статье: Впервые на Эверест с Севера. Китайское первопрохождение >>>>>
Однако, несмотря на мировую известность этой экспедиции многие альпинисты все же сомневались в первопрохождении китайской команды на вершину Эвереста, ведь китайцами так и не были представлены фото сделанные с самой вершины Эвереста.
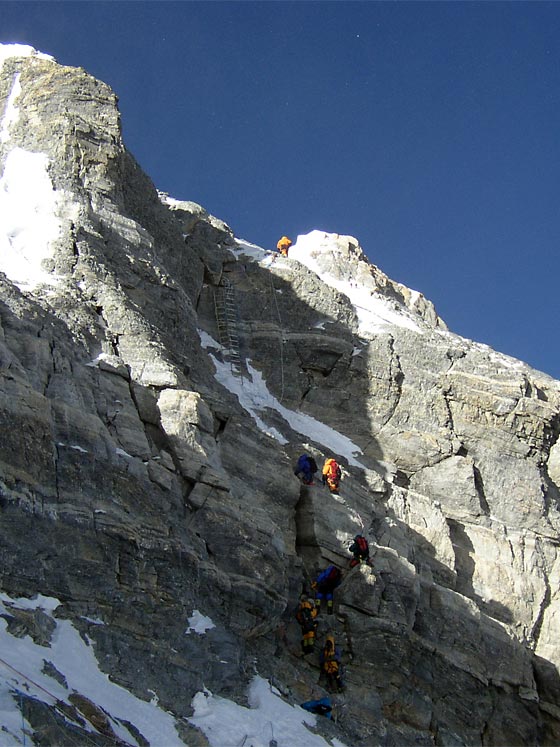
Следующая китайская экспедиция в 1975 году также была успешной, и уже в ее ходе китайцами была установлена стационарная лестница с помощью которой альпинисты могли гораздо легче преодолеть «Вторую Ступень». Эта лестница используется до сих пор.
Кроме того, член этой экспедиции, китайский альпинист Wang Hung Bao заметил тело мертвого человека примерно в 20 минутах ходьбы от их высотного лагеря Camp4 на Северной стене Эвереста. Позже он описал этого человека как «Мертвый англичанин», также он рассказывал что одежда этого человека расспалась в прах, как только он ее коснулся, а щеки были выклеваны птицями (goraks – большие тибетские вороны, которых неоднократно замечали альпинисты в высоких зонах Эвереста).
Он сообщил примерные координаты. Другие подробности остались неизвестны, так как вскоре китаец сам погиб в снежной лавине.
«Вторая Ступень» — Это крутой гладкий откос на высоте 8.570-8.600 метров над уровнем моря, его относительная высота – около 30 метров, а средняя крутизна 60-70 градусов. Он такой гладкий, что на нем почти нет никаких точек опоры.
Лестница на второй ступени Эвереста на отметке 8600 метров
В последствии все экспедиции, поднимавшиеся на Эверест тщетно искали какие либо доказательства первого его покорения в 1924 году…
А в 1933 году был найден деревянный ледоруб Ирвина на склоне Эвереста…
В 1933 году, британский альпинист Перси Вин-Харрис (Percy Wyn-Harris), совершавший попытку покорения Эвереста остановился на отметке чуть ниже «Первой ступени» чтобы согреть холодные ноги. Глядя на «Желтую Полосу» (The Yellow Band – осадочные породы из песчаника, верхняя отметка – 7620 метров на эвересте), под ногами он заметил, причудливый полуразрушенный кусок дерева. В итоге оказалось, что он нашел кусок ледоруба, и большинство альпинистов полагает что это был ледоруб Ирвина, ведь известно что до 1933 года на такой высоте могли быть лишь Мэллори и Ирвин.
Джон Мэллори с ледорубом своего отца. На спуске после штурма вершины в 1922 году Джордж Мэллори с помощью этого ледоруба спас жизнь своих товарищей
.
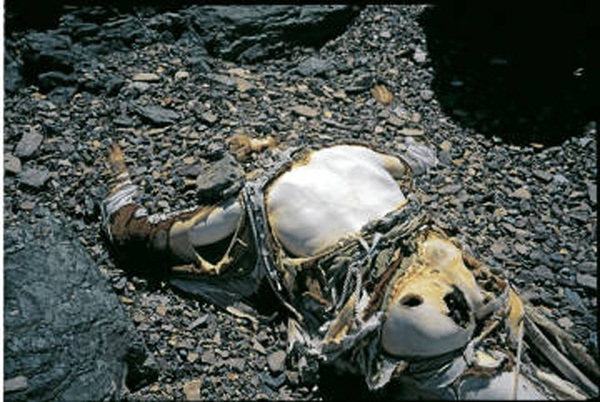
Затем в 1999 году командой альпинистов во главе с основателем IMG: Эриком Симонсоном (Eric Simonson ) была проведена обширная поисковая операция на склонах Эвереста по поиску следов Мэллори и Ирвина: Mallory & Irvine Research Expedition. Тогда, членом поисковой экспедиции Конрадом Анкером (Conrad Anker) и было найдено тело Джорджа Мэллори.
Тело Джорджа Мэллори (George Mallory) на Эвересте
Тело было обнаружено на Северной стене на отметке ниже той, на которую указывал китайский альпинист Ван Фу-чжоу. Однако ни тело Ирвина ни его фотоаппарат так и не были найдены.
Кроме того были обнаружены и многие другие вещи экспедиции 1924 года: часы, высотомер, подробные списки снаряжения, защитные очки, и веревка.
Найденные в 1999 году на Эвересте вещи экспедиции 1924 года принадлежавшие Мэллори и Ирвину.
В 2001 году Эриком Симонсоном была организована вторая поисковая экспедиция целью которой был поиск теля Ирвина и фотоаппарата, но результаты по прежнему были отрицательными. Это все равно что искать иголку в стоге сена, ведь поиск сильно осложняется постоянным снежным покровом на склоне Эвереста.
Но все же в этой поисковой экспедиции были найдены остатки высотного лагеря Camp4 Британской экспедиции 1924 года на Северном хребте Эвереста чуть ниже отметки 8230м.
Также были найдены тяжелые, шерстяные варежки которые могли принадлежать либо Мэллори либо Ирвину.
В то же время обнаружение тела Мэллори вновь подняло волну обсуждений по всему миру, и поскольку эта находка так и не приоткрыла тайны первопокорения Эвереста, то это лишь способствовало спекуляции.
Историк Эвереста и альпинист Том Хользел (Tom Holzel), тот, который проводил посковую операцию на Эвересте в 1986 году сейчас имеет основания полагать где нужно искать фотоаппарат экспедиции 1924 года. Его уверенность основана на двух фотографиях одна из которых была сделана в 1933 году, а другая в 1984 году. Оба эти фото были сделаны с борат самолета, пролетавшего над Эверестом. Причем фотография 1984 года была сделана в очень хорошем качестве.
Том Хользел, использовал для изучения и сравнения этих фото современную технологию визуализации и обнаружил, что расположение отметки места падения Мэллори и Ирвина, была смещена на 60 метров! Для Тома это было шокирующей информацией! Ведь оказалось что поисковые операции проходили не в том месте где следовало бы искать следы Мэллори и Ирвина.
В соответствии с этой новой информацией Том определил место, и обнаружил на фотографиях некое образование выделявшееся на фоне снежного покрова, которое он обозначил как «продолговатая капля» (“oblong blob”). Это место находится совсем рядом с тем местом на которое указывал в 1975 году китайский альпинист Wang Hung Bao.
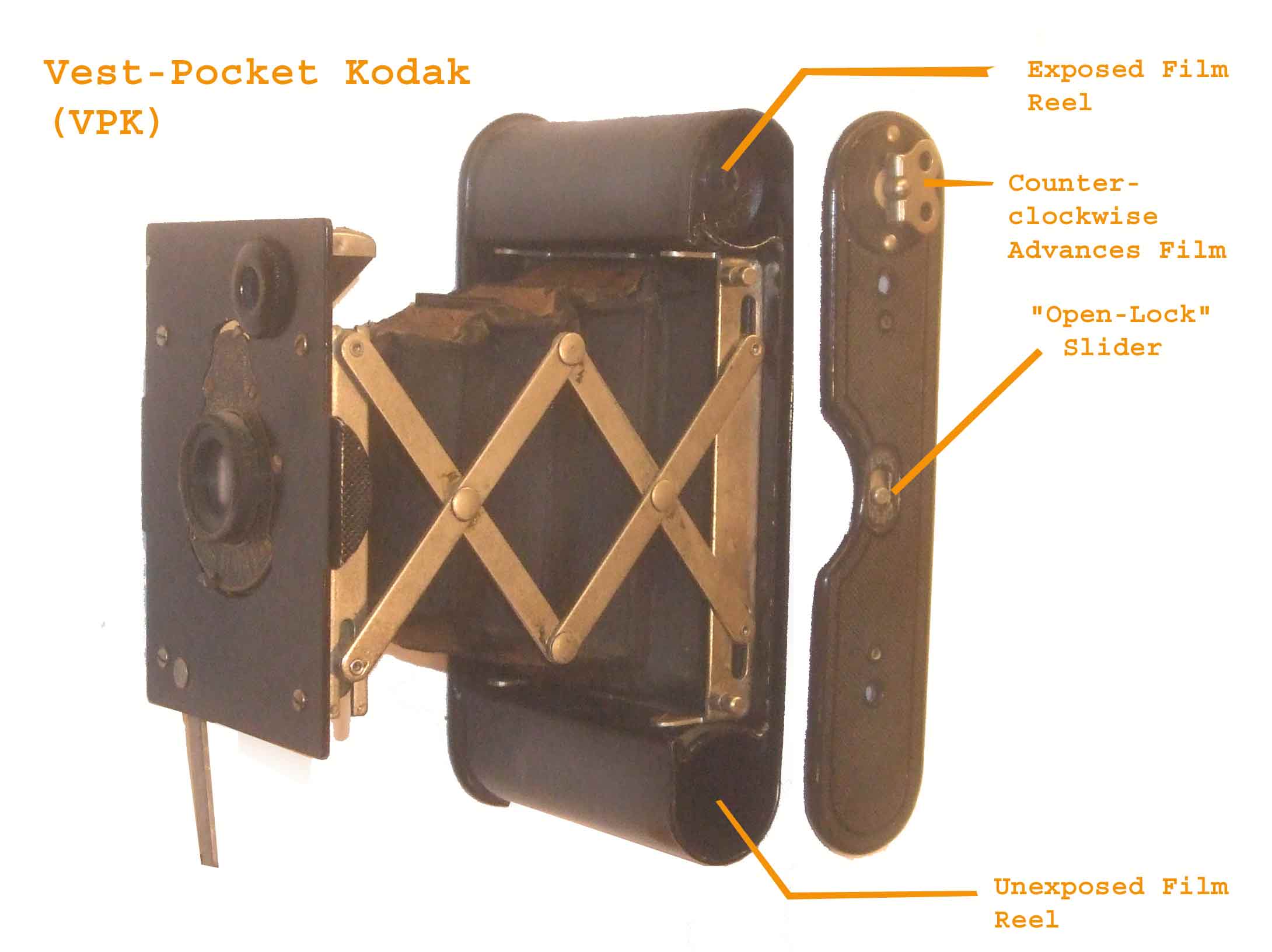
И Том уверен что эта «продолговатая капля» (“oblong blob”) и есть то самое искомое тело Ирвина, а его необычная форма вызвана тем, что Ирвин при себе нес большую фотокамеру « Kodak».
фотокамера « Kodak» которая использовалась Мэллори и Ирвином в 1924 году
Сечас Том Хользел планирует организовать проект целью которого на первом этапе будет фотографирование уже с применением современнейшей фототехники данного участка Эвереста с борта самолета. Полученные фотографии позволят, как считает Том однозначно определить место положения тела Ирвина.
Для реализации этого проекта Тому необходимо собрать еще около $ 10.000.
Для проведения поисковой операции, которая станет второй фазой проекта Том собирается привлечь лишь двух альпинистов: Тома Полларда (Thom Pollard) и Джейка Нортона (Jake Norton) – участников поисковой экспедиции 1999 года.
Также Том провел переговоры с специалистами компании Kodak, которые гарантировали, что если камера будет найдена, то компания возьмет на себя ответственность за выемку фотоснимков, чтобы быть уверенными что фотографии, хранящиеся на пленке не повредятся при попытке их проявить.
маршрут Мэллори и Ирвина и отметки находок их экспедиции
Ниже мы представляем интервью с Томом Хользелом о его происковом проекте:
Том, ты долгое время занимаешся решением загадки восхождения Мэллори и Ирвина, скажи, сейчас мы уже близько от разгадки этой тайны?
Да, я думаю что близко, однако большинство выводов сейчас сводится не к тому варианту который хотели бы услышать поклонники экспедиции 1924 года, и отчасти в этом виноват я сам. Еще в 1971 году в альпинистском журнале Mountain Magazine №17 я сделал анализ всех известных восхождений на Эверест за период с его первых попыток восхождения, я собрал около 69 различных треков, провел анализы с восхождениями в которых использовался кислород, провел анализы по времени, скорости восхождения и набору высоты и исходя из этих материалов я сделал вывод что шансы на успех Мэллори и Ирвина были сильно занижены.
В то время, до Второй Мировой Войны, Британские альпинисты считали что любое теоретическое преимущество в высокогорном альпинизме сводится на нет дополнительным весом снаряжения.
Однако, я, опираясь на данные о восхождениях, сделал вывод что при использовании кислородных баллонов на высотах выше 8000 метров скорость восхождения получает заметное преимущество по сравнению с бескислородным восхождением.
Как Вы оценивали и проводили расчеты для восхождения Мэллори и Ирвина?
Я провел оценку скорости восхождения Мэллори и Ирвина до 6 июня, когда они поднимались без кислорода. Оказалось что скорость их восхождения заметно упала, и это был в то время неизвестный фактор для Английских альпинистов…
Эверест. Джордж Мэллори и Эндрю Ирвин. 6 июня, 1924 г.
Они поднимались медленно, но выше штурмового лагеря они пошли с кислородными бьаллонами. Что это доказывает?
Это говорит нам о нескольких вещах:
Во-первых, этот факт немного проясняет ситуацию с письмом Мэллори которое он писал в базовый лагерь фотографу Джону Ноэлю, в котором он писал что Джон должнен будет видеть его и Ирвина на «Второй ступени» к 8:00 утра.
Но это не потому, что на штурм вершины альпинисты собирались вставать в 3:00 утра, а скорее из-за того, что Мэллори должно быть экстраполировал их быстрое восхождение на участке от Северного седла к высотному штурмовому лагерю Camp 6, используя при этом лишь три четверти одного кислородного баллона, или в пересчете на время: им понадобилось лишь 3 часа что бы преодолеть набор высоты в 1130 метров. Это кажется невероятным, но в то же время похожий результат был зафиксирован в Британской экспедиции 1922 года, когда с кислородными баллонами поднимались Finch и Bruce.
Когда Эрик Симонсон нашел один из баллонов Мэллори и Ирвина, мы узнали, что их скорость восхождения составляла 84 метра в час. Очень неплохое время восхождения на такой большой высоте, но гораздо меньше того, на что рассчитывал Мэллори, основываясь на восхождениях двух предыдущих дней.
Но даже если бы Мэллори правильно смог экстраполировать данные о своей скорости восхождения, он бы понял, что восхождение на вершину за один штурмовой выход, в котором им предстояло набрать еще около 300 метров высоты из расчета запаса кислорода на 3 часа восхождения малоосуществимо.
Из этогопредположения Вы выдвинули гипотезу что Мэллори мог использовать кислородный баллон Ирвина?
Да. Так он мог решить две основные проблемы: Восхождение на «Первую ступень» это физически сложный подъем, но в то же время технически – это легко, а вот затем перед альпинистами стояла задача пройти Вторую ступень: здесь было два варианта: попытаться взобраться по вертикальной стене, где не было места для организации точек страховки, или крадясь пройти вдоль огромного и скользкого Большого Кулуара (Great Couloir).
Мэллори, возможно чувствовал что смог бы преодолеть эту проблему, но перетаскивание Ирвина через Вторую ступень было бы смертельной задачей для их обоих
Мог ли Мэллори сказать Ирвину вернуться в штурмовой лагерь а сам стал бы продолжать восхождение используя кислородные баллоны?
Не думаю что так было… Я полагаю что Мэллори сделал то же самое что сделали Norton и Somervell за несколько дней до восхождения Мэллори: тогда Somervell остался на месте, и смотрел как далеко сможет зайти Norton по Большому Кулуару. После того, как у Нортона кончились силы, он повернулся обратно и они вдвоем благополучно спустились в низ.
Фото Нортона идущего через Большой Кулуар. Фотографировал Somervell, ожидая его возвращения
То есть предположительно, когда Мэллори не смог преодолеть Большой Кулуар он вернулся к ожидавшему его Ирвину и они вместе пошли к «Первой ступени»?
Думаю да, кроме того Jim Wickwire в доказательство приводит тот факт что два альпиниста, у которых уже заканчивались силы смогли бы пойти на такой напряженный обход. И я думаю он прав. Но при этом мы знаем, что по крайней мере одного человека поднимавшегося на Ступень видел в бинокль Оделл.
Этот факт дал мне основание полагать, что Мэллори, вероятно всеже попытался пройти по Большому Кулуару по треку Нортона, в то время как Ирвин отдыхал у начала Кулуара и следил за Мэллори. После того, как Мэллори вернулся обратно с неудавшейся попытки траверса, он был полностью вымотан… Но при этом у Ирвина было больше сил. Ирвин по видимому предложил продолжать восхождение преодолев Вторую Ступень, по крайней мере они должны были сделать фотографии участка, лежащего за этой ступенью и Северо-Восточного склона Эвереста. Вдвоем они подошли к началу Второй Ступени, где их видел Оделл. Но здесь Мэллори сдался, и Ирвин продолжал восхождение один. Вот его то и видел Оделл в краткий миг в просвете туч. Там был лишь один человек – и это я полагаю был Ирвин.
Когда Ирвин спустился со Второй Ступени обратно, они вместе с Мэллори начали возвращаться в штурмовой лагерь, попав при этом в шквальный ветер и снегопад.
Сейчас Вы утверждаете что знаете где точно находится тело Ирвина. Но также думали и многие другие альпинисты которые искали следы экспедиции 1924 года..
Но ни одна из этих догадок так и не оправдалась. Так что моя версия также может иметь право на реализацию.
Вы можете привести доказательства своей теории о месте расположения тела Ирвина?
Мои предположения косвенные, можно даже сказать сильно косвенные. Они основываются на анализе аэрофотоснимков Эвереста, на которых я обнаружил странное выпуклое образование в снегу, по форме напоминающее человеческое тело.
И все же какие у Вас доказательства?
Во первых, мы знаем что в том месте где был найден ледоруб в 1933 году и произошла трагедия с Мэллори и Ирвином.
Предположение о том, что ледоруб был оставлен ими по дороге к вершине не выдерживает никакой критики: ни один здравомыслящий альпинист не оставит свой ледоруб находясь на склонах горы.
Таким образом мы имеем точную точку на склоне Эвереста где произошла трагедия, и есть вероятность того что и тело Ирвина находится где то неподалеку.
Но ведь тело Мэллори было обнаружено в 300 м ниже относительно ледоруба, значит случилось что-то еще кроме истощения и обморожения альпинистов
Да, тело Мэллори как то оказалось в 300 метрах ниже, но в этом нет ничего станного, ведь спускаясь вниз по «Желтой Полосе» (The Yellow Band) в сильный шторм со снегом так легко оступиться или быть снесенным порывом ветра….
И это по всей видимости и случилось, когда Мэллори пытался скользить вниз на снежное поле на отметке 8200 метров.
Снежный покров при этом скольжении был достаточно глубоким для того, что бы тормозить свое движение ледорубом, но затем Мэллори попал на скальный участок и его падение уже было неконтролированным.
Его нашли в 1999 году в положении с завернутой назад ногой со следами сильной черепно-мозговой травмы в следствии падения на камни.
Но мы также знаем что Ирвин не упал рядом с Мэллори, его тело рядом не нашли, кроме того на Желтой Полосе видели тело «англичанина» по крайней мере два альпиниста: в 1960 году Ван Фу-чжоу и в 1995 году Sherpa Dorji Chhiring. Но они оба были сильно истощены после восхождения на Эверест причем без использования кислородных баллонов, и не могли четко описать увиденное и где конкретно на Желтой Полосе они видели тело.
маршрут Мэллори и Ирвина и отметки находок их экспедиции
На Северной стене Эвереста не так уж и много лежит погиблих альпинистов?
В настоящее время, да. Но в 1960 году на этом склоне не должно было быть ни одного погибшего, и даже к 1995 году на Желтой Полосе также никто не погибал.
Так что свидетельства двух альпинистов о теле на Северном склоне в районе Желтой Полосы можно считать правдой, причем китайский альпинист Ван Фу-чжоу рассказывал что он спускался не по стандартному маршруту 1924-1933 годов (а этот маршрут Китайская экспедиция приняла за базовый при восхождении на Эверест), а решил спуститься более прямым путем.
И когда я взглянул более подробней на аэрофотоснимки этой области Эвереста я увидел и «стандартный маршрут» и развилку, с которой можно уйти вниз по более прямому пути.
Но, я предполагал, что, когда Ирвин потерял Мэллори, он продолжал двигаться вниз по «стандартному маршруту», по тому же самому пути как они поднимались вверх.
Но и Китайский альпинист был уверен что свернул со «стандартного маршрута» на новый путь.
На аэрофотоснимке я отчетливо заметил красную полосу – слой камня в 20-и метрах ниже стандартного маршрута и лишь в 15-и метрах правее линии по которой спускался Ван Фу-чжоу.
Как оказалось Sherpa Dorji Chhiring также спускался с Эвереста по стандартному маршруту, но после Второй ступени также решил срезать, так что и он точно не мог сказать где видел тело.
Эта красная полоса камня была как раз той местностью которую и указал Ван Фу-чжоу как ориентир к обнаруженному телу.
Вы собрали достаточно доказательств своей теории, почему же так тяжело проходит подготовка к осуществлению поисков?
Я пытался собрать деньги для максимально простой поисковой команды. Я общался с BBC о частичном финансировании проекта а также с несколькими частными спонсорами, но к сожалению сейчас уже мало кого можно склонить на свою сторону одиними лишь косвенными доказательствами.
Спонсоры хотят 100% гарантии мероприятия.
Тоесть ваш проект заморожен на неопределенное время, до тех пор пока не будут найдены убедительные доказательства. А сейчас Вам достаточно будет проведения новой аэрофотосъемки предполагаемого места Ирвина?.
Да, так и есть. Сейчас мне не хватает для реализации первой стадии проекта – аэрофотографии около $ 10 000.
Благодаря новейшим современным технологиям в фотографии я бы мог сделать важный шаг в решении этой загадки века.
Альтернативным вариантом и второй частью поисковой экспедиции должен стать выход альпинистов на склон Эвереста, но это уже бюджет за $ 100 000.
по материалам http://www.alanarnette.com
На эту статью распространяется закон об «Авторском праве». Перепечатка материала на другие ресурсы возможна только с разрешения администрации сайта! Спорные вопросы разрешаются в судебном порядке
|
George Mallory |
|
|---|---|
 |
|
| Born |
George Herbert Leigh Mallory, 18 June 1886, Mobberley, Cheshire, England |
| Died | 8–9 June 1924 (aged 37),
North Face, Mount Everest, Tibet |
| Cause of death | Mountaineering accident |
| Body discovered | 1 May 1999 |
| Alma mater | Magdalene College, Cambridge |
| Occupation(s) | Teacher, lecturer, rock climber, and mountaineer |
| Spouse |
Christiana Ruth Turner (m. 1914–1924) |
| Children |
|
| Military career | |
| Allegiance | |
| Service/branch | |
| Years of service | 1915–1918 |
| Rank | Lieutenant |
| Battles/wars | World War I |
| Olympic medal record | ||
|---|---|---|
| Men’s Alpinism | ||
| Representing |
||
| Olympic Games | ||
| 1924 Chamonix | Everest expedition |
George Herbert Leigh-Mallory (18 June 1886 – 8 or 9 June 1924) was an English mountaineer who participated in the first three British Mount Everest expeditions from the early to mid-1920s.
Born in Mobberley, Cheshire, Mallory became a student at Winchester College, where a teacher recruited him for an excursion in the Alps, and he developed a strong natural ability for climbing. After graduating from Magdalene College, Cambridge he taught at Charterhouse School while honing his climbing skills in the Alps and English Lake District. He served in the British Army during the First World War and fought at the Somme.
After the war, Mallory returned to Charterhouse before resigning to participate in the 1921 British Mount Everest reconnaissance expedition. In 1922, he took part in a second expedition to make the first ascent of the world’s highest mountain, in which his team achieved a world altitude record of 27,300 ft (8,321 m) using supplemental oxygen. Once asked by a reporter why he wanted to climb Everest, Mallory purportedly replied, «Because it’s there.»
During the 1924 expedition, Mallory and his climbing partner, Andrew «Sandy» Irvine, disappeared on the Northeast Ridge of Everest. The last sighting of the pair was approximately 800 vertical feet (245 m) from the summit. Mallory’s body was discovered and identified 75 years later, on 1 May 1999, by a research expedition that had set out to search for the climbers’ remains. Whether Mallory and Irvine reached the summit before they died remains a subject of debate, various theories, and continuing research.
Early life, education, and teaching career[edit]
Childhood[edit]
George Herbert Leigh-Mallory was born at Newton Hall, Mobberley, Cheshire, on 18 June 1886,[1][2] the first son and second child of the Reverend Herbert Leigh Mallory (1856–1943),[3]rector of the parish.[4][5] His mother was Annie Beridge Leigh-Mallory (née Jebb; 1863–1945),[3][n 1] the posthumous daughter of the Reverend John Beridge Jebb of Walton, Chesterfield, Derbyshire.[4] Mallory had two sisters, Mary Henrietta (1885–1980)[3] and Annie Victoria (Avie) (1887–1989),[3] and a younger brother, Trafford (1892–1944),[3] the World War II Royal Air Force commander.[7][8][n 2] Mallory’s two sisters, Mary Henrietta and Annie Victoria, were also born at Newton Hall.[5] At the end of 1891, the Mallorys moved from Newton Hall, Mobberley, to Hobcroft House, Hobcroft Lane, Mobberley, where Mallory’s brother Trafford was born.[5] The family resided there until 1904, when they moved to Birkenhead.[11][5] Mallory exhibited an early audaciousness for climbing.[12] At age seven, his first venture into climbing was the roof of his father’s church, St Wilfrid’s, in Mobberley, Cheshire.[12] His sister Avie recalls, «He climbed everything that it was at all possible to climb.»[12] Included in his climbing escapades were the drainpipes of the Mallory family home, Hobcroft House and the walls which divided the farmers’ fields.[12] In 1914, Mallory’s father, Herbert Leigh Mallory, adopted the surname of Leigh-Mallory, by Royal License.[4]
1896–1905: West Kirby, Glengorse, and Winchester College[edit]
In 1896, Mallory was sent to Glengorse boarding school in Eastbourne on the south coast of England after the headmaster of his first preparatory school in West Kirby near Birkenhead died, resulting in its abrupt closure.[13][14][15][16] During the summer of 1900, Mallory won a mathematics scholarship to Winchester College, Hampshire, where he started as a mathematical scholar in September of that year.[17][15] At Winchester, he was proficient at sports, in addition to his academic excellence.[18] Mallory played soccer for College VI in Winchester’s idiosyncratic version of inter-house six-a-side football.[18][19] As a gymnast, he became the most superlative in the school, the only one capable of performing the giant swing on the horizontal bar.[20][18] In July 1904, Mallory was a Winchester Shooting VIII team member, which won the Ashburton Shield at the annual Bisley competition, competing against other public schools.[18][21]
Robert Lock Graham Irving was a senior master in Mallory’s house at Winchester, an accomplished mountaineer and a member of the Alpine Club.[22][23] In 1904, Irving was searching for new climbing companions after the death of his climbing partner in an accident, with whom he had done most of his climbing.[22][23] He resolved to find some Winchester students and train them as recruits.[24] Irving recruited Mallory and his fellow pupil and friend, Harry Olivier Sumner Gibson (1885–1917),[25][n 3] for a trip to the Alps.[24][22][23][26] In early August 1904, Irving, Mallory and Gibson travelled to the Alps, which would be Mallory’s first foray into the daunting world of high-altitude mountaineering.[24][22] In his final year at Winchester, Mallory studied history instead of mathematics.[27] After sitting his exams, he was awarded a history scholarship to Magdalene College, Cambridge known as a sizarship.[27]
1905–1909: Magdalene College, Cambridge[edit]
In October 1905, at the start of the Michaelmas term, Mallory entered Magdalene College to study history under his tutor, Arthur Benson, the newly appointed supervisor in history at the college.[28][29][30][31] During his second year at Magdalene, Mallory made several new friends outside the college.[32] On 6 February 1907, at Christ’s College, he dined with the zoologist Arthur Shipley.[32] Other guests included his tutor, Arthur Benson and his younger brother, the clergyman Robert Hugh Benson; the physicist Charles Galton Darwin, grandson of Charles Darwin, author of On the Origin of Species; and under-librarian Charles Edward Sayle.[32] At Sayle’s house on Trumpington Street, Mallory met several undergraduates with whom he established enduring friendships;[33] the French painter Jacques Raverat, surgeon, and author Geoffrey Keynes were among them.[33] He also became good friends with the poet Rupert Brooke and the psychoanalyst James Strachey.[33][34] On 12 February 1909, Mallory met Geoffrey Winthrop Young at the Charles Lamb Dinner in Cambridge and developed a good friendship.[35][36] Through his companions James Strachey and Geoffrey Keynes, Mallory got to know their elder brothers, Lytton Strachey and John Maynard Keynes, who were members of the Bloomsbury Group.[34][37] Through the Stracheys, he met and befriended their cousin, the painter Duncan Grant,[n 4] also a Bloomsbury member.[42][37]
Athletically, Mallory developed into an accomplished oarsman for his College, Magdalene.[32][43] In October 1906, at the beginning of his second academic year, he was elected secretary of the Magdalene Boat Club and captain of the college boat club from 1907 to 1908.[44][45][46] In July 1908, an eight, with Mallory rowing at number 7, was sent to compete at the Henley Royal Regatta, performing admirably in the Ladies’ Challenge Plate and Thames Challenge Cup.[47][48][46][n 5][n 6]
Politically, Mallory joined the Cambridge University Fabian Society, established in 1906, and acted as college secretary on behalf of Magdalene on the Cambridge University Women’s Suffrage Association committee.[52][53] The Marlowe Society, in February 1907, was established at Cambridge University;[54] in November of that year, Doctor Faustus, its first production, was staged at the Amateur Dramatic Club Theatre;[54][55] Mallory took part as the Pope and one of the Scholars; Geoffrey Keynes, the Evil Angel; Rupert Brooke, Mephistophilis; Justin Brooke, Faustus and Cosmo Gordon, a magician.[54][56]
Academically, on 26 May 1907, Mallory sat part one of the history tripos in his examinations at Magdalene, achieving a third class.[57][58] In 1908, in the second part of the history tripos, he improved on the previous year, attaining a class two degree.[48][58] Equipped academically with his degree, Mallory had to consider a future career.[59] In 1907,[52] he had consulted the deputy headmaster of Winchester, Howard Rendall, about the possibility of becoming a teacher there, but Rendall gave him a stern retort;[59] Mallory informed his tutor at Magdalene, Arthur Benson; «He says that as I have nothing to teach and would probably teach it badly, there is not the least chance of ever getting to Winchester.»[52][59] Rendall, to Mallory, also suggested that he go into the church and find a good country parson who required a curate.[52][59] For a time, Mallory unenthusiastically pondered following in his father’s footsteps, contemplating «parish work of some kind … I’m at variance with so many parsons that I meet. They’re excessively good, most of them much better than I can ever hope to be, but their sense of goodness seems sometimes to displace their reason.»[52][59][60] Arthur Benson offered an alternative suggestion to Mallory to return to Magdalene for a fourth consecutive year, where he could improve upon his degree. Mallory returned a decisive affirmative and settled in new quarters at Pythagoras House, a short distance from Magdalene College.[61][62][58]
In February 1909, Geoffrey Winthrop Young invited Mallory to Wales for a climbing trip at Easter.[63] After the trip on Mallory’s return to Magdalene, Young sent him an application form to fill out for membership in the Climbers’ Club, and in May 1909, Mallory was elected a new member.[63] The under-librarian, Charles Edward Sayle, announced that the subject for the Members’ Prize Essay in 1909 would be James Boswell, the biographer of Samuel Johnson; and Mallory decided to compete.[64][62][58] Upon completing his academic essay on Boswell, he submitted it to the judges, who awarded him second place, known as a proxime accessit.[65][66] Later, with Arthur Benson’s encouragement, he suggested that Mallory submit his essay for publication as a book.[67][68] In October 1912, his book, Boswell the Biographer, was published by Smith, Elder & Co.[69][70][71]
In June 1909, Mallory received a letter from the headmaster of Winchester College, Dr Hubert Burge, which communicated the possibility of a teaching job opening at Winchester at Easter 1910, in French, German and mathematics.[72][73][74] He travelled to Winchester and discussed the outlook, but Burge turned him down, explaining that the teaching post required too high a degree of mathematical knowledge for his academic qualifications.[75][76][74] In July 1909, at the end of the term, Mallory’s education at Magdalene was finally complete.[74]
1909–1910: Interim[edit]
In October 1909, the painter Simon Bussy, whose wife Dorothy was the sister of Lytton and James Strachey, invited Mallory to spend the winter months with them at their villa in Roquebrune in the Alpes-Maritimes.[77][78] Mallory, who had recently received a small family legacy, accepted their offer and travelled to France in early November to stay with the Bussys’.[79][74] During his stay, Simon Bussy painted a portrait of Mallory,[80] which the National Portrait Gallery later acquired.[81][82][83] Near the end of February 1910, Mallory left Roquebrune and travelled to Italy, where he visited the cities of Florence, Pisa, Milan and Genoa.[65][84][83] In mid-March, he travelled to stay in Paris, stopping to visit two Cambridge friends, Hugh Wilson in Basel, Switzerland, and Jacques Raverat in Prunoy, France.[65][84] Upon his arrival in Paris, Mallory rented a room at 52 Rue Gay Lussac, a short distance from the Jardin du Luxembourg.[84][83] He stayed in Paris for one month, seizing the opportunity to improve his French language and linguistic proficiency by reading, attending the theatre and music hall, attending Sorbonne lectures, and conversing.[65][85][83]
In April 1910, Mallory returned to Cambridge, contemplating his future career prospects.[86][87][83] At the beginning of May, he took a temporary teaching post at the Royal Naval College, Dartmouth, which lasted two weeks.[86][88][83]
In July 1910, Mallory received a letter from the headmaster of Charterhouse, Gerald Henry Rendall,[n 7] offering a job teaching Latin, mathematics, history and French, and hoped it possible that he could teach history to students who were candidates for scholarships to Cambridge and Oxford, on a probationary basis, with an annual salary of £270, which he promptly accepted.[91][89][90]
1910–1914: Charterhouse School[edit]
«He was wasted at Charterhouse … the boys generally despised him as neither a disciplinarian nor interested in cricket or football. He tried to treat his classes in a friendly way, which puzzled and offended them because of the school tradition of concealed warfare between boys and masters.»
— Robert Graves, one of Mallory’s students at Charterhouse.[92][93]
In September 1910, at the start of the Michaelmas term, Mallory began teaching at Charterhouse, one of England’s excellent public schools, as an assistant headmaster and took up residence with two colleagues at Nercwys House.[94][95][96] One of the problems he faced as a teacher was his highly youthful appearance, and consequently often misperceived by their parents as one of the students.[97][98] His teaching methods relied on infectious enthusiasm and avuncular mannerisms rather than imposing his authority.[99][98] He followed the teaching styles of Robert Lock Graham Irving and Arthur Benson, who sought to educate through mutual respect and trust, getting to know their pupils as individuals and repudiating the authoritarian regimes of most British public schools.[95] Several of Mallory’s colleagues developed a hostile attitude towards him due to his informal approach to teaching methods, which they considered undermining their attempts to maintain discipline.[98] He recommended that his students read literature extensively, write essays on subjects such as hypocrisy, candour and popularity, and he engaged with them in discussions of politics and literature.[97][98] He also took them on out-of-school excursions to places of aesthetic scenery and landmarks of architectural importance.[97][98]
The poet Robert Graves, a student at Charterhouse from 1909 to 1914, said Mallory was the most exemplary teacher and the first genuine friend he ever had.[100][n 8] In his autobiography, Goodbye to All That, Graves wrote fondly of Mallory, who encouraged him in his interest in literature and poetry and,[105] during the school vacations, took him climbing in Snowdon.[106] Robert Lock Graham Irving and Geoffrey Winthrop Young proposed Mallory for the Alpine Club, and in December 1910, he was elected a new member.[107][108][109] During the Summer of 1913, Mallory collaborated with Robert Graves and two other Charterhouse students, Cyril Hartmann and Raymond Rodakowski, to produce a new school magazine called Green Chartreuse, intended to rival other school magazines, The Carthusian and The Greyfriar, with its first publication appearing on Old Carthusian Day, 5 July 1913.[110][111][112] Mallory presented a series of lectures on Italian painting at Charterhouse in the spring of 1914, engaging the students in a «rather philosophical» discussion about Botticelli, Michelangelo, and Raphael.[112]
‘My dearest Ruth,’[edit]
Christiana Ruth Leigh-Mallory. (née Turner)
Christiana Ruth Turner (1891–1942)[113][114] was the second daughter of prosperous architect Hugh Thackeray Turner (1853–1937)[3][n 9] and Mary Elizabeth Turner (née Powell; 1854–1907),[3][116][117][118] who passed away after developing pneumonia when Ruth was fifteen.[119] She had two siblings, Marjorie (1890–1972)[3] and Mildred (1893–1985),[3] and resided with her father and sisters at Westbrook House, an elegant mansion built by their father near Godalming, Surrey.[120][121][118] Mallory and Christiana Ruth Turner met for the first time in the autumn of 1913 at a dinner hosted by Arthur Clutton-Brock at his residence on Hindhead Road (later renamed Frith Hill Road),[122] Godalming, Surrey.[121] Ruth’s father, Thackeray Turner, invited Mallory to their home at Westbrook to play billiards and go walking.[116][121][118] From Mallory, invitations were sent to the Turner family at Westbrook to take part in a play reading at Charterhouse, where he, Ruth, and her sisters, Marjorie and Mildred, acted in a garden performance of The Princess.[123][121] Mallory and the Turner family developed a close friendship, and he became a regular visitor to their dwelling at Westbrook.[118] In March 1914, Thackeray Turner and his three daughters were on a family holiday in Italy, and he invited Mallory to join them there.[120][124][118] He travelled to Italy and, on 3 April, rendezvoused with the Turners at a train station in Verona, from where they journeyed to Venice, where he spent the ensuing week in their company, during which time he and Ruth fell precipitately in love.[125][124][118] On 1 May 1914, at Westbrook, Mallory and Ruth became engaged to be married.[125][118][126] Thackery Turner felt that Mallory’s schoolmaster’s income was inadequate to support Ruth in the manner customary for her, and he provided his daughter with an annual income of £750, to which Mallory consented.[127][126] For them, he also purchased a six-bedroom house, costing £1600, named The Holt,[n 10] situated on Hindhead Road (later renamed Frith Hill Road), Godalming, Surrey.[131][126] On 29 July 1914, six days before Britain entered the First World War, Mallory and Ruth were married in Godalming,[n 11] with Mallory’s father, Herbert, performing the ceremony and Geoffrey Winthrop Young acting as best man.[134][135][136] Mallory and Ruth had two daughters and a son: Frances Clare (1915–2001),[137][3][138] Beridge Ruth, known as «Berry» (1917–1953),[139][140] and John (1920–2011).[3][141][142][143]
World War I[edit]
Schoolmasters exemption[edit]
Mallory’s inquiries about enlisting in the military were met with strong resistance by the headmaster of Charterhouse, Frank Fletcher.[128][129][144] Fletcher, chairman of the Headmasters’ Conference committee,
asked the government for a policy concerning the enlistment of schoolmasters.[145][146] On 9 December 1914, Lord Kitchener replied from the War Office, instructing headmasters to implement discretion and judgement in deciding which teachers could be permitted to enlist without diminishing the work of their schools and the training of the Officers’ Training Corps.[147][129][144] In March 1915, due to Fletcher’s objections, Mallory was denied the opportunity to work with William Arnold-Forster, who ran an anti-contraband department at the Admiralty.[147][148][144] A pamphlet, composed by Mallory, entitled War Work for Boys and Girls, was intended to teach schoolchildren the ideals of international understanding and the «good life» for every nation and individual from all backgrounds.[147] These ideals, he believed, could only be achieved with an education encouraging the growth of the spirit and self-discipline;[147] and to boys and girls curious how they could support the war effort, they were encouraged to foster the development of clear thought, devoting themselves to acquire knowledge in «learning what is right for England.»[147][148]
Military training[edit]
In May 1915, two friends of Mallory,[n 12] Eddie Marsh and Will Arnold-Forster, travelled to visit him in Godalming and suggested that, though over age, he should try for a commission in the Royal Naval Air Service.[151][152] Given Kitchener’s policy, Fletcher opposed it, stating, «I cannot consent to your going,» denying Mallory’s opportunism.[151][152] In December 1915, aided by his brother-in-law, Ralph Brooke,[n 13] an instructor at Woolwich Common, Mallory was commissioned as a second lieutenant in the Royal Garrison Artillery.[137][154][155] In a letter to a friend in charge of running an artillery training course at Weymouth Camp, Brooke had recommended Mallory based on his expertise in mathematics and trigonometry.[154][156] Fletcher’s persistence finally relented, granting Mallory leave, as the initiative coincided with his finding of a teacher who took Mallory’s post at Charterhouse.[154][157][158] In January 1916, Mallory commenced a training course involving artillery training at Weymouth Camp for subalterns who might prove competent for further training at Lydd Military Training Camp in Kent.[159][160] On 1 April 1916, Mallory journeyed from Weymouth to Lydd for additional training at the School of Siege Artillery at Lydd Camp and received instructions on utilising heavy howitzers.[159][161]
Active military duty[edit]
During the night of 4 May 1916, Mallory travelled across the English Channel, and arrived in the early morning at Le Havre, France.[159][162] After arriving, he spent a week at No. 1 General Base Depot for Royal Garrison Artillery, near Le Havre, undergoing final preparations for active military service, including training in using a gas mask and shooting practice with his new revolver.[159][163] After the culmination of his preparations for active duty, Mallory took a troop train from Rouen northeast to Armentières.[159][164] When he reported to headquarters, he was assigned to the 40th Siege Battery, operating north of Armentières, in the northern section of the Western Front, a short distance from the front line, in a unit of four-six-inch howitzers eight miles south of the Ypres Salient.[165][164][166] The commanding officer of the 40th Siege Battery was a Scotsman, Captain James Lithgow.[167][168] Lieutenant D.A. Bell was second in the line of command, with Mallory third as a second lieutenant.[167] Bell was in charge of No. 4 gun detachment and shared a billet with Mallory.[169][168] Some of Mallory’s duties consisted of taking charge of the firing of the howitzers and being positioned at observation posts.[167] During his first night at an observation post near the front line, a bullet passed between him and a soldier who was in very close proximity to his position.[170][158] On 24 May 1916, a German shell destroyed the rear of the cottage he shared with Lieutenant Bell; fortunately, Mallory’s room was undamaged.[168] Ruth dispatched him food and provisions from England, including potatoes and butter, sausages, tea, whisky, gin, Turkish cigarettes, matches, newspapers, books, clothes, pencils, and notebooks.[167]
Battle of the Somme[edit]
«The trenches were in a filthy state, owing to a more or less futile attack made by our men the night before. I don’t object to corpses so long as they are fresh. I soon found that I could reason thus with them … But this is an accepted fact that men are killed … your jaw hangs and your flesh changes colour and blood oozes from your wounds. With the wounded it is different. It always distresses me to see them.»
— George Mallory, in a letter to his wife, Ruth. 15 August 1916.[171][172]
On 29 May 1916, the 40th Siege Battery deployed south.[173] After several days of bombardment at Vimy, they travelled farther south, rejoining the other half of the battery and occupied a new position in Picardy just north of the river Somme, at Pioneer Road, near Albert, by mid-June.[174][168] Mallory lived in a dugout excavated into the chalk terrain.[168] Below ground was the stench of rats and the malodorous scent of decay; above ground was the smell of sweat and cordite.[168] Mallory’s 40th Siege Battery unit was allied with the 30th Heavy Artillery Group and the 2nd Corps Heavy Artillery.[175] On 24 June 1916, the artillery bombardment preliminary to the Somme offensive, initiated by the Allies, began, with Mallory, Lieutenant Bell, and their crews bombarding particular villages and German trenches with shells in four-hour shifts for seven consecutive days.[170][176] On 1 July 1916, the Battle of the Somme began with British and French infantries attacking the Germans along the Somme.[170][177][178] The 40th Siege Battery’s primary duty was to fire a lifting barrage at the opposing force.[170] On 11 July 1916, just before the beginning of the second phase of the offensive, Mallory was ordered to the trenches, where he occupied an observation post for three days, aided by two Scottish signallers.[179][176] His assignment was to register artillery fire on a distant windmill at 8,500 yards, east of Pozières.[179][176] On 15 July 1916, he observed for the first time the devastating gruesome effects of flamethrowers utilised by the French against enemy soldiers.[180][176] On 28 July 1916, two men from Mallory’s unit, the 40th Siege Battery, Scots, Alexander Craig and John Cameron Forrest, were killed instantly by an exploding shell as they were walking a short distance behind Mallory and the rest of his party while returning from observation duty in the trenches.[181][182][183]
In mid-August 1916, Captain Lithgow succumbed to bed rest due to a fever, and Lieutenant Bell took leave, with four days rest, giving Mallory command of the battery for a few days.[171][184] On 17 August 1916, he was sent to a rest camp, a ten-day sojourn near Amiens, living in a tent, mingling with several Army Service Corps officers in their mess.[171][184] On 27 August 1916, Mallory returned to active military duty with the 40th Siege Battery, inhabiting his dugout, which he called «Fathom Five.»[185] The entire place had an infestation of rats and mice; he discovered lice in his clothing, and the water supply was foul for a period.[185][186] On 15 September 1916, the Battle of Flers–Courcelette began;[187] as the advance on the Flers Line persisted, Mallory, positioned in a forward observation post, spent as much time as possible there, seeing little of the other officers in the battery.[188] On 18 October 1916, the 40th Siege Battery progressed to new quarters seized from the Germans.[188] With the onset of one of the most extreme European winters in living memory,[189] the bitter cold set in, with daytime temperatures seldom exceeding four degrees Celsius and merciless rain, which turned the entire place into a quagmire, reducing artillery warfare to a minimum.[188] On 29 October 1916, Robert Graves wrote to Eddie Marsh, informing him that Mallory did not have leave for six months.[190] On 30 October 1916, rain played havoc, flooding Mallory’s dugout.[188] On 18 November 1916, Douglas Haig, commander in chief of the British forces in France, called a halt to the Somme offensive.[191]
Military leave and return to France[edit]
On 9 December 1916, aided by the interposition of Eddie Marsh, Mallory was granted military leave.[189][190] A few days later, he was at home in England, spending ten days at Westbrook House with his wife Ruth and daughter Clare before returning to France on Boxing Day.[192] After reporting for military service, he was reassigned as an orderly officer, serving as a colonel’s assistant at the 30th Heavy Artillery Group headquarters, three miles behind the front line, for the first weeks of 1917.[193][194][190] At the beginning of February 1917, the command recommended Mallory for a staff lieutenancy; he rejected it and was instead assigned a liaison officer position to a French unit.[193][195] At the end of March 1917, he applied to rejoin the 40th Siege Battery, which had moved to a new location.[195] On 7 April 1917, during the prelude to the Battle of Arras, he was back at the front with the 40th Siege Battery in an exposed observation post, directing artillery fire.[190]
Surgery[edit]
Mallory increasingly experienced right ankle pain after returning to France in December 1916, which made walking difficult.[196] A doctor’s medical diagnosis concluded that the injury he sustained in a fall in Birkenhead in 1909 was a fracture,[n 14] which was left untreated, had failed to heal properly and was causing the pain.[196] He returned to the front under advisement to use bandages for supporting his ankle, continued to suffer pain, and after re-examining by a doctor informed, it necessitated an operation to further his duty in the British Army.[196] Invalided out of the armed forces, Mallory was sent home to England in May 1917 and underwent a surgical operation on his right ankle that month in the Officers’ Hospital, Portland Place, London.[199][200][201]
Further military training[edit]
In September 1917, the army medics passed Mallory fit to resume active duty.[202] He was sent, under new orders, to Avington Park Camp near Winchester, was transferred from the Siege Battery to a Heavy Battery, and trained at the camp with the Royal Artillery’s new generation of sixty-pound heavy artillery guns, which had a range of more than six miles.[203][204][205] In October 1917, Mallory obtained an exalted military status after being advanced to the rank of lieutenant and commenced a training course for newly promoted officers at Avington Park Camp.[206][205][207] On 8 October 1917, Mallory was travelling to Avington Park Camp on a motorcycle he had borrowed from a Winchester teacher when he collided with a gatepost at the entrance to the camp and crushed his right foot.[208][209] He explained to Ruth, «As I turned into the camp, my brake, which I endeavoured to apply as I hadn’t quite sufficiently slowed down, failed to act.»[206] As a repercussion of the motorcycle accident, he spent a week in a hospital, was discharged on 16 October 1917, and, although moderately debilitated, returned to Avington Park Camp, where he completed his training course.[208][210] At the end of December 1917, Mallory was again passed fit for military service.[206][210] He fully anticipated being sent back to France but was ordered to undergo a battery commanders’ course at the School of Siege Artillery at Lydd Military Training Camp in Kent under his brother-in-law Ralph Brooke, the commanding officer of the course.[211][212]
Second return to France[edit]
«The German Government requests the President of the United States of America to take steps for the restoration of peace … The German Government accepts … the programme laid down by the President of the United States in his message to Congress of January 8, 1918, and in his subsequent pronouncements, particularly in his address of September 27, 1918 … the German Government requests the President to bring about the immediate conclusion of a general armistice on land, on water, and in the air.»
— Germany requests an armistice. 4 October 1918.[213]
On 23 September 1918, after completing a final training course at Newcastle, Mallory crossed the English Channel to Calais, France, and was reassigned to the 515th Siege Battery, stationed between Arras and the French coast.[214][215] His commanding officer was Major Gwilym Lloyd George, the second son of British Prime Minister David Lloyd George.[215] The battery was positioned a safe distance from the front line and expected to conduct military operations with an airborne observer but found little opportunity for activity.[214][215] The 515th Siege Battery was assigned two 14-inch Mark I guns, shipped to France in sections, intended to be assembled and utilised as super-heavy railway guns; the first arrived in September 1918, the second after the Armistice; neither saw any action.[216] On 29 September 1918, the Allied forces successfully breached the Hindenburg Line, a pivotal moment which turned the tide dramatically in favour of the Allies.[217] The German government’s request for an armistice, dated 4 October 1918, was forwarded to Washington, D.C., United States, via Switzerland on 5 October 1918.[218] On 3 November 1918, Mallory’s commanding officer, Major Gwilym Lloyd George, received a directive to join his father in Versailles, Paris.[214] On 10 November 1918, Mallory was at a casualty clearing station near Cambrai with his friend and compatriot Geoffrey Keynes, a surgical specialist.[214] That night, as they were turning in for sleep in Keynes’s bell tent, they heard shouts, from which they discerned an armistice was imminent.[214][219] On 11 November 1918, at 5:00 a.m. (French time), the Allies and Germany signed the Armistice.[220] The Allied and German plenipotentiaries’ signatories were Ferdinand Foch, Rosslyn Wemyss, Matthias Erzberger, Alfred von Oberndorff, Detlof von Winterfeldt and Ernst Vanselow, at 5:10 a.m., with 5:00 a.m. agreed upon as the official time of signing.[220] On the evening of 11 November 1918, at the officers’ club in Cambrai, Mallory celebrated peace with his brother Trafford.[214][221][n 15] Due to the British requirement to demobilise more than a million men after the armistice and the dearth of ships that could transport them across the English Channel, Mallory did not return to England until the second week of January 1919.[223][224][n 16]
Post–World War I[edit]
Return to Charterhouse School[edit]
«If the individual man is conscious of himself as belonging to various groups … why should his group consciousness stop with the state? Why should not an English man become conscious of Europe as a group and then of the whole world; become, in fact, a citizen of the world so that patriotism merged in cosmopolitanism? … we shall still love our country as citizens of the world.»
— George Mallory advocated a new form of patriotism in a lecture at Charterhouse in 1920.[226][227]
Following his return from France, Mallory, Ruth, and their two young daughters, Frances Clare and Beridge Ruth, who had been residing at Westbrook House, re-established themselves by returning to live in their previous residence, The Holt in Godalming, Surrey.[228][224] At the end of January 1919, Mallory resumed his prior teaching position at Charterhouse, where he now taught predominantly English and partly history.[229][230] He was able to transcend his grievances and disdain of Frank Fletcher, the headmaster of Charterhouse, owing to the elation of his first six months back home, but still held strong convictions about the deficiencies and shortcomings of the public school.[231] Deep down, he felt dissatisfied as a schoolmaster, devoting more attention to mountaineering issues, the direction of international politics, and the fundamental objectives of education, and pondering how he could find more time for writing.[232][233] In collaboration, Mallory, with his friends Geoffrey Winthrop Young and David Randall Pye, contemplated establishing a school and met several times at the Holt to discuss the concept.[231][227] Mallory prepared a draft prospectus for the school consisting of critical points which emphasised its core principles and ideals and, along with Young and Pye, created more in-depth plans.[234][227] Ultimately, they lacked the collective motivation to follow the scheme, resulting in an obsolete conceptualisation.[234][227] Through his teachings at Charterhouse, Mallory strived to advance an understanding of contemporary political issues and the development of an improved world, which he considered the conflict of World War I had been fought for, vanquishing the enemy.[235][227] The League of Nations’ initial meetings inspired him, and he promoted a new brand of patriotism in one of his lectures.[227]
On 14 June 1920, Mallory wrote a speculative letter to Gilbert Murray, an activist, the Regius Professor of Greek at Oxford University and secretary of the League of Nations Union, a voluntary organisation established to support the League of Nations.[236][237] In his letter to Murray, Mallory queried whether the Union could find any use for his services and communicated his preparedness to resign from his current employment at Charterhouse.[236][238] The letter also cited his experience as a historian and lecturer, his interest in writing and literature, and, most importantly, his passion for international politics.[236] Mallory’s eagerness was apparent in the letter, as he offered to meet Murray in Oxford; and had informed Frank Fletcher that, if his application was successful, he might leave Charterhouse when the summer term concluded, but in the end, nothing came of his approach to Murray.[236][238]
Trip to Ireland[edit]
During the Christmas holidays of December 1920,[238] Mallory arrived by mailboat at the Royal Harbour Of George The IV, renamed Dún Laoghaire Harbour in 1924,[239] in County Dublin, the Irish Republic, and boarded a train which brought him to the centre of Dublin City.[240] Mallory’s objective in Ireland was to gain first-hand knowledge of the realities of life during the Anglo-Irish War, raging at the time of his visit.[241] Although his objective is clear, his incentive is unknown.[241] The British, who had refined their black propaganda techniques throughout World War I, were proficient at propagating atrocity stories about the Irish republican movement, and Mallory proclaimed he wanted to discover the truth.[241] There are two motives posited for Mallory’s objective in Ireland.[241] He and Ruth had resolved that he should leave Charterhouse, so it is conceivable that he was considering the possibility of a career as a writer, and the trip to Ireland allowed him to gain experience as a reporter.[241] A possible request to Mallory from Gilbert Murray, secretary of the League of Nations Union, to provide him with a first-hand account of what had become recognised in British liberal circles as «the terror in Ireland» was also a likely motive for Mallory to travel to Ireland.[242][243] Conor O’Brien, a yachtsman, Mallory’s friend and fellow climber,[244] who had assisted in landing firearms for the Irish Volunteers in 1914, consequently was a priceless asset for his visit in the form of a valuable contact, whether acting as a journalist or political consultant.[241][242] O’Brien introduced Mallory to prominent figures, Irish republican Erskine Childers, author of The Riddle of the Sands and Irish nationalist Desmond FitzGerald, «director of propaganda» at Dáil Éireann.[245][241] FitzGerald provided Mallory with a pass by inscribing, «Mr G. Mallory is anxious to have first-hand information as to acts of oppression and terror. I shall be glad if he can be assisted,» on the rear side of an identification photograph of Mallory effectively granting him official authorisation.[245][241] Throughout the week he spent in Dublin, Mallory progressively experienced his sympathies shifting toward a people determined to fight for their independence and became familiarised with the pernicious fear impacting the city.[241][238] Aware of the risks, Mallory maintained an inconspicuous approach: concealed his notes before going out in public, kept his hands free from his pockets, eschewed the notorious Black and Tans, knocked on his friends’ doors in an audible yet unsuspicious manner and avoided running, for fear of appearing to be someone attempting to flee.[246][247] He was awakened one night in his lodgings at 1:30 a.m. and interrogated by a stranger brandishing a revolver in one hand and holding a flashlight in the other, demanding to know who he was, what his name was, where he was born, and whether or not he was a Protestant.[246][248] Mallory witnessed the body of a young child whom impetuous British troops had slain.[241] His Irish contacts accompanied him on a trip into the countryside, where he met the relatives of republicans who had perished battling the British and learned about the Black and Tans’ summary executions.[249][250]
Even though he acknowledged injustices on both sides, ultimately, he expressed empathy for the Irish in their struggle for independence.[251] Mallory returned to London during the early days of January 1921.[252]
Resignation from Charterhouse and the lure of Everest[edit]
In January 1921, representatives of the Royal Geographical Society and the Alpine Club jointly established the Mount Everest Committee to organise and finance an expedition to Mount Everest.[253][254] The committee consisted of four RGS members and four Alpine Club members; from the RGS were Sir Francis Younghusband, Arthur Robert Hinks, Edward Lygon Somers-Cocks, and Colonel E. M. Jack; Professor John Norman Collie, John Percy Farrar, Charles Francis Meade, and John Edward Caldwell Eaton were from the Alpine Club.[255][256] The committee’s primary objective in 1921 was a thorough reconnaissance of the mountain and its approaches to determine the most viable route to the summit, and in 1922 to return for a second expedition, using this route for an all-out attempt to reach the summit.[257] On 23 January 1921, Mallory received written correspondence from John Percy Farrar, secretary of the Alpine Club, its former president and the nascent Mount Everest Committee member.[258] In the letter, Farrar asked Mallory if he would be interested in participating in an expedition to Everest: «It appears an attempt on Everest will occur this summer. The party would depart in early April and return in October. Any ambitions?»[258] Although grateful for the invitation, Mallory initially felt reluctant to accept it, knowing that his participation would mean a lengthy separation from his wife and young children, and he also expressed scepticism regarding the viability of the expedition.[259][260] Geoffrey Winthrop Young visited him at the Holt, Godalming when he learned of his hesitance and swiftly persuaded him and Ruth not to disregard the opportunity, that it would be an incredible adventure and earn him reputable renown for prospects in future professions as an educator or writer.[261][259] Young’s arguments convinced Ruth, and she concurred that Mallory should join the expedition; realising it was «the opportunity of a lifetime,» Mallory ultimately decided to participate.[260] On 9 February 1921, in Mayfair, London, Mallory met with Sir Francis Younghusband, chairman of the Mount Everest Committee, John Percy Farrar, a committee member, and Harold Raeburn, the assigned mountaineering leader of the 1921 British Mount Everest reconnaissance expedition.[262][260] At the meeting, Younghusband formally invited Mallory to join the expedition and was surprised to observe that he accepted without any evident emotion and exhibited no indication that he was brimming with enthusiasm.[263][260] In February 1921, Mallory officially tendered his resignation from his mastership at Charterhouse, changing his previous intended decision of resigning at the end of the summer term.[260]
On 17 March 1921, Mallory underwent a medical evaluation in Harley Street, London, concerning his designation as a member of the 1921 expedition.[264][265] He passed physically and physiologically fit on all the required assessment criteria and had a well-developed physique, with his height and weight documented at 5 ft 11 in (1.80 m) and 11 st 5 lb (72.1 kg; 159 lb), respectively.[266][264] George Finch, whom the Mount Everest Committee had selected as one of the expedition mountaineers,[267] was also given a medical examination on 17 March 1921.[268] He was declared unfit, and with Mallory’s recommendation, the committee chose Guy Bullock as his replacement.[269] On 8 April 1921, Mallory departed from the Port of Tilbury in Essex, England, on board SS Sardinia, and brought the final shipment of expedition supplies.[270][271] It was a solitary voyage, as the other expedition members had theretofore departed or were already in India.[272] To remain in adequate physical condition while travelling, he frequently ran around the deck and discovered a hidden place in the bows, where in solitariness, he read Charles Dickens Martin Chuzzlewit and Lytton Strachey’s Queen Victoria.[271] On 9 May 1921, Sardinia docked in Calcutta, India.[271] Mallory travelled by train north to Darjeeling, where he joined the rest of the expedition members at Government House (Raj Bhavan).[271] On 11 May 1921, Lord Ronaldshay, the Governor of Bengal, hosted a formal banquet in their honour.[273][271] On 29 October 1921, following the culmination of the 1921 reconnaissance expedition, Mallory departed from Bombay, India, on board SS Malwa.[274][275] On 9 November 1921, Sir Francis Younghusband wrote a letter to Mallory requesting him to participate in the second expedition to Everest in 1922.[276] He also expressed that waiting until 1923 was not an alternative option because they could not afford to squander the opportunity that the current benevolence of the Tibetans presented.[276] This letter awaited him in Marseille, France, the port of call of Malwa.[274] Before reaching Marseille, Mallory wrote a letter to his sister Annie Victoria (Avie), expressing reservations about returning to Everest in 1922.[277] On 12 November 1921, the same day Malwa docked in Marseille, Mallory wrote a letter to Arthur Robert Hinks, deferring his decision to join the 1922 Expedition.[278] His wife Ruth awaited him in Marseille, where they spent a brief holiday touring Provence and visiting the Pont du Gard while staying at the Hôtel Louvre et Paix.[279][274] Mallory and Ruth carefully discussed the circumstances concerning his participation in the 1922 expedition during their holiday in Provence and concluded that he should not decline the opportunity.[279][280] On 16 November 1921, Mallory wrote a letter to Hinks elucidating his position.[280][281] On 25 November 1921, they arrived at their residence, the Holt, Godalming.[279] A few days after his return home, Mallory met Hinks in London and, within a week, was included on a list of mountaineers who assented to participate in the 1922 expedition.[279][280]
Public lectures, writing, and preparations for the 1922 British Mount Everest expedition[edit]
On 20 December 1921, in the Queen’s Hall, London, Mallory and Charles Howard-Bury delivered a narrative on the 1921 reconnaissance expedition at a combined meeting of the Royal Geographical Society and the Alpine Club.[276] In exchange for a quarter of the revenue earned, the Mount Everest Committee requested that Mallory deliver a series of lectures throughout Britain and contribute to the official expedition book, Mount Everest: The Reconnaissance, 1921.[279] On 10 January 1922, Mallory delivered his initial public speech in the Queen’s Hall and thenceforth journeyed extensively around Britain, filling approximately thirty lecture engagements.[276][280] On 20 February 1922, his lecture tour officially concluded with a talk in Newcastle, followed by one further lecture at Winchester College.[282] The financial results of his lecture tour were lucrative as his twenty-five per cent share earned him £400, which exceeded his annual salary as a Charterhouse teacher.[283] Preceding his departure for the 1922 British Mount Everest expedition, Mallory completed his written contribution to the book Mount Everest: The Reconnaissance, 1921,[276] titled The Reconnaissance Of The Mountain, consisting of six chapters: The Northern Approach, The Northern Approach (continued), The Eastern Approach, The Assault, Weather And Conditions Of Snow and The Route To The Summit.[284] Mallory and Ruth evaluated his share of the profits for his contribution to the book.[282] Furthermore, he reviewed expedition equipment and assisted the Mount Everest Committee in preparations for the 1922 expedition.[285]
Itinerary for the 1922 British Mount Everest expedition[edit]
On 2 March 1922, Mallory, Howard Somervell, John Noel, Edward Strutt, George Finch, and Arthur Wakefield,[286] destined for the 1922 British Mount Everest expedition, crossed the English Channel from Folkestone to Boulogne, then travelled by train south to Marseille, from where they departed on board the P&O passenger liner Caledonia (1894)[287] on 3 March 1922.[288][289] Mallory engaged in deck tennis with Somervell and Wakefield and attended Finch’s oxygen class, which enabled him to overcome initial ambivalence about its implementation.[290] During the voyage to India, Caledonia docked in the Port of Aden, where Somervell disembarked, ascended a nearby mountain, and then returned and boarded the vessel before her departure.[289] On 17 March 1922, Caledonia reached her port of call, berthing in Bombay, India.[291] They travelled across India by train from Bombay, arriving in Darjeeling on 20 March 1922, where they coalesced with the rest of the expedition.[291][292] The expedition members left Darjeeling in groups for the march to Phari.[293][294] On 26 March 1922, Mallory’s group departed Darjeeling with and under expedition leader General Charles Granville Bruce,[293] arriving in Phari on 6 April 1922 and joined the following day by the remainder of the expedition.[295] On 24 April 1922, they reached Shelkar and arrived at the Rongbuk Monastery on 30 April 1922.[296][297] On 1 May 1922, the expedition pitched Base Camp at an altitude of 16,500 ft (5,029 m), 2.75 miles (4.43 km) below the junction of the Rongbuk Glacier and East Rongbuk Glacier.[298][299] On 5 August 1922, following the cessation of the 1922 expedition, Mallory departed from India, voyaging by ship, and arrived in England in mid-August 1922.[300]
Because it’s there[edit]
Announcement of a third expedition, public lectures, and writing[edit]
The announcement that the Tibetan government had formally authorised the third expedition to Mount Everest came on 16 October 1922 at a combined meeting of the Royal Geographical Society and the Alpine Club at Central Hall, City of Westminster, London.[301] In October 1922, the Mount Everest Committee resolved that the third expedition to Mount Everest would commence in the spring of 1924, again under the leadership of General Charles Granville Bruce.[302] The committee was eager to generate money to cover some of the 1924 expedition’s costs and discussed terms for a comprehensive lecture program with Gerald Christie, the agent who had previously represented them in 1921.[303] Following the conclusion of the negotiations, a large-scale lecture tour was organised, with Mallory and George Finch selected as the two public speakers.[304][305] On 20 October 1922, Mallory and Finch at the Central Hall, City of Westminster, delivered their first public lectures concerning the 1922 expedition, including photo illustrations, at 3 p.m. and 8:30 p.m., respectively.[305][306] During the winter, Mallory presented an extensive round of talks throughout Britain and the island of Ireland, filling engagements in places such as Aberdeen, Torquay, Brighton and Dublin,[307][308] receiving thirty per cent of the proceeds, earning £75 in November 1922, £225 in December 1922 and £100 in early January 1923.[308][309] In addition to authoring Everest and Himalaya-related articles for periodicals and encyclopaedias to supplement his income, the committee requested him to contribute to the official book of the 1922 expedition, The Assault on Mount Everest: 1922.[310]
Lecture tour of the United States, Canada, and writing[edit]
The Mount Everest Committee formulated arrangements for Mallory to travel to the United States and Canada on a three-month lecture tour, and under the recommendation of Gerald Christie, the committee chose Lee Keedick of New York to serve as the tour manager.[311][312][n 17] Mallory and Ruth concurred that he should strive for steady employment when he returned from the United States.[310] In mid-January 1923, Mallory embarked on a journey across the Atlantic to the United States on board RMS Titanic‘s sister ship RMS Olympic, where she docked in New York on 17 January 1923.[311] After meeting his lecture agent Keedick, Mallory was dismayed that Keedick had arranged only a meagre number of lecture engagements, and according to the schedule, he had to wait nine days to deliver his first public speech.[314][312] During his free time, he amended his lecture materials to improve impressions for his audiences and effectuated by writing his finalised contribution to the 1922 expedition book, The Assault on Mount Everest: 1922.[314][315] His first contribution was titled The First Attempt, consisting of three chapters: The Problem, The Highest Camp and The Highest Point and his second, The Third Attempt, with two chapters: The Third Attempt and Conclusions.[316] On 26 January 1923, in Washington, D.C., Mallory delivered two lectures, one in the afternoon and one in the evening, which grossed $1000.[317][312] His next engagement was in Philadelphia, where he delivered two separate lectures for a combined audience of approximately 3000, grossing $1500.[318][319] After a comprehensive evaluation by medical professionals at the Presbyterian Hospital when he returned to New York, they determined that his lung capacity was twofold that of the average person.[320][321] On 4 February 1923, Mallory gave a lecture at the Broadhurst Theatre, New York, in front of an audience of some 550, filling only half of the 1100 seating capacity in the auditorium, resulting in a loss of money.[322][323] The next day, 5 February 1923, The New York Times ran a story under the headline, SAYS BRANDY AIDED MT. EVEREST PARTY; A Swig 27,000 Feet Up ‘Cheered Us All Up Wonderfully,’ Mallory Tells Audience, which in effect diverted its coverage of the lecture tour into anti-prohibition propaganda.[324][325] Mallory travelled by train from New York to Canada, where he had lectures scheduled in Toronto and Montreal.[326] The Toronto appointment resulted in a cancellation, whereas the Montreal appearance grossed a meagre $48.[323] In Boston, he delivered a lecture to members of the Appalachian Mountain Club, gave a further speech in Cambridge, made a second visit to Philadelphia, where he at the University Museum, spoke to an audience of 1200, and delivered additional lectures in Toledo, Rochester, Iowa City, and Hanover, before filling a second and final engagement in Boston.[327][328] Under the headline, CLIMBING MOUNT EVEREST IS WORK FOR SUPERMEN, The New York Times of 18 March 1923 quoted Mallory as having replied to the question, «Why did you want to climb Mount Everest?» with the retort, «Because it’s there.»[329][330] The expression describes an existential desire to accomplish a physical and spiritual goal that all mountaineers share.[328] Questions have arisen over the quote’s authenticity and whether Mallory said it.[331][332] Some have suggested that it was an innovative paraphrase created by the newspaper reporter.[331][333] The lecture tour was a financial failure; Mallory regretted that he, Ruth and the children would have to live on less money than he had anticipated generating for some time because he had no immediate prospects for permanent employment.[327] On 31 March 1923, Mallory departed New York on board Saxonia, destined for England, where she docked in Plymouth in early April 1923.[334][328][335]
[edit]
George Herbert Leigh-Mallory
When the Reverend David Cranage, Secretary of the Board of Extra-Mural Studies (BEMS) at the department of the University of Cambridge, and Arthur Robert Hinks of the Mount Everest Committee travelled together on a train from London to Cambridge while Mallory was still in America, it marked the initiation of his future employment prospects.[336][337][338] Cranage advertised a vacancy for a history lecturer to educate in towns and villages outside of Cambridge and assist in organising other extramural courses.[339] The hired individual would conduct lectures in cooperation with the Workers’ Educational Association (WEA), established in the early years of the labour movement, to support working people who had missed the opportunity of education in favour of the privileged.[339] During the train journey, Cranage apprised Hinks about the available job and questioned whether he knew of any possible candidates, and Hinks suggested Mallory.[336] Hinks informed Mallory of the Cambridge extramural lecture vacancy soon after Mallory had arrived back in England.[339] On 20 April 1923, Mallory applied for the position and, following a successful interview on 8 May 1923, was appointed on 18 May 1923.[340] The occupation provided an annual income of £350, supplemented by separate lecture fees approximating £150 yearly.[339] At the end of June 1923, necessitated by the location of his new job, Mallory took lodgings in West Road, Cambridge, leaving Ruth and the children at the Holt, Godalming, until he could find a suitable new residence.[341][342] Soon after moving into his rented accommodation, he found the family a new dwelling, Herschel House on Herschel Road, Cambridge.[342] Ruth’s father, Hugh Thackeray Turner, provided the money for the house, a sixty-eight-year lease costing £4000, under the stipulation of the lease being in Ruth’s name.[342] Mallory immersed himself into his new employment with great zeal, assisted with organising the Golden Jubilee of Cambridge Local Lectures in July 1923 and helped arrange the summer schools during the Long Vacation.[343] In the fall of 1923, he commenced a sequence of lectures in Hunstanton on the emergence of contemporary democracy in the 17th century, in Raunds, tutorial classes in modern history,[n 18] and also conducted classes in Halstead.[341][343] On 18 October 1923, Arthur Robert Hinks wrote to the Reverend David Cranage requesting that Mallory obtain leave from the university to participate in the 1924 British Mount Everest expedition.[344] On 24 October 1923, the Lecture Committee at Cambridge, not eschewing the request, unanimously recommended six months’ leave at half-pay for Mallory, pending the formal approval of a comprehensive syndicate meeting.[345][346] On 28 October 1923, the Mallorys took up residence at their new dwelling, Herschel House.[345] On 31 October 1923, the lecture syndicate officially authorised Mallory’s leave under the conditions recommended by the Lecture Committee.[347]
Olympic medal and third Everest expedition[edit]
On 6 November 1923, after a medical examination by a physician recommended by the Mount Everest Committee, Mallory was declared «fit in every respect,» eliminating the last remaining potential obstacle between him and his participation in the 1924 expedition.[347] On 5 February 1924, at the closing ceremony of the inaugural Winter Olympics, hosted in Chamonix, France, Pierre de Coubertin presented 13 gold medals for alpinism in recognition of the achievements of the 1922 British Mount Everest expedition members to Lt Col Edward Strutt, deputy leader of the expedition.[348][n 19] On 13 February 1924, Mallory committed himself to the 1924 British Mount Everest expedition by signing an official agreement with the Mount Everest Committee.[7][356] On 29 February 1924, he and three other 1924 British Mount Everest expedition members, Andrew Irvine, Bentley Beetham and John de Vars Hazard, departed from Liverpool on board SS California, destined for the third Everest expedition.[357][358] During the voyage to India, Mallory read Maurois’s Ariel, studied Hindustani, and worked through the logistics of supplies and aspects of the organisation for the expedition.[358] Determined to remain physically healthy, he exercised regularly in the gymnasium, threw a medicine ball with Irvine and Beetham, and periodically ran ten laps around the deck.[359][360] In mid-March 1924, California arrived at her destination, berthing in Bombay, India.[361] Mallory, Irvine, Beetham and Hazard travelled across India by train, from Bombay to Darjeeling, where they rendezvoused with the other expedition participants.[361][358] On 25 March 1924, the entire expedition departed Darjeeling for the march to Everest Base Camp.[362] The trek of some 350 miles (560 km) took them from Darjeeling to Kalimpong, Guatong, Jelep La, Yatung, Phari, Tang La, Donka La, Kampa Dzong, Tinki Dzong, Tinki La, Chiblung, Shekar Dzong, Chödzong, Rongbuk and arrived at Base Camp on 29 April 1924, at an altitude of 16,800 ft (5,120 m).[363][364]
Climbing in Great Britain[edit]
In England[edit]
Napes Needle on Great Gable
Mallory’s first rock climbing experience in England transpired during a nine-day excursion to the Lake District in September 1908 with Geoffrey Keynes, Harry Olivier Sumner Gibson, and Harold Edward Lionel Porter (1886–1973),[365] where they took lodgings at Wasdale Head.[366][367] Mallory and Keynes climbed together predominantly, while Gibson and Porter joined them on some climbs.[368] Their initial climb was Kern Knotts Crack on Great Gable, at 70.00 ft (21.336 m) and graded Mild Very Severe, with success, and first ascended by Owen Glynne Jones and Hubert Cecil Bowen on 28 April 1897.[366][369] The following day they climbed Napes Needle, the famous rock pinnacle on Great Gable, at 55.77 ft (17 m), graded Very Difficult and first climbed by Walter Parry Haskett Smith (solo) in June 1886.[366][370] Also on Great Gable, they climbed Eagle’s Nest Ridge Direct, at 164.0 ft (50 m), and graded Mild Very Severe with the first ascent achieved by George Percival Baker, William Cecil Slingsby, Godfrey Allan Solly, and William Anderton Brigg on 15 April 1892.[366][370] They accomplished a successful ascent of North Climb on Pillar Rock,[368] at 320.0 ft (97.536 m), graded Hard Difficult and initially ascended by Walter Parry Haskett Smith, Geoffrey Hastings, and William Cecil Slingsby on 27 July 1891.[371][372] On Scafell, they climbed two challenging routes: Slingsby’s Chimney, at 68.90 ft (21 m), graded Difficult and first ascended by William Cecil Slingsby, Geoffrey Hastings, Edward Hopkinson, and Walter Parry Haskett Smith, on 15 July 1888;[373][374][375] and Keswick Brothers’ Climb, at 242.8 ft (74 m), graded Very Difficult and first climbed by George Dixon Abraham, Ashley Perry Abraham, and James William Puttrell, on 12 July 1897.[368][376][377] On 21 September 1908, they claimed two new routes on the Ennerdale face of Great Gable:[368] Mallory’s Left-Hand Route, at 98.43 ft (30 m), graded Very Difficult, and Mallory’s Right-Hand Route, at 121.4 ft (37 m), graded Mild Very Severe.[366][378][379] In August 1913,[380] Mallory and Geoffrey Winthrop Young achieved a new route, Pinnacle Traverse, at 196.9 ft (60 m), graded Difficult, on the crag, Carn Lés Boel in Cornwall, England.[381][382] On 7 September 1913, Mallory and Alan Goodfellow, a Charterhouse student, created Mallory’s Variation, a new route on Abbey Buttress, Great Gable, where Mallory finished the route by ascending a twenty-foot slab on tenuous grips, rather than exiting to the right.[383][384] On 8 September 1913, with Mallory leading Goodfellow, the pair established another new route, this time on the West Face of Low Man, Pillar Rock, at 213.3 ft (65 m), and graded Hard Very Severe, which they named North-West by West and now known as Mallory’s Route.[383][385] Compared to Mallory’s Route, Conrad Anker rated the Second Step on Mount Everest at 5.10, using the Yosemite Decimal System.[386]
In Scotland[edit]
On 3 April 1906, Mallory, Robert Lock Graham Irving, the teacher who first acquainted him with climbing at Winchester College in 1904, and Guy Leach, a 20-year-old student at New College, Oxford, arrived at Fort William, Scotland, taking accommodation at St Andrew’s Choir School, for a 10-day climbing excursion, which was Mallory’s first experience of a climbing trip in the British Isles.[387] On 6 April 1906, Mallory, Irving and Leach reached the summit of Ben Nevis at 4,413 ft (1,345 m),[n 20] climbing in snow via Observatory Gully and Tower Gully on the northeast face of the mountain.[390] The following day, 7 April 1906, the trio ascended Stob Bàn, following the corniced main arête to the summit at 3,278 ft (999 m).[391] On 9 April 1906, they climbed to the summit of Càrn Mòr Dearg at 4,003 ft (1,220 m), which preceded a second successful ascent of Ben Nevis on the same day via North Trident Buttress.[392] On 10 April 1906, they successfully climbed a feature on Ben Nevis—that they termed East Zmutt Ridge after the Zmutt Ridge on the Matterhorn—which was most presumably Ledge Route on Number Five Gully Buttress, rated Grade II and first ascended in 1895.[393] On 12 April 1906, Mallory, Irving and Leach undertook the last climb of their trip, attaining a successful ascent of Ben Nevis in snow and ice via North-East Buttress, now rated Grade IV.[394] Their achievement was the second recorded winter ascent of this route, the first by Willie Naismith, Alexander Kennedy, William Wickham King, Frances Conradi Squance, and Walter Brunskill, on 3 April 1896.[393][395] On 28 July 1918, Mallory, David Randall Pye, and Leslie Garnet Shadbolt (1883–1973),[396] climbing together, made a new route on the North Face of Sgùrr a’ Mhadaidh on the Isle of Skye, Scotland.[102][397] On 31 July 1918, the triad established another new route with Mallory leading on the Western Buttress of the crag, Sron na Ciche, which has a maximum altitude of 2,818 ft (859 m), located in the Cuillin mountains on the Isle of Skye, Scotland; this route is now known as Mallory’s Slab and Groove, at 984.3 ft (300 m), and graded Very Difficult.[398][399][400] On 1 August 1918, Mallory and Ruth left the Isle of Skye, while Pye and Shadbolt remained, creating a new route on 5 August 1918 on Sron na Ciche, named Crack of Doom, at 541.3 ft (165 m), and graded Hard Severe.[401][402][403]
In Wales[edit]
The cliffs of Clogwyn Du’r Arddu
On 13 September 1907, Mallory, Geoffrey Keynes and Hugh Wilson,[n 21] the son of James Wilson, Canon of Worcester, arrived in Wales for a twelve-day climbing trip, where they stayed at a farm called Gwern-y-Gof-Isaf, near Capel Curig, in Snowdonia National Park, which was Mallory’s first climbing excursion in Wales.[404][405][46] They climbed on Tryfan, Y Lliwedd, Glyder Fawr, Crib Goch and Craig yr Ysfa.[404] On 14 September 1907, Mallory accomplished his first two climbs in Wales: North Gully on Tryfan, first ascended by Roderick Williams and his brother Tom in 1888;[406] and North Buttress, also on Tryfan, first climbed by Owen Glynne Jones, George Dixon Abraham, and Ashley Perry Abraham at Easter 1899.[407][408][409] On 18 September 1907,[407] Mallory, Keynes, and Wilson climbed Terminal Arête, at 400.0 ft (121.92 m), graded Moderate, on Lliwedd’s East Buttress, first ascended in 1903,[410] and purportedly, inadvertently dislodged a large rock as they were finishing their climb.[411][412] Much to their consternation, the rock narrowly missed James Merriman Archer Thomson and his partner E.S. Reynolds as they climbed below on a new route, which they aptly named Avalanche Route.[413][414] On Craig yr Ysfa, the triad climbed two routes: Great Gully, at 731.6 ft (223 m), graded Very Difficult and first climbed by James Merriman Archer Thomson, R.I. Simey, and W.G. Clay on 22 April 1900;[415][416] and Amphitheatre Buttress, at 961.3 ft (293 m), graded Very Difficult with the first ascent completed by George Dixon Abraham, Ashley Perry Abraham, Darwin Leighton, and James William Puttrell in 1905.[407][417] Mallory returned to Snowdonia in August 1908, accompanied by his younger brother Trafford.[418] With their bikes weighed down with gear and climbing ropes looped over their shoulders, they cycled 40 miles (64 km) from Birkenhead to Snowdonia and camped inside a cowshed by the Afon Llugwy River in Capel Curig.[418] During the same month on this trip, Mallory, climbing solo, established the first ascent of The Slab Climb on East Buttress of Lliwedd,[419] now known as Mallory’s Slab, at 220.0 ft (67.056 m), and graded Very Difficult.[418][420] The ascent of The Slab Climb, allegedly occurred due to Mallory scaling it to retrieve his pipe, which he had left behind, on a ledge known as Bowling Green.[421]
In April 1909, Mallory and Geoffrey Winthrop Young journeyed to Pen-y-Pass for a climbing trip, a week before the main party of climbers, who stayed at the Gorphwysfa Hotel, where Mallory and Young joined them after camping for a week in a corrugated-iron outbuilding, which they called the shanty.[422] On the cliffs of Craig yr Ysfa, Mallory and Young established three new ascents and climbed The Slab Climb (Mallory’s Slab) on East Buttress of Lliwedd, which Young described as «The hardest rocks I have done.»[422] When the remainder of the climbing party arrived at Pen-y-Pass, Mallory, Young, Marcus Beresford Heywood, and two Irish climbers, Edward Evans, and Page Dickinson, made the third ascent of Route 1 (Central Route), on Lliwedd,[423] at 400.0 ft (121.92 m), graded Very Difficult, pioneered by James Merriman Archer Thomson, and Oscar Eckenstein, on 24 April 1903.[424][425] In April 1909, during the same trip, Mallory and Evans climbed an unintended new route on East Buttress of Lliwedd.[426] They intended to ascend Great Chimney,[426] at 740.0 ft (225.55 m), graded Very Difficult,[427] first climbed by James Merriman Archer Thomson, Oscar Eckenstein, and Humphrey Owen Jones in April 1907.[428] Due to the misty conditions, route-finding became difficult;[34] as a result, they missed the starting point of Great Chimney and ascended a different line, which, as a consequence, they named Wrong Chimney,[426] at 760.0 ft (231.64 m), now graded Severe.[429] In July 1910, Mallory travelled to Pen-y-Pass in the company of Hugh Wilson, and they completed Lliwedd’s Girdle Traverse, at 3,281 ft (1,000 m), graded Very Difficult,[430] and first traversed by James Merriman Archer Thomson, and E.S. Reynolds, in September 1907.[431][428] In early September 1911, Mallory and his sister Mary travelled to Wales, joined by Harold Edward Lionel Porter, Mallory’s climbing partner, for a week-long excursion, and stayed at the Snowdon Ranger Inn, situated on the shore of Llyn Cwellyn.[432][433] During this trip, Mallory and Porter pioneered several new routes that exalted Mallory to the pinnacle of modern British climbing.[434] On Y Garn, with Porter leading Mallory on the climb’s crux, they ascended a new route, now known as Mallory’s Ridge, at 393.7 ft (120 m), now graded Hard Very Severe.[434][435] This route defeated James Merriman Archer Thomson in 1910, abandoning his attempt on the most challenging pitch, a sixty-foot segment of vertical rock.[434] In October 1910, also on this route, Swiss climber J. Anton Stoop tragically perished in a fall after some large boulders collapsed beneath him.[434][436] Mallory and Porter created a further two new routes: on Llechog, Eastern Gutter at 280.0 ft (85.34 m), now graded Very Severe; on Lliwedd, Far East Cracks (Direct Finish), at 400.0 ft (121.92 m), also graded Very Severe.[437][438]
In September 1912, Mallory returned to Snowdonia National Park for a climbing trip and again took lodgings at the Snowdon Ranger Inn.[439] His primary climbing partner was Ralph Todhunter (1867–1926), who, on 12 July 1926, died in a fall while climbing with his nephew Ernest Bozman on the Southwest wall of Cima della Rosetta, which has a maximum altitude of 8,999 ft (2,743 m), in the Dolomites, near San Martino di Castrozza, Italy.[439][440] During three days of climbing, Mallory, in unison with Todhunter, endeavoured to discover new climbs away from well-established climbing locations, to be featured in Geoffrey Winthrop Young and James Merriman Archer Thomson’s prospective climbing guidebook.[439] On Craig Cwm Du, the pair pioneered three first ascents: Pis-Aller Rib, at 462.6 ft (141 m), now graded Severe;[441] Yellow Buttress, at 508.5 ft (155 m), also graded Severe;[442] and Adam Rib, at 400.0 ft (121.92 m), graded Hard Severe—straightening out a route established in 1911 by James Merriman Archer Thomson and his party by overcoming difficulties he had circumvented on the finishing pitch.[439] On Clogwyn Du’r Arddu, also called «Cloggy,» which had only two routes, established in 1905, Mallory and Todhunter created the third, East Gully, at 500.0 ft (152.4 m).[439] On Craig Yr Ogof (Cwm Silyn), they recorded its first rock climbing route, Four Pitch Gully, at 300.0 ft (91.44 m), later graded Difficult.[439] On 27 December 1913, Mallory, Geoffrey Winthrop Young, and Siegfried Wedgwood Herford established a milestone by completing the first recorded double traverse on the snow and ice-covered north face of Lliwedd.[443][444] They commenced on Far East Buttress, completing Girdle Traverse at Slanting Buttress, and re-traversed the entire face by following a higher line than previous.[445][446] In December 1915, Mallory, Conor O’Brien, and Herbert Vincent Reade travelled to Wales for a climbing trip and stayed at Pen-y-Pass.[447] On Clogwyn y Ddysgl, they merged two already-existing lines to create a new route that they named, The Black Gates, at 216.5 ft (66 m), now graded Very Difficult.[447][448] On 31 December 1915, Mallory, O’Brien, and Reade created Three Pinnacle Face (to Bilberry Terrace only) on Lliwedd’s West Peak by adding a new start to an old line.[447][449] In January 1919, Geoffrey Winthrop Young initiated the re-establishment of the Easter Pen-y-Pass parties and determined that out of a total of sixty climbers, of whose identities were listed in the Pen-y-Pass book until 1914, twenty-three of them had perished in World War I, and eleven more had suffered injuries, including himself.[450][451][452] On 31 August 1917, while serving on the Isonzo Front during the Eleventh Battle of the Isonzo as an ambulance driver in the First British Ambulance Unit for Italy, based at Villa Trento, Dolegnano, near Udine, Italy, and commanded by George Macaulay Trevelyan, an Austrian shell struck Young, at Monte San Gabriele.[453][454][455] His left leg was extensively injured, necessitating amputation at the knee.[202] At Easter 1919, Mallory and his wife Ruth were among the twenty-eight guests who stayed at the Gorphwysfa Hotel for the Pen-y-Pass climbing trip.[456] On Easter Monday, 21 April 1919, Mallory, Ruth, David Randall Pye, and Claude Aurelius Elliott established two new routes on Lliwedd’s East Buttress: Bowling Green Buttress, at 280.0 ft (85.34 m), graded Very Severe and Garter Traverse, at 800.0 ft (243.84 m), also graded Very Severe.[457][458]
Climbing in continental Europe[edit]
First expedition in the Alps[edit]
Southeast Ridge of Finsteraarhorn
Frontier Ridge of Mont Maudit
West Face of Dent Blanche
Aiguille du Midi, with an illustration of the Mallory-Porter route, which they ascended in 1919
On 2 August 1904, Mallory and his fellow Wykehamist, Harry Olivier Sumner Gibson, the first cousin of Laurence Olivier,[459] left Southampton, England, with and under the guidance of Robert Lock Graham Irving, and arrived in Bourg-Saint-Pierre, Switzerland, on 4 August 1904, which was Mallory’s first climbing trip to the Alps.[460][22] On 5 August 1904, Irving, Mallory, and Gibson attempted their first climb, Mont Vélan, located on the Swiss-Italian border, but after a valiant endeavour, had to retreat approximately 600.0 ft (182.88 m) below the summit because both Mallory and Gibson suffered from altitude sickness.[461][462] On 8 August 1904, after climbing via the west arête, they crossed the vast snowfield from Combin de Valsorey and successfully reached the summit of Combin de Grafeneire.[463][462] On 13 August 1904, at 11:20 a.m. (Swiss time), Irving, Mallory and Gibson reached the summit of Dufourspitze at
15,203 ft (4,634 m), the third-highest peak in Western Europe.[464] On 26 August 1904, at 7:00
a.m., with Gibson departed, Irving and Mallory commenced an assault on Mont Blanc, at 15,773.65 ft (4,807.81 m), the highest mountain in Western Europe.[465] They ascended via the west branch of the Glacier du Dôme and thence an ice slope beneath the ridge which connects the Tour des Aiguilles Grise with Bionnassay arête.[466] After climbing to the top of the ice slope, they turned right and followed the ridge to Piton des Italiens, at 13,133.2 ft (4,003 m),[467] from where they ascended to Dôme du Goûter and reached the Vallot Hut shortly after midday.[466] After a meal at the Vallot, they proceeded up the Bosses du Dromadaire toward the summit of Mont Blanc, which they attained in an hour and fifteen minutes from the refuge.[468]
Second, third, and fourth expeditions in the Alps[edit]
In January 1905, Robert Lock Graham Irving established the Winchester Ice Club.[27] With Irving as the club’s president, Mallory, Harry Olivier Sumner Gibson, Harry Edmund Guise Tyndale (1888–1948),[469] and Guy Henry Bullock became members.[470] In August 1905, the Ice Club travelled to the Alps.[27] On 21 August 1905, at 3:15 a.m. (Swiss time), Irving, Mallory, and Bullock left the Bertol Hut, crossed the vast snowfield at the head of the Mont Miné and Ferpècle Glaciers, arrived at the South Ridge of Dent Blanche at 7:15 a.m., climbed the arête, and reached the summit, at 14,294.62 ft (4,357 m), before midday.[471][472] After the 1909 Pen-y-Pass party, Geoffrey Winthrop Young invited Mallory to join him for a climbing trip in the Alps.[73] On 29 July 1909, after a four-year hiatus, Mallory departed for the Alps in the company of Young,[473] where they arrived on 31 July 1909 and,[474] on 2 August 1909, were joined by Charles Donald Robertson (1879–1910).[475][474][476][n 22] On 1 August 1909, at 5:30 a.m., Mallory and Young set out from Belalp, climbed Unterbächhorn via the Enkel Ridge, and reached the summit at 12:35 p.m.[475][474] On 4 August 1909, at 3:00 a.m., Mallory, Young, and Robertson left Belalp, crossed the Unterbäch Glacier, and at 9:00 a.m. reached the summit of Unterbächhorn.[478][474] Their objective was to ascend the formidable unclimbed Southeast Ridge of Nesthorn.[474] They followed the narrow exposed ridge from the summit of Unterbächhorn, reaching the col that marked the beginning of the unconquered arête, which they successfully climbed, and at 7:00 p.m., they attained the summit of Nesthorn, at 12,539 ft (3,822 m), for a historical first ascent.[478][479] On 6 August 1909, Mallory, Young, and Robertson ascended to the Konkordia Hut from Belalp, and on 7 August 1909, they crossed the mountain pass Grünhornlücke, followed by the upper part of the Fiescher Glacier, and climbed to the summit via the Southeast Ridge of the highest mountain in the Bernese Alps, Finsteraarhorn, at 14,022 ft (4,274 m).[480][481] On 9 August 1909, the triad reached the summit of Jungfrau at 13,642 ft (4,158 m).[480] On 13 August 1909, Mallory, Young, and Robertson, accompanied by the Swiss mountain guide Josef Knubel, traversed Aiguille Verte and descended via the Moine Ridge.[480][482] Their culminating route was a traverse of Aiguille du Chardonnet on 20 August 1909, ascending via the Forbes Ridge and descending by the Col du Passon.[483][482] In August 1910, Mallory travelled to the Alps with fifteen-year-old John Bankes-Price under his guidance and introduced him to alpine climbing.[484] Mallory and Bankes-Price ascended the peaks of Trifthorn and Riffelhorn, and additionally, Mallory completed a traverse of Mont Collon.[485]
Fifth expedition in the Alps[edit]
At the beginning of August 1911, Mallory returned to the Alps with Robert Lock Graham Irving and Harry Edmund Guise Tyndale.[486] Within the Graian Alps, they ascended Gran Paradiso, at 13,323 ft (4,061 m), via its precipitous East Face, and on 8 August 1911, Ciarforon, at 11,949 ft (3,642 m), by the Northwest Ridge.[487][488][489] On 9 August 1911, at approximately 3:30 p.m. (Italian time), they reached the summit of Herbétet, at 12,395 ft (3,778 m), by way of a first ascent of its Western Ridge.[488][490] On 11 August 1911, after departing Cogne at midnight, Irving, Mallory, and Tyndale completed the first traverse of the main ridge between the Colle Superiore delle Sengie, at 10,951 ft (3,338 m) and Punta d’Ondezana, at 11,457 ft (3,492 m).[488][491][492] This route took them over several cols and peaks, including Cima Occidentale di Valeille, at 11,014 ft (3,357 m), and Punta Scatiglion Orientale, at 11,178 ft (3,407 m), reaching the summit of Punta d’Ondezana just before 2:00 p.m.[491][492] On 14 August 1911, at 3:30 a.m., the trio left the Pousset Hut, crossed the Trajo Glacier, and ascended Grivola, at 13,022 ft (3,969 m), via its North Ridge, summiting at approximately 12:30 p.m.[489] On 18 August 1911, at 3:30 a.m., Irving, Mallory, and Tyndale left the Col du Géant; at 3:30 p.m., they reached the summit of Mont Maudit, at 14,649 ft (4,465 m), via the third ascent of its Southeast Ridge (Frontier Ridge),[n 23] and thence attained the summit of Mont Blanc at 6:30 p.m.[497][493][496] In 1917, Mallory rewrote an impassioned account, begun in 1916 while serving in France, about the Mont Maudit ascent with Irving and Tyndale.[208] It was published as an article in the Alpine Journal of 1918, and titled Mont Blanc from the Col du Géant by the Eastern Buttress of Mont Maudit,[498] and contained the question, «Have we vanquished an enemy? None but ourselves.»[102][499] Irving, Mallory, and Tyndale’s final climb of the August 1911 trip commenced in Saint-Gervais-les-Bains, ascending to the Col de Miage, from where they followed the ridge to the head of the Glacier de Tré-la-Tête, then climbed to the summit of Tête Carrée, at 12,244 ft (3,732 m),[500] via its North-northwest Ridge, and descended to Les Mottets from the Col du Mont Tondu.[432]
Sixth expedition in the Alps[edit]
In August 1912, Mallory undertook his sixth expedition to the Alps, along with mountaineering partners Harold Edward Lionel Porter and Hugh Rose Pope (1889–1912).[501][n 24] On 8 August 1912, Mallory, Porter, and Pope ascended to the summit of Pointe des Genevois, at 12,054 ft (3,674 m), from where they traversed 1,312 ft (400 m) along the arduous and exposed narrow ridge to the summit of Dent de Perroc, at 12,060 ft (3,676 m).[504] The triad set out at 3:30 a.m. on 10 August 1912, and climbed by its precipitous North Face to the summit of Pigne d’Arolla, at 12,454 ft (3,796 m), then descended to the Col de la Serpentine, from where they ascended to the summit of Mont Blanc de Cheilon, at 12,697 ft (3,870 m).[505] The following day, 11 August 1912, Mallory awoke with extremely painful swollen eyes and was diagnosed with snow-blindness by a doctor, who advised him to stay in a darkened room for several days.[505][504] On 15 August 1912, Mallory, Porter, and Pope, along with Canon George Harford and Mabel Capper, traversed the Douves Blanches Southwest arête.[506] On 17 August 1912, Mallory, Porter, and Pope established a new route; they ascended a line on the West Face of Dent Blanche, joined the South Ridge a short distance below the summit, which they reached at 10:30 a.m., then descended via the South Ridge (Wandfluh Ridge) and arrived in Zermatt, Switzerland, at 7:30 p.m.[507][504][508] Mallory’s final outing of the 1912 Alpine expedition, his last for seven years, was with Geoffrey Winthrop Young and Hugh Rose Pope in an ascent to the summit of Tête du Lion, at 12,182 ft (3,713 m),[509] before returning to Zermatt via the Col Tournanche, at 11,388 ft (3,471 m).[510][511][512][513]
Seventh and eighth expeditions in the Alps[edit]
At the end of July 1919, Mallory returned to the Alps, accompanied by climbing partners Harold Edward Lionel Porter and Claude Aurelius Elliott.[514] On 1 August 1919, Elliott, as a consequence of a knee injury, could not further participate in mountaineering activity and travelled back to England.[515] On 2 August 1919, Mallory and Porter set out from Montanvert and proceeded up the Mer de Glace to the Glacier de Trélaporte, from where they ascended a new route to the summit of Aiguille des Grands Charmoz, at 11,302 ft (3,445 m), via its forbidding East Face and North East arête.[516][517] On 5 August 1919, at 2:30 a.m., Mallory and Porter left the Refuge du Plan de l’Aiguille, crossed the northern section of the Glacier des Pélerins, and climbed a new route on its Northwest Face to the summit of Aiguille du Midi,[518] at 12,605 ft (3,842 m), which they reached at 12:15 p.m. (French time).[516][519] This route, rectified by the climber Jean-Louis Urquizar on 25 July 1971, is now known as Rectified Mallory-Porter, totalling
5,020 ft (1,530 m) in elevation gain and graded AD+.[520][521] On 8 August 1919, Mallory and Porter, with British climbers Arthur Cecil Pigou and William Mclean, left Purtud, walked up the Val Veny, went up the Miage Glacier and Glacier du Mont Blanc, and reached the Quintino Sella Hut at 8:00 p.m.[522][516] The following day, 9 August 1919, at 5:15 a.m., Mallory, Porter, Pigou, and Mclean left the Quintino Sella Hut and completed a traverse of Mont Blanc by following a route known as Tournette Spur—pioneered by Jean-Antoine Carrel, Thomas Stuart Kennedy, and Johann Fischer on 2 July 1872—and reached Grand Mulets by descent at 4:15 p.m.[523][524] On 24 July 1920, Mallory departed England for his eighth and final expedition to the Alps with Herbert Vincent Reade, Claude Aurelius Elliott, and David Randall Pye.[236] The adverse weather and physical conditions of some of Mallory’s climbing partners hampered their objectives.[236] By the time Elliott left the expedition due to a recurring knee injury and Pye because of physical fitness issues, the mountaineering party had ascended Aiguille de Talèfre at 12,238 ft (3,730 m),[525] and traversed Aiguille de Triolet, at 12,697 ft (3,870 m), from the Glacier de Pré de Bar to the Glacier de Triolet.[526][527] Mallory and Reade journeyed to Zermatt, where they rendezvoused with two new climbing partners, George Ingle Finch and Thomas Guy Burton Forster (1886–1962).[528][529] Mallory, Reade, Finch, and Forster ascended to the Matterhorn summit at 14,692 ft (4,478 m), and two days later, they attained the summit of Zinalrothorn at 13,848 ft (4,221 m).[528][527]
One of Mallory’s closest friends and climbing companions, whom he met in Zermatt, Switzerland, on 31 August 1909, was a young woman named Cottie Sanders, who became a novelist using the pseudonym of Ann Bridge.[530][531] Their relationship was elusive; Sanders was either a «climbing friend» or a «casual sweetheart.»[532] After Mallory died, Cottie wrote a memoir of him, which was never published but provided much of the material used by later biographers, such as David Randall Pye and David Allan Robertson, and the novel Everest Dream.[533][534]
Climbing in Asia[edit]
1921 British Mount Everest reconnaissance expedition[edit]
Mallory participated in the first historical expedition to Mount Everest in 1921, which was coordinated and subsidised by the Mount Everest Committee and had the express objective of undertaking a detailed reconnaissance of the mountain and its approaches to discover the most accessible route to its summit.[254] From the Survey of India, expedition surveyors Henry Morshead and Oliver Wheeler, with the assistance of Indian surveyors Lalbir Singh Thapa, Gujjar Singh, and Turubaz Khan, produced the first accurate maps of the Mount Everest region.[538][539][540] On a 1⁄4 -inch scale, the expedition surveyed 12,000 square miles (31,080 km2) of new territory, and they also revised an existing 1⁄4 -inch scale, 4,000 square miles (10,360 km2) map of Sikkim.[541][542] Using photo-topographical surveying instruments, Major Wheeler single-handedly completed a methodical and detailed photographic survey of the environs of Mount Everest, covering an area of 600 square miles (1,554 km2) on a 1-inch scale.[543][542] From the Geological Survey of India, expedition geologist Alexander Heron conducted a geological reconnaissance by mapping an area of 8,000 square miles (20,720 km2) on a 1⁄4 -inch scale.[544][545] The area’s natural history was explored in considerable detail by expedition naturalist and medical officer Sandy Wollaston, with mammals, birds, and plants collected, including new specimens.[546][542] On 18 August 1921, at 3:00 a.m., after an arduous two-month-long reconnaissance of Everest’s northern and eastern approaches, Mallory, Guy Bullock, Henry Morshead, and a porter named Nyima left their high camp at approximately 20,000 ft (6,096 m).[547][548] From the western head of the Kharta Glacier, they ascended to the col of Lhakpa La, at 22,470 ft (6,849 m), which they reached at 1:15 p.m.[548][549] From the col of Lhakpa La, 1,200 ft (366 m) directly below them, was the head of the East Rongbuk Glacier, across which rises a 1,000 ft (305 m) wall of snow and ice leading to Everest’s North Col, at 23,031 ft (7,020 m), from where mountaineers can attain the summit via the North Col-North Ridge-Northeast Ridge route.[548][550] Their preliminary reconnaissance was complete; they discovered the gateway to the mountain.[548][551] On 23 September 1921, at 11:30 a.m., Mallory, Bullock, Wheeler, and ten porters left their camp on Lhakpa La, descended into the East Rongbuk Glacier, and pitched camp at approximately 4:00 p.m., at an elevation of 22,000 ft (6,706 m),[552] 1 mile (1.6 km) from the beginning of the ascent to the North Col.[553][554][555] On 24 September 1921, at 7:00 a.m., the three expedition members and three porters, Ang Pasang, Lagay, and Gorang, departed from their camp, traversed 1 mile (1.6 km) across the East Rongbuk Glacier to the foot of the 1,000 ft (305 m) precipitous wall of snow and ice, which they arduously ascended, and reached the North Col at 11:30 a.m.[553][554][556] On the col and above, gale force winds blew from the northwest, which made further advance impossible, and they descended to their camp on the East Rongbuk Glacier, where they spent the night.[557] Wheeler suffered from the first stages of frostbite in each of his lower extremities below the knee, and Bullock was exhausted.[558][559] The next day, 25 September 1921, the severe winds had not abated; the porters were at the limits of their physical reserves, and Mallory made a definitive decision by ending the reconnaissance and expedition.[560][561][562]
1922 British Mount Everest expedition[edit]
First summit attempt, Mallory, Somervell, Norton, and Morshead[edit]
North Face of Everest, with illustrations of the maximum elevations attained by the 1922 British Mount Everest expeditions’ first and second summit attempts.[n 26][n 27]
In 1922, Mallory returned to the Himalayas as a member of the 1922 British Mount Everest expedition led by Brigadier-General Charles Bruce.[568] The expedition’s primary objective was to attain the summit of Mount Everest and become the first mountaineers to accomplish this.[569] On 20 May 1922, at 7:30 a.m., Mallory, Howard Somervell, Edward Norton, Henry Morshead, and four porters began their day at Camp IV, situated on the North Col at an elevation of 23,000 ft (7,010 m).[570][571] At 8:00 a.m., after getting roped up, the eight men commenced their ascent from the North Col without supplemental oxygen.[572][573] They aimed to climb the North Ridge and establish Camp V at an altitude of 26,000 ft (7,925 m), from where they planned an attempt to reach the summit.[574][575] At 11:30 a.m., they attained an elevation of 25,000 ft (7,620 m), a gain of 2,000 ft (610 m) from the North Col, in 3+1⁄2 hours, a vertical climbing rate of 571 ft (174 m) per hour, including stops.[576] Mallory estimated that from their present position, it would necessitate an approximate three hours to ascend 1,000 ft (305 m) and pitch Camp V there, which left little time for the porters to return to Camp IV on the North Col before nightfall and was uncertain of finding a well-sheltered area from the strong winds on the lee-side of the North Ridge above them.[577][578] Therefore, they abandoned their initial plan and erected Camp V at their current altitude of 25,000 ft (7,620 m).[577][578] The four porters departed for the North Col camp at 3:00 p.m., and Mallory, Somervell, Norton and Morshead spent the night at Camp V.[579][580]
The next day, 21 May 1922, at 8:00 a.m., the four mountaineers were roped up and commenced their attempt to reach the summit from Camp V.[581] After a few steps, Morshead, who was suffering from frostbite in his fingers and toes, declared that he was unable to continue and stayed behind at Camp V.[577][582] Adverse weather conditions prevented the climbers from beginning their ascent at 6:00 a.m. as planned, leaving them decidedly behind schedule.[583] Other than possible mountaineering difficulties, the fate of their summit bid depended predominantly on time and speed.[584] Mallory’s arithmetical computation estimated their vertical ascent rate at an unsatisfactory 400 ft (122 m) per hour, not including stops, from which it was apparent they would be climbing after nightfall, a risk they were unwilling to take, and decided that 2:30 p.m. was their retreat time.[585] At 2:15 p.m., Mallory, Somervell, and Norton halted and lay against rocks on the North Ridge, where they remained for fifteen minutes and nourished their weary bodies with sustenance.[586] Their aneroid barometer read 26,800 ft (8,169 m), a height later rectified and confirmed by a theodolite as 26,985 ft (8,225 m), a new world altitude record.[587] At 2:30 p.m., they began their descent, and at 4:00 p.m., they reached Camp V, where Morshead was waiting to join them for the return to Camp IV on the North Col.[588][589] The four climbers roped up and recommenced their descent to 23,000 ft (7,010 m).[589] As they descended, Morshead, who was third on the rope, slipped, and his impetus dragged Somervell and Norton down a slope leading directly to the East Rongbuk Glacier, several thousand feet below.[588][590] Mallory, who was leading at the time of this near-catastrophic incident, immediately reacted by forcing the pick of his ice axe into the snow and hitching the climbing rope around the axe’s adze.[590] He stood in a secure position and held the rope in his right hand above the hitch, pressed downward with his left hand on the axe’s shaft, and, using his entire weight, leaned towards the incline, securing the pick of his axe in the snow.[590] Commonly, in such circumstances, either the belay will not hold applying this technique, or the climbing rope will snap.[591] Fortunately, the axe and rope held because their bodies’ combined weight and momentum did not come upon the rope at once, which saved the lives of Somervell, Norton, and Morshead.[591][592] They regained their positions and reached their tents after nightfall at 11:30 p.m. on the North Col., exhausted, hungry, frostbitten and dehydrated.[593][594][595]
Second summit attempt, Finch and Bruce[edit]
On 27 May 1922, at 6:30 a.m., George Finch, Geoffrey Bruce, and Tejbir Bura departed from Camp VI at 25,500 ft (7,772 m) on the North Ridge, using supplemental oxygen for the expedition’s second attempt to reach the summit of Everest.[596] Their plan of assault was to take Bura, who was shouldering two spare oxygen cylinders, as far as the Northeast Shoulder at 27,400 ft (8,352 m), where he would begin his descent, leaving Finch and Bruce to continue their ascent.[597] When they reached 26,000 ft (7,925 m), Bura, at the limits of his endurance, collapsed, unable to continue.[598] He commenced his descent to Camp VI, where being a solitary figure, he would await the return of his two climbing partners.[599] Finch and Bruce continued their endeavour to reach the summit, loaded up the extra oxygen cylinders that Bura had been shouldering, and dispensed their climbing rope to enable themselves to advance faster.[600] By the time they attained an elevation of 26,500 ft (8,077 m) on the North Ridge, the wind, which had been gradually increasing, had intensified to such a strength that it necessitated a change in their line of ascent, which they hoped would reduce the possibility of the onset of exposure by providing more shelter.[600] Therefore, Finch and Bruce left the North Ridge and continued their climb toward the summit by traversing across the Yellow Band on the North Face of Everest.[600] When they attained 27,000 ft (8,230 m), they changed course and climbed diagonally upwards, toward a point on the Northeast Ridge, approximately halfway between the Northeast Shoulder and the summit.[565] Not long after, Bruce, about 20 ft (6 m) below Finch when his oxygen apparatus failed, struggled valiantly upwards as his climbing partner came to his aid, and they soon repaired the equipment.[565] The time was approximately midday, and their aneroid barometer registered an elevation of 27,300 ft (8,321 m), surpassing the previous attempt by 315 ft (96 m), a new world altitude record.[601][602] Weakened by hunger and debilitated by exhaustion, they were not in any physical condition to continue their summit bid.[603] They began their descent, regained the North Ridge just after 2:00 p.m. and reached Camp VI at 2:30 p.m.[604]
Third summit attempt, Mallory, Somervell, Crawford, and the North Col avalanche[edit]
At the beginning of June 1922, during the onset of the impending monsoon season, the expedition arranged a third attempt to reach the summit.[605] Despite their awareness of the apparent dangers of the prevailing monsoon conditions, they were intent on implementing their plan.[606] Their objective was to ascend to their old Camp V at 25,000 ft (7,620 m) without using supplemental oxygen and, from there, use a cylinder of oxygen each to attain an elevation of 26,000 ft (7,925 m), where they would establish their new Camp V, from where they would use supplemental oxygen for their endeavour to reach the summit.[607] On 7 June 1922, at 8:00 a.m., Mallory, Somervell, Colin Crawford and fourteen porters left Camp III at 21,000 ft (6,401 m), traversed across the head of the East Rongbuk Glacier in snow, in which they sank to their knees and at 10:00 a.m., reached the base of the 1,000 ft (305 m), wall of snow and ice rising to the North Col.[608] At 10:15 a.m., four men roped up in the following order: Somervell leading, then Mallory, a porter, and Crawford, initiated the climb to the North Col.[609] At approximately 1:30 p.m., Mallory, Crawford and the porter halted, some 600 ft (183 m) below Camp IV, which allowed time for the thirteen porters ascending below, on three separate ropes, to join them.[610][611][612] Unroped at this time, Somervell, who was a short distance ahead, was cutting steps in the snow to gain time.[612] At about 1:50 p.m., soon after the seventeen men had recommenced their ascent, an avalanche emanated from an ice cliff above them, sweeping over the entire group.[613][610][614] Mallory, Somervell, Crawford, and the porter extricated themselves from beneath the snow.[615] They peered down the slope and observed a group of four porters roped together, approximately 150 ft (46 m) below them, who had been climbing in the second party directly behind and laboriously had just struggled to their feet.[610][616] The porters were pointing urgently down the slope toward a crevasse, into which the avalanche had swept two groups totalling nine porters, of which four were on one rope and five on another.[610][617] Immediately implemented was a rescue mission comprising Mallory, Somervell, Crawford, four porters, and expedition members John Noel and Arthur Wakefield later joined them.[618][619] They recovered eight of the aggregate of nine porters swept into the crevasse, of which only two were alive, and they could not find the one remaining porter, who tragically was killed along with the six others.[618] The names of the seven porters who perished were, Lhakpa, Narbu, Pasang, Pema, Sange, Temba, and Antarge.[354][355] At Camp III, a memorial cairn was constructed in their honour, made of boulders from a glacier moraine.[620] This catastrophic event marked the end of the third summit attempt and the 1922 British Mount Everest expedition.[621]
Mallory’s last climb[edit]
1924 British Mount Everest expedition[edit]
The personnel of the expedition[edit]
Mallory participated in the 1924 British Mount Everest expedition, led again, as in 1922, by Brigadier-General Charles Bruce.[622] The other members of the 1924 expedition team were: Edward Norton as second-in-command and mountaineering leader; mountaineers Andrew Irvine, Howard Somervell, Geoffrey Bruce, Bentley Beetham, and John de Vars Hazard; mountaineer and oxygen officer Noel Odell; photographer and cinematographer John Noel; naturalist and medical officer Richard Hingston; and transportation officer Edward Shebbeare.[623][624][622] On 9 April 1924, General Bruce collapsed due to recurrent malaria and had ongoing cardiovascular issues during the trek to Everest Base Camp.[625][626] As a result, Norton took charge of the expedition leadership, appointed Mallory as deputy and mountaineering leader, and General Bruce returned to India.[627][628]
First summit attempt, Mallory and Bruce[edit]
On 1 June 1924, at 6:00 a.m., Mallory and Bruce, without supplemental oxygen on the expedition’s first summit attempt, and eight porters commenced their ascend from Camp IV on the North Col at 23,000 ft (7,010 m).[629][630] They planned to climb the North Ridge and establish Camp V at approximately 25,500 ft (7,772 m), where they would sleep overnight; the following day, 2 June 1924, they would ascend to about 27,200 ft (8,291 m), where they would pitch Camp VI, sleep there overnight, and from there, on 3 June 1924, attempt to reach the summit, without oxygen.[631][632] The precise elevation for establishing Camps V and VI depended on the porters’ physical abilities to carry heavy loads in the rarefied air and weather conditions.[632] As the two climbers and eight porters ascended the North Ridge with an average gradient of 45 degrees, they exposed themselves to a penetrating northwest wind.[633] At approximately 25,000 ft (7,620 m), four of the porters could not ascend any further after reaching the limits of their endurance.[633] Mallory, Bruce, and the four remaining porters progressed to an elevation of 25,200 ft (7,681 m), where they established Camp V.[629][634] Five of the eight porters descended to Camp IV, leaving three to shoulder loads the following day up to the location where the expedition intended to pitch Camp VI.[635] Mallory, Bruce, and the three porters slept at Camp V that night, and on the next day, 2 June 1924, only one porter was able to proceed, and two declared themselves sick and physically unable to carry loads.[635] Without enough porters to assist both climbers, the summit attempt, destined to fail, was abandoned immediately, and the party returned to the North Col, which they reached by midday.[636][635]
Second summit attempt, Somervell and Norton[edit]
On 2 June 1924, at 6:30 a.m., Somervell and Norton began their summit attempt from Camp IV, without supplemental oxygen, along with the assistance of six porters carrying loads.[637] During their ascent on the North Ridge, they encountered Mallory, Bruce, and their porters descending from Camp V after their summit bid, which proved unavailing.[638] Because Camp V, part of which the previous party had intended to use for their higher Camp VI, had been left where it was, in its entirety, with tents and sleeping bags, Somervell and Norton sent a pair of their porters down, who descended with Mallory, Bruce, and their porters, as they no longer required their services or the loads that they were shouldering.[639] At approximately 1:00 p.m., Somervell, Norton, and their four porters reached Camp V at 25,200 ft (7,681 m), which the preceding party on the sheltered eastern side of the North Ridge had pitched.[639] The two mountaineers and their four porters spent the night at Camp V.[640] On the following morning of 3 June 1924, one of their porters, Lobsang Tashi, suffering from altitude sickness, could not continue and descended alone to Camp IV on the North Col.[641] At 9:00 a.m., Somervell, Norton, and their three remaining porters, Narbu Yishé, Llakpa Chédé and Semchumbi, departed from Camp V and continued their ascent up the North Ridge.[642] At approximately 1:30 p.m., the valiant Semchumbi, who was lame with a swollen knee, had reached his limits and could not continue.[643] As a result, Norton brought the entire party to a halt at about this time, and he selected a site to pitch Camp VI at their current altitude.[644] At an elevation of 26,700 ft (8,138 m), they established Camp VI in a narrow cleft, which provided some possible shelter from the northwest wind.[644][567] At about 2:30 p.m., the services of the three porters, Narbu Yishé, Llakpa Chédé and Semchumbi, were no longer required, and Norton sent them down to Camp IV on the North Col.[644] Somervell and Norton camped that night at 26,700 ft (8,138 m), the highest elevation at which anyone had ever slept up to that time.[645]
On 4 June 1924, at 6:40 a.m., Somervell and Norton left Camp VI and commenced their assault to reach the summit of Mount Everest, a vertical height of 2,331.7 ft (710.7 m) above.[645] The weather conditions were fine, clear, and almost windless but bitterly cold, a perfect day for a summit attempt.[646] After approximately an hour of ascent up the North Ridge, they reached the lower edge of the Yellow Band, a stratum of sandstone about 1,000 ft (305 m) deep that crosses the entire North Face.[645] From this location, they changed their line of ascent by leaving the North Ridge and traversing diagonally across the Yellow Band, following a line roughly parallel to and approximately 500 ft (152 m) to 600 ft (183 m) lower than the crest of the Northeast Ridge.[647] Towards midday, Somervell and Norton reached a point below and in proximity to the top periphery of the Yellow Band and were a short distance east of the Norton Couloir.[648] At midday, as they neared 28,000 ft (8,534 m), Somervell, who was suffering from an extremely sore throat and a severe cough as a result, felt that, from his perspective, it was impracticable for him to continue.[649][650] To Norton, he expressed that he was only delaying him and encouraged him to continue alone and reach the summit.[651][652] Somervell sat on a ledge while Norton proceeded solo.[652] At 1:00 p.m., suffering from temporary visual impairment due to oxygen deficiency,[n 28] exhausted from his efforts, and knowing that from his present location and the current time, he stood no chance of reaching the summit and returning safely, Norton retreated from a point where he had attained a new world altitude record of 28,126.0 ft (8,572.8 m).[654][n 29] During their descent on the North Ridge, at around 25,000 ft (7,620 m), Somervell experienced intense coughing and dislodged something in his throat, severely obstructing his breathing.[659] He was close to death and saved his own life by forcibly pressing on his chest with both hands, dislodging the obstruction that came into his mouth and coughing up blood.[659] The obstruction was a slough from the mucous membrane lining of his larynx caused by frostbite.[659] At 9:30 p.m., Somervell and Norton reached Camp IV on the North Col.[660]
Third summit attempt, Mallory and Irvine[edit]
On 4 June 1924, at 2:10 p.m., Mallory and Andrew Irvine, using supplemental oxygen for the final half of their ascent, left Camp III at 21,000 ft (6,401 m) and reached Camp IV on the North Col at 23,000 ft (7,010 m) in 3 hours, at 5:10 p.m., including approximately 1⁄2 an hour at a dump choosing and testing oxygen cylinders.[661][662][663] That night at Camp IV, Mallory shared a tent with Norton, who had just returned from his summit attempt with Somervell, and informed Norton that if his summit bid with Somervell had failed, he had planned to make one further attempt with supplemental oxygen.[664] Mallory further elucidated that he went down to Camp III and recruited enough porters with Bruce’s assistance for another endeavour.[664] He also chose Irvine as his climbing partner because of the initiative and mechanical expertise he exhibited with the oxygen apparatus.[665] On 6 June 1924, at 8:40 a.m., Mallory and Irvine, who would use supplemental oxygen for part of their ascent, set off in excellent weather from Camp IV on the North Col for Camp V on the North Ridge at 25,200 ft (7,681 m), accompanied by eight porters.[666][667][668] Both mountaineers shouldered modified oxygen apparatus, each man carrying two cylinders apiece, and their eight porters, not using oxygen, took provisions, bedding, and extra oxygen cylinders.[667] Mallory and Irvine progressed steadily and attained Camp V in good time, and shortly after 5:00 p.m. that evening, four of their porters arrived back at Camp IV, with a note from the climbing party stating, «There is no wind here, and things look hopeful.»[666][667] The two climbers and their four remaining porters spent the night at Camp V.[667] On 7 June 1924, Mallory, Irvine, both using oxygen for part of their climb, and their four porters ascended to Camp VI at 26,700 ft (8,138 m) on the North Ridge.[666][667] That same day, expedition member Noel Odell, in support of Mallory and Irvine and his porter Nema climbed to Camp V from the North Col.[670][668] Soon after they had attained Camp V, Mallory and Irvine’s four remaining porters reached Camp V from Camp VI, and they gave Odell a handwritten note from Mallory, which read:[671]
Dear Odell,
«We’re awfully sorry to have left things in such a mess—our Unna Cooker rolled down the slope at the last moment. Be sure of getting back to IV to-morrow in time to evacuate by dark, as I hope to. In the tent I must have left a compass—for the Lord’s sake rescue it: we are here without. To here on 90 atmospheres for the 2 days—we’ll probably go on 2 cylinders—but it’s a bloody load for climbing. Perfect weather for the job!»
Yours ever, G. Mallory.[671][672]
Odell’s porter, Nema, was suffering from altitude sickness, so consequently, that evening of 7 June 1924, he sent him down, along with the other four porters, to Camp IV.[673][668] When the five porters reached Camp IV on the North Col, one of them, known as Lakpa, gave expedition member John Noel a second handwritten note from Mallory, which read:[674]
Dear Noel,
«We’ll probably start early tomorrow (8th) in order to have clear weather. It won’t be too early to start looking for us either crossing the rock band under the pyramid or going up skyline at 8.0 P.M.»
Yours ever, G. Mallory.[675][672]
John Noel’s filming location was above Camp III, on the ledge of a buttress at 22,000 ft (6,706 m) on the Eastern Ridge of Changtse, which he called «Eagle’s Nest Point.»[676] From this vantage point, Noel had a clear view across the head of the East Rongbuk Glacier, the ice slope leading to the North Col, the Northeast Ridge and the North Face of Mount Everest.[676] Lakpa the porter who had given Noel the note informed him that Mallory and Irvine were in good health, had reached Camp VI and that the weather was fine.[674] The message from Mallory reminded Noel of the locations and the approximate time of where and when to look for him and Irvine during their summit attempt, which they had formerly discussed and organised.[677] Mallory erroneously wrote 8:00 p.m. on Noel’s note; he meant 8:00 a.m.[678]
The following morning, 8 June 1924, at 8:00 a.m., after spending the night alone at Camp V, Odell, again supporting Mallory and Irvine, commenced his ascent up to Camp VI and, on his way, intended to conduct a geological study.[679] That same morning, Noel perched himself at «Eagle’s Nest Point,» where he directed the long lens of his motion picture camera towards the summit pyramid of Mount Everest to film Mallory and Irvine.[680] He had two assistant porters, peering through a telescope in turns, who saw nothing; 8:00 a.m. arrived and went by without sighting the two mountaineers, and by 10:00 a.m., cloud and mist had enshrouded their view of the entire summit ridge.[678] As Odell ascended to Camp VI, in a limestone band at approximately 25,500 ft (7,772 m), he discovered the first definite fossils on Mount Everest.[668] When he reached an elevation of about 26,000 ft (7,925 m), Odell climbed a small crag close to 100 ft (30.48 m) in height, and above him, as he reached its top at 12:50 p.m., he witnessed a rapid clearing of the atmosphere and consequently saw the entire summit ridge and final peak of Mount Everest revealed, and he sighted Mallory and Irvine on a prominent rock step on the ridge:[681]
«At 12:50, just after I had emerged in a state of jubilation at finding the first definite fossils on Everest, there was a sudden clearing of the atmosphere, and the entire summit ridge and final peak of Everest were unveiled. My eyes became fixed on one tiny black spot, silhouetted on a small snow crest beneath a rock step in the ridge, and the black spot moved. Another black spot became apparent and moved up the snow to join the other on the crest. The first then approached the crest rock step and shortly emerged at the top. The second did likewise. Then the whole fascinating vision vanished, enveloped in cloud once more. There was but one explanation. It was Mallory and his companion, moving, as I could see even at that great distance, with considerable alacrity … The place on the ridge mentioned is a prominent rock step at a very short distance from the base of the final pyramid.»
— Noel Odell, support climber and last man to see Mallory and Irvine alive, 8 June 1924. This version of Odell’s sighting appeared in the Aberdeen Press and Journal on 5 July 1924.[682]
The location where Odell presumably last saw Mallory and Irvine before they disappeared into the clouds and were never to be seen alive again was above the Second Step and near the crest of the Northeast Ridge, approximately halfway between the Second and Third Steps, and was determined by expedition member John de Vars Hazard using a theodolite to be at an elevation of 28,227 ft (8,603.5 m).[683][684][n 30] At approximately 2:00 p.m., as Odell reached Camp VI at, 26,700 ft (8,138 m), snow began to fall, and the wind strengthened.[687] Inside Mallory and Irvine’s tent, he discovered spare clothes, food scraps, sleeping bags, oxygen cylinders, and parts of the oxygen apparatus; outside, he found additional parts of the oxygen apparatus and the duralumin carriers.[687] They left no note specifying when they had commenced their summit attempt or what might have transpired to create a delay.[688] Odell departed from Camp VI, ascended about 200 ft (61 m), in the direction of the summit, in sleet and poor visibility of no more than a few yards, and whistled and yodelled in an attempt to direct Mallory and Irvine towards Camp VI, in case they happened to be within hearing distance, but it was to no avail.[688] Within one hour, he retreated and at approximately 4:00 p.m., as he re-attained Camp VI, the weather cleared; the entire North Face became bathed in glorious rays of sunshine, and the upper crags became visually observable, but there was no sign of Mallory and Irvine.[688] Odell left Mallory’s compass, which he had retrieved from Camp V, inside the tent at Camp VI and, at about 4:30 p.m., began his descent to Camp IV on the North Col, which he reached at 6:45 p.m.[689]
On the morning of 9 June 1924, Odell and Hazard thoroughly inspected Camps V and VI using binoculars, with no sign of either mountaineer.[690][691] At 12:15 p.m., Odell and two porters, Nima Tundrup and Mingma, left Camp IV and, at 3:30 p.m., reached Camp V, where they spent the night.[692][693] The following morning, 10 June 1924, he sent his two porters back to Camp IV, as they were indisposed and unable to ascend with him to Camp VI.[694] In a strong, bitter westerly wind, Odell climbed alone to Camp VI, using supplemental oxygen for part of the way, to about 26,000 ft (7,925 m), before disuse.[695] At Camp VI, which he reached soon after 11:00 a.m., it became immediately apparent that Mallory and Irvine had not returned to camp, as everything was as he had left it two days previously.[696][697] Odell discarded his oxygen apparatus and forthwith set off along the presumed route, which both climbers might have taken, to search within the limited time available to him.[697] After trudging on for almost two hours with no sign of either Mallory or Irvine, he ascertained that the likelihood of finding them was remote in the broad expanse of crags and slabs, and a more extensive search towards the final pyramid necessitated a larger party.[697] Odell returned to Camp VI at 26,700 ft (8,138 m), and after taking shelter for a short time from the relentless strong wind, he hauled two sleeping bags from the tent up to a precipitous snow-patch, where he positioned the bags in the shape of a T, communicating the signal that there was no trace of either Mallory or Irvine.[698] At 2:10 p.m., Hazard, 3,700 ft (1,128 m) below at Camp IV on the North Col, saw the T-shaped signal and knew what it meant, as he and Odell had previously drawn up a code of signals before Odell had left the North Col on 9 June 1924, for Camp V.[699][700][701] At approximately 2:15 p.m., Hazard placed six blankets in the shape of a cross on the snow surface at the North Col, which relayed a signal of death, to the watchers at Camp III.[699][700][702] Expedition member John Noel was the first to see the signal through his telescope from Camp III, at the head of the East Rongbuk Glacier.[700] After being informed about the situation, expedition leader Edward Norton ordered a response sign for Hazard on the North Col.[703] Richard Hingston positioned three lines of blankets arranged apart on the glacier a short distance beyond Camp III, conveying the message, «Abandon hope and come down.»[703] After retrieving Mallory’s compass and an oxygen apparatus at Camp VI, Odell descended to Camp IV, which he reached shortly after 5:00 p.m.[704]
On 8 June 1924, the same day that Mallory and Irvine were last seen alive by Odell, Mallory’s wife Ruth and their three children were on holiday in Bacton, Norfolk.[699] On 13 and 14 June 1924, Howard Somervell and Bentley Beetham oversaw the carving and building of a memorial cairn at Base Camp in memory of those who perished in the 1921, 1922, and 1924 British Mount Everest expeditions, with the inscription: In Memory Of Three Everest Expeditions; 1921, Kellas; 1922, Lhakpa, Narbu, Pasang, Pema, Sange, Temba, Antarge; 1924, Mallory, Irvine, Shamsher, Manbahadur.[705][354][706] On 15 June 1924, the expedition evacuated Base Camp for the journey home.[707] On 19 June 1924, Arthur Robert Hinks, who was then in London, received a coded telegram that read: «Mallory Irvine Nove Remainder Alcedo,» sent from expedition leader Edward Norton. «Nove» expressed the message that Mallory and Irvine had died, and «Alcedo» meant that everyone else was unharmed.[699] That same day, Hinks sent a telegram to Cambridge, where shortly after 7:30 p.m. that evening, a delivery boy arrived with it at the Mallory residence, Herschel House, Herschel Road, Cambridge, to communicate the tragic news and the condolences of the Mount Everest Committee to Mallory’s wife, Ruth.[708]
Message from the King and memorial service at St Paul’s Cathedral[edit]
St Paul’s Cathedral, London
On 24 June 1924, a message sent from King George V to Sir Francis Younghusband of the Mount Everest Committee appeared in The Times, in which the King requested to convey «an expression of his sincere sympathy» to the families and committee concerning the tragic deaths of the «two gallant explorers,» Mallory and Irvine.[709] On 17 October 1924, a solemn memorial service at St Paul’s Cathedral, London, was held in honour of the two climbers, at which the presiding, Right Reverend Henry Paget, the Bishop of Chester, from whose diocese both men had come, delivered the sermon.[710] The other clergy present included the Archdeacon of London Ernest Holmes, Canon William Newbolt, and Canon Simpson.[711] The parents of both mountaineers, the widow of the deceased, Mrs Christiana Ruth Leigh-Mallory, their relatives and close friends, members of the 1921, 1922, and 1924 Everest expeditions, members of the Mount Everest Committee, the Alpine Club, the Royal Geographical Society, and several other distinguished explorers and scientists also attended.[711] Additionally present were representatives of the royal family; Sir Sidney Robert Greville represented the King; Prince of Wales by Lieutenant-Colonel Sir Piers Walter Legh; Duke of York by Lieutenant Colin Buist; Duke of Connaught by Lieutenant-Colonel Douglas Gordon and Prince Arthur of Connaught by Major Eric Henry Bonham.[712][711]
Mallory’s will was proven in London on 17 December; he bequeathed his estate of £1706 17s. 6d. (roughly equivalent to £103,517 in 2021[713]) to his wife.[714]
Lost on Everest for 75 years[edit]
Discovery of the ice axe, 1933[edit]
On 30 May 1933, at 5:40 a.m., during the 1933 British Mount Everest expedition, Percy Wyn-Harris and Lawrence Wager commenced their summit attempt from Camp VI, at 27,495 ft (8,380.4 m), on the Yellow Band, below the Northeast Ridge.[715][716] After approximately one hour of climbing, Wyn-Harris, who was leading, found an ice axe located about 60 ft (18 m) below the crest of the Northeast Ridge and some 751 ft (229 m) east of and below the First Step, at an elevation of 27,723 ft (8,450 m).[717][718] Wyn-Harris and Wager left the ice axe exactly where the former had discovered it, and after retreating from a failed summit attempt where they had reached approximately the same place as Edward Norton in 1924, at 28,126.0 ft (8,572.8 m), Wyn-Harris retrieved the ice axe and presumably left his own in its place.[719][720][n 31] The ice axe, discovered, was positively ascertained to be a possession of either Mallory’s or Irvine’s, to the exclusion of all others.[722] During his descent with Edward Norton on 4 June 1924, Howard Somervell dropped his ice axe in the Yellow Band near the Norton Couloir,[n 32] further west from where Wyn-Harris had found the ice axe, and no mountaineers from the Everest expeditions before 1933, other than Mallory and Irvine, were at the location where Wyn-Harris discovered the ice axe.[723][724] Although it is definitive that the ice axe found by Wyn-Harris was, in fact, Mallory’s or Irvine’s, there was no decisive evidence to prove which mountaineer owned the axe after its discovery.[725] In 1934, Noel Odell inspected the ice axe when it was shown to him by Wyn-Harris, and saw three parallel horizontal nick marks on its shaft, which he learned neither Harris nor Wager had seen.[725][724] He thought it might have been a mark used by Irvine on some of his equipment, although not verified by visual inspection of such items returned to Irvine’s family, some of whom seemed to remember seeing a similar marking.[725] Mallory’s widow Ruth informed Odell that, «as far as she was aware»—which may indicate she was not entirely sure—Mallory never marked his equipment with triple marks or any other type of mark and assumed it most probable the axe belonged to Irvine.[725] To Odell, Wyn Harris suggested that a porter may have cut the triple mark on the axe of the shaft to identify his masters’ property during the 1924 expedition, though such was not the practice of many, if any, of the 1924 porters.[725] Wyn Harris assured Odell that his porter Pugla cut the X mark, seen lower down on the shaft of the axe found in 1933, during the return journey from the 1933 expedition.[725] A number of the 1933 British Mount Everest expedition members considered it likely that the ice axe belonged to Mallory because it had Swiss manufacturers, Willisch of Täsch, stamped upon it, and Mallory had journeyed to the Alps a short time before the 1924 expedition when he may have acquired it.[725] They were unaware that this manufacturer had supplied all members of the 1924 expedition with light axes and that Mallory or Irvine might have utilised them during their fatal summit attempt.[725] In 1962, a brother of Andrew Irvine found a military swagger stick, which is presumed to have belonged to Irvine, and upon it is three horizontal identification nick marks resembling those on the ice axe discovered by Wyn-Harris in 1933; therefore, the axe is possibly Irvine’s, but it is inconclusive.[724][726]
In a 1971 letter published in The Sunday Times, Wyn-Harris recalled that his porter cut the cross mark on the ice axe discovered in 1933:[727]
«When I picked up the axe there was no mark on it. The cross, over which there has been so much controversy, was not put on either by Mallory or Irvine. It was in fact cut by my personal Sherpa porter, Kusang Pugla, who did it under threats from me that it must not be lost or mixed up with other axes.»
— Percy Wyn-Harris, The Sunday Times, 17 October 1971.[727]
In July 1977, Walt Unsworth, author of Everest: The Ultimate Book of the Ultimate Mountain, examined the ice axe discovered in 1933 and observed four sets of marks on its shaft.[727] On the axe’s shaft, in addition to the three parallel horizontal nick marks seen by Odell and the cross mark cut by Pugla, he saw a single horizontal nick mark above the three observed by Odell and another three nick marks, though fainter in appearance, on the other side of the shaft opposite the cross mark.[727]
Frank Smythe’s sighting, 1936[edit]
In 1937, Frank Smythe wrote a letter to Edward Norton in reply to Norton’s approbation for Smythe’s book Camp Six, an account of the 1933 British Mount Everest expedition.[728] Amongst other things mentioned in his letter was the discovery by Wyn-Harris of the ice axe in 1933 found below the crest of the Northeast Ridge, where Smythe felt certain marked the scene of an accident to Mallory and Irvine in 1924.[729][730] Also in the letter, Smythe disclosed to Norton that during the 1936 British Mount Everest expedition he scanned the North Face of Everest with a high-powered telescope from Base Camp and spotted an object which he presumed was the body of either Mallory or Irvine and that it not be written about because he feared press sensationalism:[731][730]
«Since my search for the two Oxford fellows, I feel convinced that it marks the scene of an accident to Mallory and Irvine. There is something else … it’s not to be written about, as the press would make an unpleasant sensation. I was scanning the face from the Base camp through a high-power telescope last year[1936] when I saw something queer in a gully below the scree shelf … it was a long way away and very small … but I’ve a six/six eyesight, and I do not believe it was a rock … when searching for the Oxford men on Mont Blanc, we looked down onto a boulder-strewn glacier and saw something which wasn’t a rock either—it proved to be two bodies. The object was at precisely the point where Mallory and Irvine would have fallen had they rolled on over the scree slopes below the yellow band. I think it is highly probable that we shall find further evidence next year.»
— Frank Smyth, in a letter to Edward Norton, 4 September 1937.[732][728]
Smythe’s sighting was unknown to the public until his son Tony revealed the information in his book, My Father, Frank: Unresting Spirit of Everest, released in 2013; the author discovered a copy of the letter that his father had written to Norton in the back of a diary.[733]
Tom Holzel, Mount Everest historian[edit]
Everest historian, German-American Thomas Martin Holzel, the co-author with Audrey Salkeld of The Mystery of Mallory and Irvine, first became interested in the Mallory and Irvine mountaineering enigma after reading a brief reference about the subject in a 1970 edition of The New Yorker.[734] Holzel devised a theory regarding the Mallory and Irvine mystery, initially published in the 1971 September edition of Mountain magazine.[735] His theory was that the two mountaineers split up soon after Noel Odell had sighted them ascending the Second Step at 12:50 p.m., and when successfully climbed, each had only 1+1⁄2 hours of supplemental oxygen remaining, not sufficient for both men to reach the summit in two or three hours from that location.[736] Holzel argued that given this dilemma, Mallory took Irvine’s oxygen equipment, belayed him down the Second Step, from where he descended towards Camp VI at 26,700 ft (8,138 m), and with the additional oxygen, Mallory recommenced the attempt to reach the summit alone.[737] He further surmised that as the exhausted Irvine descended after parting with Mallory shortly after 1:00 p.m., the «rather severe blizzard» described by Noel Odell,[738] which lasted from approximately 2:00 p.m. until 4:00 p.m.,[739] covered the mountain with snow, turned his descent into a deadly endeavour, and caused him to slip and fall to his death.[737][740] Holzel added that Mallory presumably reached the summit in the late afternoon, and during his descent, darkness prevented him from descending the Second Step; left with no alternative, he bivouacked and froze to death overnight.[740] He also theorised that where the ice axe was found—presumably the scene of an accident—by Percy Wyn-Harris in 1933, a body tumbling down the North Face from the area of its discovery would come to a halt on a snow terrace below at approximately 26,903 ft (8,200 m).[737]
On Valentine’s Day, 14 February 1980, Holzel received a letter dated 7 February 1980 from Hiroyuki Suzuki, foreign secretary of the Japanese Alpine Club.[741] Suzuki’s letter was in reply to Holzel, who had written to the Japanese inquiring about their 1979 Sino-Japanese Mount Everest reconnaissance expedition and requesting that they look out for Irvine’s body—which Holzel had predicted might be discovered on a snow terrace at about 26,903 ft (8,200 m)—and the camera he may have carried.[742] The letter from Suzuki contained grievous news and unexpected information.[743] He expressed that on 12 October 1979, at 2:12 p.m., as their reconnoitring party attempted to reach the North Col, an avalanche occurred at an elevation of 22,474 ft (6,850 m) that swept three Chinese, Wang Hongbao, Nima Thaxi, and Lou Lan, into a crevasse, resulting in their deaths.[743][744][745] In the latter part of the letter, Suzuki told Holzel that on 11 October 1979—the day before the avalanche caused his death—Hongbao informed their expedition climbing leader, Japanese Ryoten Hasegawa, that during the 1975 Chinese Mount Everest expedition, he had seen «two deads.»[743][746] One of them he had seen close to a side moraine in the East Rongbuk Glacier below the 1975 expedition Camp III, and the other was on the Northeast Ridge route at an altitude of 26,575 ft (8,100 m).[743][746][747] Suzuki further expressed in the letter that Hongbao was a non-English speaker but repeated the word «English, English» to Hasegawa.[743][746] Suzuki added that the first was possibly Maurice Wilson, questioned who the second he saw at 26,575 ft (8,100 m) was, and informed Holzel that Hongbao touched the latter’s torn clothes, some of which the wind had blown away, and he buried the corpse by placing snow on it.[743][746][n 33]
The 1986 Mount Everest North Face Research Expedition[edit]
On 25 August 1986, the Mount Everest North Face Research Expedition (MENFREE), which Holzel instigated, congregated at Mount Everest’s North Base Camp in Tibet.[751] The expedition aimed to resolve the enigma surrounding Mallory and Irvine’s disappearance on 8 June 1924.[751] Their primary objective was to ascend to the 27,000 ft (8,230 m) snow terrace, where they intended to locate the remains of the «English dead» Wang Hongbao had sighted during the 1975 Chinese Mount Everest expedition.[752] They assumed that if found, the cameras both mountaineers may have carried would resolve the 62-year-old mystery of whether or not they attained the summit before they died.[752] Their secondary objective was to search the area immediately above the Second Step, where they hoped to discover Mallory and Irvine’s empty oxygen cylinders, proving that they had reached that elevation and thus had possibly gained the summit.[752] The expedition leader was Andrew Harvard, and the other members were Tom Holzel, Audrey Salkeld, David Breashears, Ken Bailey, Mary Kay Brewster, David Cheeseman, Catherine Cullinane, Sue Giller, Alistair Macdonald, Al Read, Steve Shea, David Swanson, Roger Vernon, Mike Weis, Jed Williamson, Mike Yager, and a team of fifteen Sherpas led by Nawang Yonden.[753] They successfully established Camp V on the North Ridge at an elevation of 25,500 ft (7,772 m) but were hampered by snowstorms and avalanches, which prevented them from reaching 27,500 ft (8,382 m), where they had planned to establish Camp VI, from which they intended to search for the bodies of Mallory and Irvine.[754][755][756] Despite the adverse weather and snow conditions, they discovered two oxygen cylinders from the 1922 British Mount Everest expedition.[755] On 17 October 1986, nine days before the expedition retreated from Mount Everest, one of their team, Sherpa Dawa Nuru, perished in an avalanche below the North Col.[757][756]
During the Mount Everest North Face Research Expedition, their liaison officer, Zhiyi Song, also a 1975 Chinese Mount Everest expedition member, on which Wang Hongbao had presumably seen «two deads,» informed Holzel that he heard about Hongbao’s story and declared, «None of it is true. Wang never reported finding an English mountaineer.»[758] Holzel asked Song if it was conceivable that Hongbao had discovered an English body and suggested that perhaps he did not officially report it and only informed his friends.[758] Song knowledgeably replied, «If that is so,» he knew who Hongbao’s mountaineering partners were in 1975 and that Holzel could meet them on the return journey to Peking, China.[758] In Lhasa, Tibet, after the cessation of the Mount Everest North Face Research Expedition, Song introduced Holzel to Chen Tianliang, Hongboa’s 1975 group climbing leader.[759] During the interview with Holzel, Tianliang denied that Hongbao had discovered an English body at 26,575 ft (8,100 m) in 1975 and asserted that he would know because he was with Hongbao the entire time they were at high altitudes on Everest.[759] Tianliang was positive that if Hongbao had come across mortal remains, it must have only been that of a missing Chinese mountaineer whom Tianliang was assigned to search for and was located a few days later by expedition members.[759] As the interview continued, Tianliang agreed with Holzel that Hongbao could not have found the remains of the missing Chinese climber because he would have identified and reported his find immediately.[759] As their conversation neared its conclusion, Holzel asked Tianliang if there were anything he would like to add, and Tianliang declared that during a rest period at Camp VI,[n 34] he received a radio call instructing him to ascend to Camp VII to search for the missing climber.[759] Tianliang and a Tibetan porter left Camp VI and ascended to Camp VII to search, leaving two remaining climbers at Camp VI, Wang Hongbao and Zhang Junyan.[759] Holzel asked Tianliang did he think it possible that Hongbao might have found an English body’s mortal remains after he and his porter departed for Camp VII, and Tianliang conceded that it was conceivable and added that Zhang Junyan now resided in Peking.[759] Zhiyi Song, the research expeditions’ liaison officer, arranged a meeting for Holzel in Peking with Zhang Junyan.[761] At the interview, through his interpreter, Holzel questioned Junyan about what had occurred at Camp VI after Tianliang and his porter left to search for the missing Chinese climber.[762] Junyan stated that he remained in his sleeping bag, and Hongbao exited the tent to go for a walk; he was gone for approximately twenty minutes, and later, as they descended, Hongbao informed him that during his walk, he had discovered the remains of a foreign mountaineer and that Hongbao had also mentioned this to a few additional climbers.[762][n 35]
The 1999 Mallory and Irvine Research Expedition[edit]
The 1999 Mallory and Irvine Research Expedition was funded jointly by WGBH/Boston’s Nova series and the BBC.[765] The Seattle-based Internet site MountainZone, sponsored by Lincoln LS, also provided daily expedition dispatches on their website.[766][767] The expeditions’ other sponsors were Mountain Hardwear, Outdoor Research, Lowe Alpine, Eureka!, Starbucks, PowerBar, Vasque Footwear, Slumberjack, and Glazer’s Camera.[768] The expedition personnel were Eric Simonson, mountaineer and expedition leader; mountaineer and high-altitude cameraman Dave Hahn; and mountaineer and assistant film producer Graham Hoyland.[768][770] Mountaineers Conrad Anker, Jake Norton, Tap Richards, and Andy Politz.[768][770] Mountaineering historian, researcher, and support climber Jochen Hemmleb; mountaineering historian, researcher, and expedition organiser Larry Johnson; and expedition doctor Lee Meyers.[771][770] High-altitude cameraman Thom Pollard; film producers Liesl Clark and Peter Firstbrook; film sound technician Jyoti Lal Rana;[768][770] photographer Ned Johnston and a team of twelve Sherpas led by Sirdar Dawa Nuru.[770][772] The expedition’s objective was to search for evidence of the 1924 British Mount Everest expedition and to obtain information about the high point attained by Mallory and Irvine, which may have either supported or refuted whether or not they reached the summit.[770][773]
After he had re-examined the historical record of Mount Everest North Face expeditions, Jochen Hemmleb recognised that the only seemingly factual information about Mallory and Irvine—other than artefacts such as the ice axe, found in 1933—was that during the 1975 Chinese Mount Everest expedition, Wang Hongbao had discovered a body that he had intransigently expressed as «English, English!» during what he asserted was a brief twenty-minute walk from Camp VI.[774] The initial challenge was to identify the location of the 1975 Chinese Camp VI and use it as the centre point of a circular search zone with a twenty-minute walk or more, if necessary, radius.[775][776] From a photograph of the 1975 Camp VI, published in the book Another Ascent of the World’s Highest Peak—Qomolangma, Hemmleb believed that the Camp was on an ill-defined rib of rock that bisects the snow terrace on the North Face.[775] On 1 May 1999, at approximately 10:00 a.m., Anker, Hahn, Norton, Politz, and Richards reached 26,900 ft (8,199 m), where they were to establish Camp VI.[777] From there, the five mountaineers set out at 10:30 a.m. for the «ill-defined rib» identified in Hemmleb’s search guidelines and traversed west over the North Face’s precipitously angled terrain.[778][776] Anker searched on intuition and descended to the lower margin of the snow terrace, where it drops away approximately 6,562 ft (2,000 m) to the head of the central Rongbuk Glacier and soon after zig-zagging back up the slope in the direction of Camp VI, he looked to the west and saw a «patch of white,» which he proceeded towards, and ascertained that it was an old body; it was 11:45 a.m., and 26,760 ft (8,156 m) was the elevation where the corpse lay.[779][780][781] The body was partially frozen into the scree and well preserved due to the cold, dry air and constant freezing temperatures; it was lying prone, fully extended, with both arms somewhat outstretched and the head pointed uphill.[782][783][784] The right leg had broken, and the left leg was crossed over it, possibly for protection, suggesting the mountaineer was still consciously aware after coming to rest.[785][786] The rear of the body was predominantly exposed, as the clothing had been partially destroyed by the elements and blown away by the wind.[785][787] The exposed skin was bleached white, and although the corpse was frozen, purportedly, some elasticity remained in the frozen tissue; the hands and forearms appeared dark.[785][788] Despite the body being notably intact, Everest’s goraks had damaged the right leg, the buttocks, and the abdominal cavity by pecking at them and consuming most of the internal organs.[789][790] Tied to the corpse’s waist were the remnants of a braided cotton climbing rope, with some tangled around the body from which its broken frayed end trailed.[789][791] On the right foot was an intact green leather hobnailed boot; only the tongue of the left boot remained, jammed between the left foot’s bare toes and the heel of the right boot.[786][792]
The prevalent assumption was that Irvine had fallen in 1924 from where in 1933, Percy Wyn-Harris had discovered the ice axe, presumably Irvine’s; therefore, Anker, Hahn, Norton, and Richards expected the body to be his, but Politz said, «this is not him.»[793][n 36] When they found the remains, before they touched them and determined who it was, they documented photographically and cinematographically both the body and the discovery site.[795][790] Richards, an archaeologist by training, and Norton carefully separated the remaining layers of tattered garments, protected somewhat from the elements that still covered part of the body: multiple layers of cotton, silk underwear, a flannel shirt, woollen pullover and pants, and an outer garment that resembled canvas.[796] Close to the nape of the neck, Norton turned over part of the shirt collar and found affixed to it a clothing label with red print, reading, «W.F. Paine, 72 High Street, Godalming,» and below it a second label, again with red print, reading, «G. Mallory.»[797] They discovered another label with «G. Leigh. Ma,» written in black, and a third label.[797] The expedition members realised, to their surprise, that they had not found Irvine as expected but had discovered the remains of Mallory.[798][783] Because the corpse had frozen into the surrounding scree, the mountaineers used their ice axes and pocketknives to excavate the site to find crucial artefacts and, most importantly, Howard Somervell’s Vest Pocket Kodak camera that he «allegedly» had lent to Mallory for his summit attempt with Irvine.[799][800] Presumably, if they had discovered the camera, it might have solved the mystery of whether or not the summit of Mount Everest was reached for the first time in 1924, twenty-nine years before the first confirmed successful ascent of the world’s highest peak by Edmund Hillary and Tenzing Norgay on 29 May 1953.[801][802] Experts from Eastman Kodak Company have said that it might be possible to develop images from the camera’s film using sophisticated techniques and have drawn up specific professional guidelines for an expedition that might discover the camera.[801][803][804]
The injuries on Mallory’s body were severe; above the hobnail boot on his right foot, both the tibia and fibula of his right leg—which lay at a grotesque angle—were broken.[789][791] His right scapula was somewhat deformed, and his right elbow was fractured or dislocated.[791] Along his right side were multiple still-noticeable cuts, bruises and abrasions; on his torso, his ribs had fractured, and black and blue bruises were visible on his chest’s skin.[789][786] The broken climbing rope, which had been looped around his waist and secured with a bowline knot, had severely crushed his ribs and burned his skin; the indentation marks caused by the rope tugging on his skin were still observable around his torso; undoubtedly, he had fallen.[789][805] The rope-jerk injuries around Mallory’s torso indicate that he and Irvine were roped to each other when the accident occurred; the exact circumstances surrounding their deaths are unknown.[805][791]
After chipping at the ice and rock for one hour with their axes, the expedition members had freed one jacket pocket in which they discovered an altimeter manufactured by Cary, London, that could record altitude to a maximum of 30,000 ft (9,144 m); broken was its crystal and the hands were absent.[789][806] Norton reached underneath Mallory’s body and found a pouch that hung from his neck.[789] After cutting the pouch’s underside with his knife, he discovered a tin of Brand & Co’s Savoury Meat Lozenges.[807] Also found were a pair of nail scissors in a leather case and a letter inside an envelope, flawlessly preserved.[808] Other artefacts were discovered in a pouch on Mallory’s right side and from separate pockets: a handkerchief—wrapped around some letters.[n 37] addressed to Mallory—with a burgundy, blue, and green foulard pattern, decorated with the monogram G.L.M.; a second-handkerchief with a red, yellow, and blue pattern, also monogrammed with the initials G.L.M.; a tube of petroleum jelly wrapped in a white handkerchief; one fingerless glove; a W.E. Oates of Sheffield manufactured Lambfoot antler-handle pocket knife with a leather case; an intact box of still usable Swan Vestas matches; and a variety of boot laces and straps.[812] Other artefacts found were: a pencil and safety pin; adjustable straps attached to a metal spring clip—used to connect an oxygen mask to Mallory’s fur-lined leather helmet; a note from expedition member Geoffrey Bruce; gear checklists, written by pencil on scraps of paper; a bill addressed to G.H. Leigh Mallory, Esq., Herschel House, Cambridge, from A.W. Gamage Ltd, Holborn, London, E.C.1.; and discovered deep inside a pocket was a pair of unbroken snow goggles.[813][n 38] The artefacts and samples of each layer of garments were placed one by one in resealable plastic Ziploc bags for examination.[808][816] To the dismay of Anker, Hahn, Norton, Richards, and Politz, the most sought-after artefact, the Vest Pocket Kodak camera that Mallory had «allegedly» borrowed from Somervell, was not found after a thorough search.[816] With the prior permission of Mallory’s son, John Mallory, Anker cut a small skin sample from Mallory’s right forearm for DNA analysis.[817] The five expedition mountaineers buried Mallory by covering his remains with rocks, and Politz read a Church of England committal ceremony provided by Barry Rogerson, the Anglican Bishop of Bristol.[818][817]
North Face of Everest, altitudes of various discoveries, the Three Steps, and its summit
On 16 May 1999, expedition members Andy Politz and Tom Pollard returned to Mallory’s burial site for one last search for the camera that he had reportedly carried, this time using a metal detector.[819] After removing the rocks that covered his remains, Politz, using the metal detector, discovered a Borgel wristwatch in Mallory’s pants pocket—an artefact the team had missed during their initial search on 1 May 1999.[819][820][821] At the time of its discovery, the watch’s crystal and minute hand were missing, and neither were discovered in Mallory’s pocket or elsewhere; the second hand and hour hand were still in place on the watch when found; subsequently, the hour hand became dislodged from the watch.[822][823] Politz also recovered a piece of Mallory’s climbing rope—brittle from seventy-five years of exposure to the elements—and removed the hobnail boot from Mallory’s right foot to add to the assemblage of artefacts.[820] Again, the search for a camera proved unsuccessful after they thoroughly searched the site using the metal detector.[819] Pollard resolved that he wanted to see Mallory’s face frozen into the scree and remove the ice and dirt surrounding his head.[820] After excavating, he had uncovered and freed Mallory’s head adequately so that he could lie on the ground and look straight at his face, which was, to a small extent, distorted; his eyes were closed; there was stubble on his chin, and on his forehead above his left eye was a puncture wound from which two pieces of skull protruded, and there was dried blood.[819][820] Politz and Pollard reburied Mallory’s remains by covering him with rocks and repeated the committal ceremony.[819][824] Expedition leader Eric Simonson discovered an old oxygen bottle below the First Step on 15 May 1991, the same day he reached the summit of Everest for the first time and subsequently realised that it may have belonged to one of the pioneering British Mount Everest expeditions.[825][826] On 17 May 1999, at 2:00 a.m., Anker, Hahn, Norton, Richards, and two Sherpas, Dawa and Ang Pasang, left Camp VI at 26,903 ft (8,200 m) and began their summit bid.[827] At about 10:30 a.m., Norton, Richards, and the two Sherpas abandoned, retreating at an altitude of circa c. 28,084 ft (8,560 m) between the First and Second Steps; Anker and Hahn would later reach the summit at 2:50 p.m.[828] Shortly after Norton and Richards had decided to retreat, they radioed Eric Simonson at Advanced Base Camp and informed him about their decision, and Simonson asked them to search for the oxygen cylinder he had found in 1991.[829] After approximately half an hour of searching, Richards radioed A.B.C. and stated that he had discovered an oxygen cylinder at a location subsequently established as c. 558 ft (170 m) to 591 ft (180 m) horizontally east from the top of the First Step and at an altitude of c. 27,789 ft (8,470 m) to 27,805 ft (8,475 m).[830][831] The oxygen cylinder’s shape, size, valve assembly, and stamp, no 9, E.O.C. (Everest Oxygen Cylinder), conclusively confirmed that the bottle had belonged to the 1924 British Mount Everest expedition and had been used by Mallory and Irvine, as they were the only party who had used oxygen for a summit attempt.[831] The no 9, stamped on the bottle, corresponded to the no 9 written by Mallory—as part of a list of oxygen cylinders he and Irvine took on their summit bid—on the envelope, addressed to him from «Stella,» which also contained a letter from her, discovered on Mallory’s body on 1 May 1999.[832][n 39]
Sir Edmund Hillary—recognised, along with Tenzing Norgay, as the first mountaineers to have reached the summit of Mount Everest—enthusiastically welcomed the news of the discovery of Mallory’s body and described it as «very appropriate» that Mallory might have summited decades earlier. «He was really the initial pioneer of the whole idea of climbing Mount Everest,» Hillary said.[834]
Further research expeditions[edit]
The 2001 Mallory and Irvine Research Expedition was led by 1999 expedition leader Eric Simonson and was composed of new and returning members, and their objective was to conduct further historical research.[835][836][837] On 28 April 2001, expedition members Jake Norton and Brent Okita discovered the remnants of the 1924 British Mount Everest expeditions’ Camp VI on the North Ridge at an altitude of 26,700 ft (8,138 m), which Mallory and Irvine had departed on the morning of 8 June 1924, the day of their ill-fated summit attempt.[838][839] The following day, 29 April 2001, Norton discovered a woollen mitten of unknown origin on the Northeast Ridge at an altitude of 27,690 ft (8,440 m), but it may have probably belonged to either Mallory or Irvine.[840] There were further research initiatives on Mount Everest in 2004, 2010, 2011, 2012, 2018, and 2019, and in 2007, the Altitude Everest Expedition retraced Mallory and Irvine’s footsteps.[841][842][843]
Reaching the summit[edit]
Some members of the 1924 British Mount Everest expedition: Mallory is highlighted beside Edward F. Norton to his left and Geoffrey Bruce far right, at the Dzongpen’s Shekar.
The difficult «Second Step»[edit]
If Mallory and Irvine had chosen the Northeast Ridge route to reach Everest’s summit, they would have had to free-climb the formidable Second Step.[844] Of the Three Steps on the upper Northeast Ridge, the Second and most prominent, rising approximately 100 ft (30.48 m) and composed of precipitous, brittle rock at an extreme altitude of 28,248 ft (8,610 m), is the most demanding.[844] The final upper section of the Second Step is its crux, a 16 ft (4.87 m) nearly vertical headwall slab to which the 1975 Chinese Mount Everest expedition affixed a 15 ft (4.6 m) aluminium ladder, later replaced in 2007.[844][846] Although disputed, the first successful ascent of the Second Step occurred on 24 May 1960, during the summit attempt of the 1960 Chinese Mount Everest expedition, as all four of the summit party were breathing supplemental oxygen.[847] They used a technique called «courte-échelle» (short ladder) in which Chu Yin-hau stood on Liu Lien-man’s shoulders to successfully climb to the top of the Second Step’s crux.[847] Chu Yin-hau then belayed himself to a rock at the top of the Step and brought Liu Lien-man, Wang Fu-chou, and Konbu up on the rope.[848][847] It took three hours for the four Chinese mountaineers to ascend the 16 ft (4.87 m) crux of the Second Step, and they also used pitons which neither Mallory nor Irvine had in 1924.[844][847]
On 28 August 1985, in full-monsoon conditions and without supplementary oxygen, Òscar Cadiach climbing on lead, achieved the first successful free-climb of the Second Step, ascending the crux on belay with a sling tied to one of the rungs of the Chinese ladder and he graded the vertical crack that forms the crux V+ (5.7–5.8).[831][849][850] On 17 May 1999, during the 1999 Mallory and Irvine Research Expedition, member Conrad Anker, belayed by Dave Hahn, attempted to free-climb the Second Step’s crux to the Chinese ladder’s left but failed after being forced to step onto one of the rungs of the ladder.[851][852] Anker rated the climb 5.10 and considered it beyond the capabilities of Mallory and Irvine in 1924.[851][852] On 22 May 2001, Austrian Theo Fritsche free-climbed the crux headwall of the Second Step, free-solo style, without supplementary oxygen and assessed the climb as having a grade of IV+ to V- (5.6–5.7).[853][854] On 22 May 2003, Russian Nickolay Totmjanin, to avoid the crowd and the possibility of developing frostbite, free-climbed the 16 ft (4.87 m) crux of the Second Step without supplementary oxygen in an unknown style and provided no opinion of the climbing grade.[831][855] On 14 June 2007, as part of the 2007 Altitude Everest expedition, Conrad Anker and Leo Houlding successfully free-climbed the Second Step’s crux headwall, having first removed the Chinese ladder, with the former rating it 5.10 and the latter 5.9; Anker changed his 1999 opinion, stating, «Mallory and Irvine could have climbed it.»[843][856]
Theories[edit]
Western Disturbance[edit]
Research, published in the August 2010 edition of the Royal Meteorological Society’s Journal, Weather, and authored by George William Kent Moore, John Semple, and Dev Sikka, indicates that an extreme storm may have contributed to the deaths of Mallory and Irvine.[857][858][859] George William Kent Moore, a physicist at the University of Toronto, Canada, discovered meteorological data from the 1924 Expedition at the Royal Geographical Society’s library in London, forming the basis of their research.[857][858][859]
The data consisted of daily barometric pressure and temperature measurements recorded at Base Camp in 1924 at 16,500 ft (5,029 m).[860] Temperature measurements were recorded at several higher camps, also.[861] The data collected during the 1924 Expedition, together with a manually analysed sea-level pressure map hand-drawn by the Indian Department of Meteorology, were used to show that Mallory and Irvine’s summit attempt on 8 June 1924 occurred during a period when there was a drop in barometric pressure and temperature on Mount Everest which was likely the result of the passage of an upper-level trough.[860][862] This meteorological phenomenon is known locally as a Western Disturbance.[860] The authors hypothesised that the passage of the disturbance possibly triggered an outbreak of convective activity that resulted in the blizzard, witnessed by observation, engulfing Everest during Mallory and Irvine’s summit attempt.[860] Noel Odell described the morning of 8 June 1924 as «clear and not unduly cold,»[863] with snowfall and increasing winds, beginning at approximately 2 p.m.,[687] which he described as a «rather severe blizzard,»[738] lasting about two hours and possibly severe enough to force Mallory and Irvine to abandon their summit bid.[688][862] Records show a drop in barometric pressure at Base Camp of 18 millibars during the summit attempt.[862] A drop of a similar magnitude possibly occurred at higher altitudes on the Himalayan peak during this time.[862] This decrease in barometric pressure likely induced aggravation of their hypoxic state.[864] Also, if they had run out of supplemental oxygen during the early afternoon of 8 June 1924, this would have further exacerbated their hypoxic condition.[864] The cumulative effects of hypoxia, fatigue and bitter cold during a severe blizzard would have left Mallory and Irvine at the limits of their endurance.[864] Although the full details of what happened to Mallory and Irvine during their ill-fated summit attempt are unknown, the authors, in conclusion, believe there is persuasive evidence that the severe weather they experienced during their summit attempt may have been more extreme than previously thought.[864] The harsh weather and the decreased barometric pressure may have contributed to their tragic demise.[864]
Assessments by other climbers[edit]
Climbing partners[edit]
Harry Edmund Guise Tyndale, one of Mallory’s climbing partners, said of Mallory:
He cut a superb staircase, with inimitable ease and grace and a perfect economy of effort. In watching George at work one was conscious not so much of the physical strength as of suppleness and balance; so rhythmical and harmonious was his progress in any steep place, above all on slabs, that his movements appeared almost serpentine in there smoothness.[865]
Geoffrey Winthrop Young, an accomplished mountain climber, held Mallory’s ability in awe:
His movement in climbing was entirely his own. It contradicted all theory. He would set his foot high against any angle of smooth surface, fold his shoulder to his knee, and flow upward and upright again on an impetuous curve. Whatever may have happened unseen the while between him and the cliff, in the way of holds or mutual adjustments, the look, and indeed the result, were always the same—a continuous undulating movement so rapid and so powerful
that one felt the rock must either yield, or disintegrate.[866][867]
Edmund Hillary’s assessment[edit]
Edmund Hillary echoed John Mallory’s opinion, asking:
If you climb a mountain for the first time and die on the descent, is it really a complete first ascent of the mountain? I’m rather inclined to think, personally, that maybe it’s quite important, the getting down. And the complete climb of a mountain is reaching the summit and getting safely to the bottom again.[868]
Hillary’s daughter, Sarah, when asked about her father’s take on the debate, said, «His view was that he had got 50 good years out of being conqueror of Everest and, whatever happened, he wasn’t particularly worried. That’s my feeling as well.»[869]
Chris Bonington’s assessment[edit]
Chris Bonington, the British mountaineer, argued:
If we accept the fact that they were above the Second Step, they would have seemed to be incredibly close to the summit of Everest and I think at that stage something takes hold of most climbers … And I think therefore taking all those circumstances in view … I think it is quite conceivable that they did go for the summit … I certainly would love to think that they actually reached the summit of Everest. I think it is a lovely thought and I think it is something, you know, gut emotion, yes I would love them to have got there. Whether they did or not, I think that is something one just cannot know.[685]
Reinhold Messner’s assessment[edit]
Reinhold Messner, the Italian mountaineer and first to climb all 14 eight-thousanders gave his opinion:
Suddenly they see a huge rock step towering over them … Scaling it is impossible—it is far too high, too smooth, too exposed. Mallory risks a look at the arête on the left: unthinkable … It is impossible to climb any farther … Having failed to surmount the Second Step, Mallory and Irvine begin their descent … Night is falling quickly. Their descent is made even more dangerous by a brewing snowstorm … As it gets darker and the intensity of the storm increases, they became desperate to make it back to camp … They know that in these conditions, no one survives unprotected. Their oxygen runs out … Lethargy forces them to stop after every step, and they have difficulty finding secure footholds … The circumstances are ripe for an accident.[870]
Conrad Anker’s assessment[edit]
Conrad Anker, who found Mallory’s body in 1999, free climbed the Second Step in 2007, and has worn replica 1924 climbing gear on Everest, said he believes it is «possible, but highly improbable, that they made it to the top,» citing the difficulty of the Second Step and the position of Mallory’s body. He said that, in his opinion:
I don’t believe they made it, and I’m not saying that to make Mallory less than what he is. I don’t think it’s fair to say that, oh, that he made it because he was a great climber; he was the first. The climbing up there is so difficult, and I think that Mallory was a very good climber. And part of being a good climber is knowing when you’re at too much of a risk, and it’s time to turn back. I think he saw that. He turned back, and it was either he or Irvine; as they were descending the Yellow Band, slipped and pulled the other one off; the rope snapped, and then he came to his rest.[871]
Robert Graves’ tale of Mallory’s Pipe[edit]
Robert Graves, who climbed with Mallory, recounts in his autobiography Good-Bye to All That this story, at the time famous in climbing circles, about an ascent that Mallory made as a young man in 1908, now known as Mallory’s Slab:
My friend George Mallory … once did an inexplicable climb on Snowdon. He had left his pipe on a ledge, half-way down one of the Lliwedd precipices, and scrambled back by a shortcut to retrieve it, then up again by the same route. No one saw what route he took, but when they came to examine it the next day for official record, they found an overhang nearly all the way. By a rule of the Climbers’ Club, climbs are never named in honour of their inventors but only describe natural features. An exception was made here. The climb was recorded as follows: ‘Mallory’s Pipe, a variation on Route 2; see adjoining map. This climb is totally impossible. It has been performed once, in failing light, by Mr G. H. L. Mallory.’[872]
Legacy[edit]
Mallory Court at Magdalene College, Cambridge
At Winchester College, where Mallory was a scholar from 1900 to 1905, there is a memorial to him in the cloister adjacent to the college chapel.[873] Mallory was honoured by having a court named after him at his alma mater, Magdalene College, Cambridge, where he was an undergraduate from 1905 to 1908 and a graduate from 1908 to 1909,[874] with an inscribed stone commemorating his death set above the doorway to one of the buildings.[875][876] To memorialise Mallory’s position as Magdalene Boat Club Captain from 1907–1908, the Friends of Magdalene Boat Club changed their name to the Mallory Club, a boat club for alums of the Magdalene Boat Club.[877] A bronze memorial plaque commemorates him in the South African Cloisters at Charterhouse, where Mallory was a schoolmaster from 1910 to 1921.[878][879] A stained-glass triptych window at St Wilfrid’s Church, Mobberley, Cheshire, portraying three figures from English mythology, Saint George, King Arthur and Sir Galahad, also has two panels, one on the lower right, the other on the lower left, with both having inscriptions commemorating Mallory.[8][880] Also in the church is a brass plate memorialising Mallory’s brother Sir Trafford Leigh-Mallory.[880] In addition to his father, Herbert Leigh Mallory, the rector of Mobberley, Mallory’s grandfather George Leigh Mallory (1806–1885), was also the parish’s rector.[881] In the cloisters of Chester Cathedral, there is a joint memorial window commemorating both Mallory and Irvine.[882] Two high peaks in California’s Sierra Nevada, Mount Mallory and Mount Irvine, located 2.64 miles (4.25 km) and 2.25 miles (3.62 km) southeast of Mount Whitney, respectively, are named after them.[883][884]
The Times obituary of George Finch called Mallory and Finch the «two best alpinists of [their] time.»[885]
Sir Trafford Leigh-Mallory
Tragedy in the mountains has proved a recurring theme in the Mallory line; Mallory’s younger brother, Air Chief Marshal Sir Trafford Leigh-Mallory, met his death on a mountain range when the Avro York carrying him to his new appointment as Air Commander-in-Chief of South East Asia Command, crashed in the French Alps, 1.24 miles (2.00 km) west of Le Rivier d’Allemont, on 14 November 1944, killing all on board.[886][887][888] Mallory’s daughter, Frances Clare, married physiologist Glenn Allan Millikan, who was killed in a climbing accident on 25 May 1947 at Buzzard’s Roost in Fall Creek Falls State Park, Tennessee.[889][890][809]
Frances Mallory’s sons, Richard and George Millikan, became respected climbers during the 1960s and 1970s.[891] On 16 July 1963, Richard Millikan and six other members of the Harvard Mountaineering Club, David Roberts, Henry L. Abrons, Pete Carman, Chris Goetze, John Graham and Don Jensen, made the first ascent of the central rib of the Wickersham Wall on the north face of Mount McKinley, reaching North Peak at 19,470 ft (5,934 m).[892] On 14 May 1995, together with six other climbers, George Mallory, the grandson of Mallory, reached the summit of Everest via the North Col-North Ridge-Northeast Ridge route as part of an American Everest expedition and evoked a sense of «unfinished business» by leaving a photograph of his grandparents on the summit.[893][809][894]
Mallory was captured on film by expedition cameraman John Noel, who released his film of the 1924 expedition, The Epic of Everest.[895][896] Film director George Lowe used footage from The Epic of Everest in the 1953 documentary, The Conquest of Everest.[897] A documentary on the 2001 Mallory and Irvine Research Expedition, Found On Everest: Detectives on the Roof of the World, was produced by Riley Morton.[898][899] Brian Blessed played Mallory in Galahad of Everest, a 1991 re-creation of his last climb.[900] In Anthony Geffen’s 2010 documentary film about Mallory’s life and final expedition, The Wildest Dream, Conrad Anker and Leo Houlding attempt to reconstruct the climb, dressed and equipped like Mallory and Irvine.[843][901]
Everest, a proposed Hollywood version of the 1924 attempt, adapted from Jeffrey Archer’s 2009 novel Paths of Glory, to be directed by Doug Liman, had first Tom Hardy and then Benedict Cumberbatch slated to play Mallory,[902] but a June 2014 interview with Liman implied that the film was no longer in production.[903] As of late 2021, it is in production again, with Liman directing and Ewan McGregor starring as Mallory.[904] It was announced in April 2015 that Michael Sheen would play Mallory in a biopic titled In High Places, to be written and directed by James McEachen;[905] his website currently states it has not received funding.[906]
In September 2009, a temporary exhibition detailing Mallory and Irvine’s lives opened at the Salt Museum (now Weaver Hall Museum and Workhouse), Northwich, Cheshire, near Mobberley, Mallory’s place of birth.[907] The exhibition, «Above the Clouds – Mallory and Irvine and the Quest for Everest,» was curated by Matt Wheeler and featured items discovered in May 1999 on Mallory’s body and many artefacts and photographs from the 1924 British Mount Everest expedition.[907] It was one of the most extensive exhibitions ever conducted on the topic, and later toured Irvine’s birthplace, Birkenhead, at the Williamson Art Gallery and Museum.[908][907] On 12 May 2010, in London, it came «jointly highly commended» after being nominated in the Museums and Heritage Awards for Excellence.[909]
During Mallory’s lecture tour of the United States and Canada in early 1923, when asked why he wanted to climb Mount Everest, he purportedly answered, «Because it’s there.»[910][329] Mallory and the phrase were referenced by President John F Kennedy on 12 September 1962, in his speech at Rice University about the nation’s space effort (often referred to as the «We choose to go to the Moon» speech), regarded as one of the greatest speeches of the 20th century.[911]
Belgian rock band Girls in Hawaii’s song «Mallory’s Height» on their 2013 album Everest is a homage to Mallory; extracts of the Nova / BBC broadcast can be heard (around 3:35).[912]
See also[edit]
- List of people who died climbing Mount Everest
- List of solved missing person cases
- List of unsolved deaths
Footnotes, references, and bibliography[edit]
Footnotes[edit]
- ^ Mallory’s parents, Herbert Leigh-Mallory and Annie Beridge Jebb, were married in Kensington, London, in June 1882.[6]
- ^ In 1944, Sir Trafford Leigh-Mallory was Commander-in-Chief of the Allied Expeditionary Air Force. On 14 November 1944, Trafford and his wife Doris (née Sawyer) died when his aircraft hit a mountain in the French Alps, near Grenoble.[7][9][10]
- ^ Harry Olivier Sumner Gibson was an avid photographer who travelled to Zermatt in 1899 and Grindelwald in 1902, accompanied by his father.[24][22][23]
- ^ In 1911, in Duncan Grant’s studio at 38 Brunswick Square, London, Mallory posed for a series of nude photographs taken by Grant.[38][39] In 1912, also at 38 Brunswick Square, Grant painted a portrait of Mallory, which the National Portrait Gallery acquired.[39][40] Grant painted a second portrait of Mallory, which bears the date 1913.[39][41]
- ^ The crew who represented Magdalene College at the Henley Royal Regatta of 1908 in the Ladies’ Challenge Plate and Thames Challenge Cup were, as follows: 1, C. B. Brown (bow), 10 st 10 lb; 2, C.H. Scarlett, 9 st 2 lb; 3, A.D.G.S. Batty, 11 st 4 lb; 4, D.H. Thompson, 10 st 6 lb; 5, H.J. Higgs, 12 st 10 lb; 6, S.K. Sawday, 12 st 6 lb; 7, G.H.L. Mallory, 10 st 13 lb; 8, R.F. Kindersley (stern), 10 st 6 lb; A.R.W. Miles (coxswain), 9 st 1 lb.[49][50]
- ^ The 1908 Henley Royal Regatta Ladies’ Challenge Plate was won by Jesus College, Cambridge, against New College, Oxford, and the Thames Challenge Cup by Wadham College, Oxford, against Christ Church, Oxford.[49][51]
- ^ Gerald Henry Rendall was a cousin of Howard Rendall, the deputy headmaster of Winchester College.[89][90]
- ^ On 23 January 1918, Mallory and his wife Ruth attended the wedding ceremony and reception of Robert Graves and Nancy Nicholson. Graves and Nicholson were married at St James’s Church, Piccadilly, London, with Mallory acting as best man.[101][102][103][104]
- ^ Hugh Thackeray Turner and Mary Elizabeth Powell were married in 1888 and lived at Gower Street, London, where their three daughters—Marjorie, Ruth, and Mildred—were born.[115]
- ^ When Thackery Turner bought The Holt, there was a drawback: the house was unavailable until January 1915; in the meantime, Mallory and Ruth lived in rented accommodation, which they had to vacate in December 1915, and subsequently went to stay with the Turners at Westbrook House. They finally moved into their new residence, The Holt, on 10 March 1915.[128][129][130]
- ^ In 1939, Ruth married her longstanding family friend, William Arnold-Forster, to whom Mallory had first disclosed his love for Ruth. In 1942, aged 50, Ruth’s life sadly ended when she died of cancer.[132][9][133]
- ^ In February 1912, Mallory met Eddie Marsh while visiting the artist Neville Lytton at Crabbet Park.[149][150]
- ^ Mallory’s sister, Mary, married Ralph Brooke on 22 July 1914 in Birkenhead.[153][127]
- ^ In September 1909, in Birkenhead, Mallory went climbing at a sandstone quarry. While climbing one of the quarry’s sandstone cliffs he fell and landed heavily with one foot on a rock, sustaining an injury in his right ankle, and at the time, it seemed to him that it was a sprain.[81][197][198]
- ^ Four in every ten undergraduates with whom Mallory had been at Magdalene College, Cambridge, died in battle during World War I.[222]
- ^ On 21 February 1920, Mallory resigned his commission in the Royal Garrison Artillery, retaining the rank of lieutenant.[225]
- ^ Keedick’s commission was forty-five per cent, and the remaining fifty-five per cent went to Mallory and the Mount Everest Committee.[313]
- ^ A three-year University Tutorial Class was the arrangement for Mallory in Raunds.[341]
- ^ An additional eight gold medals, after a request to the International Olympic Committee by expedition leader General Charles Granville Bruce, were awarded to other members of the 1922 expedition.[348] One of the medalists was Nepalese Tejbir Bura, a mountaineer and NCO in the 2nd Battalion of the 6th Gurkha Rifles.[348] On 27 May 1922, Bura, unable to ascend further, reached an altitude of 26,000 ft (7,925 m) on Mount Everest, climbing with George Finch and Geoffery Bruce.[349] Later that same day, Finch and Bruce attained a world altitude record of 27,300 ft (8,321 m) using supplemental oxygen.[350][351] The seven gallant porters who tragically died in an avalanche on the North Col on 7 June 1922 were posthumously awarded the other seven medals.[352][353] There names were, Lhakpa, Narbu, Pasang, Pema, Sange, Temba, and Antarge.[354][355]
- ^ With an elevation of 4,413 ft (1,345 m), Ben Nevis is the highest mountain in the British Isles.[388][389]
- ^ On 21 September 1907, Hugh Wilson left Wales, while Mallory and Geoffrey Keynes stayed until 25 September 1907.[47]
- ^ On Good Friday, 25 March 1910, Charles Donald Robertson, a grandson of Frederick William Robertson, fell while climbing East Gully on Glyder Fach, suffering severe injuries, and died that night, just after midnight, on 26 March 1910, at Bangor Hospital.[477][87]
- ^ Between 2–4 July 1887, Alexander Burgener, Moriz von Kuffner, Josef Furrer, and a porter reached the summit of Mont Maudit via the first ascent of its perilous Southeast Ridge (Frontier Ridge).[493][494] On 22 August 1901, the Italian climbers Enrico Brocherel, Ettore Canzio, and Felice Mondini recorded the second ascent of the Frontier Ridge of Mont Maudit.[495][496]
- ^ On 7 October 1912, Hugh Rose Pope (1889–1912) died in a mountaineering accident while climbing solo on Pic du Midi d’Ossau, in the Pyrenees.[70][502][503]
- ^ On 5 June 1921, during the march to the Mount Everest region, the ninth member of the 1921 Mount Everest expedition, Alexander Mitchell Kellas, who the Mount Everest Committee designated as a mountaineer, died from suspected heart failure near Kampa Dzong, Tibet.[535][536][537]
- ^ The two altitudes shown in this image are from the official 1922 expedition book, The Assault on Mount Everest: 1922.[563] Mallory, Somervell, and Norton recorded their maximum elevation with an aneroid barometer as 26,800 ft (8,169 m), a height later rectified and confirmed as 26,985 ft (8,225 m) by a theodolite, leading to uncertainty about the actual altitude attained.[564] Photogrammetric surveys conducted by Jochen Hemmleb using this photo of the summit of Everest, taken by Somervell at their highest point, indicates an elevation of c.26,600 ft (8,108 m) to 26,700 ft (8,138 m).[564] Finch and Bruce also recorded their maximum attained height using an aneroid barometer, which registered 27,300 ft (8,321 m).[565] When compared, an image taken during the expedition and the area’s topography demonstrates that their high point was no lower than 27,460 ft (8,370 m) and possibly as high as 27,560 ft (8,400 m).[564]
- ^ In the official 1924 expedition book, The Fight for Everest: 1924, as Norton, Somervell, and their three porters ascended from Camp V to where they established Camp VI at 26,700 ft (8,138 m), Norton states, «Sometime after midday, we recognised and passed the highest point that Mallory, Somervell, and I had reached in 1922 … I remember a momentary uplift at the thought that we were actually going to camp higher than the highest point ever reached without oxygen … About 1:30 p.m., it became evident that it would be impossible to urge the gallant Semchumbi much farther, so I selected a site for our tent.»[566] The 1924 expedition Camp VI was discovered by the 2001 Mallory and Irvine Research Expedition at an elevation of 26,700 ft (8,138 m).[567] As stated in note 25, Mallory, Somervell, and Norton, on the first summit attempt of the 1922 expedition, recorded their high point with an aneroid barometer as 26,800 ft (8,169 m), a height later rectified and confirmed as 26,985 ft (8,225 m) by a theodolite.[564] Jochen Hemmleb conducted photogrammetric surveys using the photo taken by Somervell on 21 May 1922 at the highest point they attained, and he concluded that he took it at an elevation of c. 26,600 ft (8,108 m) to 26,700 ft (8,138 m).[564] Regarding Norton’s above statement, they passed their high point of 1922, «Sometime after midday,» which provides an unspecified amount of time between then and «About 1:30 p.m.,» when they halted and established Camp VI at 26,700 ft (8,138 m).[566] In conclusion, it is clear that Mallory, Somervell, and Norton’s high point in 1922 was slightly lower than 26,700 ft (8,138 m).[564]
- ^ At approximately 27,500 ft (8,382 m), Norton started to experience difficulty with his vision.[648] He was seeing double and thought it was a symptom from the onset of snow blindness, but Somervell assured him this was not the case.[648] Later, Norton learned that oxygen deficiency was the cause of the symptom.[648] After 11:00 p.m. that same day, he was awakened by discomfort in both eyes caused by snow blindness, and the following morning, he was completely blind and remained in that condition for a further sixty hours.[653]
- ^ Norton’s high point, an elevation subsequently fixed by a theodolite as 28,126.0 ft (8,572.8 m), remained a world altitude record—attained without supplemental oxygen—for fifty-four years, until Reinhold Messner and Peter Habeler exceeded it on 8 May 1978, on their way to becoming the first mountaineers to reach the summit of Mount Everest without supplemental oxygen.[655][656][657][658]
- ^ Odell was emphatically sure that he saw moving figures, not geological objects, and after returning to England, individuals persuaded him that it must have been the First Step where he had last seen them.[685] He later expressed uncertainty about whether it was the First or Second Step stating, «Owing to the small portion of the summit ridge uncovered, I could not be precisely certain at which of these two «steps» they were, as in profile and from below they are very similar, but at the time I took it for the upper «second step.» However, I am a little doubtful now whether the latter would not be hidden by the projecting nearer ground from my position below on the face.»[686] Odell also stated, «The «second rock step» is seen prominently in photographs of the North Face from the Base Camp, where it appears a short distance from the base of the final pyramid down the snowy first part of the crest of the Northeast Arête.»[686]
- ^ In the spring of 1999, Wyn-Harris’s grandson, Steve, informed Jochen Hemmleb in an email exchange that his grandfather had written in his unpublished memoirs that he had returned to Camp VI with both axes.[721]
- ^ On 4 June 1924, Somervell accidentally dropped his ice axe at an elevation c. 28,000 ft (8,534 m), which tumbled down the North Face from a location close to where he took the photograph of Norton nearing his high point.[723]
- ^ In 1986, before the 1986 Mount Everest North Face Research Expedition began, its leader Andrew Harvard arranged a meeting for a Japanese climber to interview Ryoten Hasegawa.[748] During the interview, Hasegawa wrote down for the first time what Wang Hongbao had told him on 11 October 1979 about his sighting of a dead body on 5 May 1975 at an altitude of 26,575 ft (8,100 m).[748] Later, the expedition received an English translation of the letter Hasegawa had written during the interview, in which he expressed an apology for his memory of some unclear points.[748] He also communicated that the only language he understood was Japanese, and Hongbao only spoke Chinese, and neither understood English.[748] Hasegawa explained that their communication consisted of «very simple words, by characters written on the snow and for the most part gesture,» and «English» was the only word they both comprehended from that language.[748] Hasegawa further expressed that Hongbao pointed towards the Northeast Ridge with his finger stating, «8,100-metre Engleese,» and made a gesture of sleeping by placing the palms of his hands together against his cheek, slanting his head to one side.[749] He added, «Hongbao opened his mouth, pointed his finger to his cheek, pecked it slightly, and whirled it as if to catch a dragonfly. He also gestured at his clothing, picking at it, moving his finger to his mouth and blowing off it.»[750] Hasegawa interpreted that perhaps Hongbao meant that the dead mountaineer’s mouth was agape, birds pecked at the cheek, and it was an old body with tattered clothing brought about by the elements.[750] Hasegawa was confident that he and Hongbao had also discussed the body’s posture and precise location, but he could no longer remember these specifics.[750] However, he clearly remembered when he wrote in the snow with his ice axe, in Chinese characters, «A body of an Englishman at 8,100 metres?» Hongbao nodded yes.[750]
- ^ On 24 April 2001, during the 2001 Mallory and Irvine Research Expedition, expedition member Tap Richards discovered the 1975 Chinese Mount Everest expeditions’ Camp VI on the North Face at an elevation of 26,804 ft (8,170 m).[760]
- ^ On 5 May 1975, during the 1975 Chinese Mount Everest expedition, Chinese mountaineers Wang Hongbao and Zhang Junyan were resting in their tent at Camp VI on the North Face of Everest at an elevation of 26,804 ft (8,170 m).[763] That morning, Chen Tianliang and a Tibetan porter left Camp VI and ascended to Camp VII at 28,120 ft (8,570 m), between which they searched for a missing Chinese climber Wu Zongyue who had disappeared on 4 May 1975.[763] At some point, after they departed from Camp VI to search for the lost climber on 5 May 1975, Hongbao exited his tent to go for a walk and found the body of a foreign mountaineer.[764]
- ^ The reason for Politz’s scepticism regarding the body being Irvine’s was its position; deep within his subconscious mind, his intuition had remembered that Wang Hongbao had discovered a corpse in a position with its mouth agape and had one cheek pecked at by goraks, this body was lying prone.[794]
- ^ In an interview with the Sunday Mirror in 1999, Mallory’s daughter, Frances Clare, expressed that her father climbed Mount Everest with a photograph of her mother, Ruth, and one of her letters in his jacket pocket and that Mallory told his wife, «before he set out,» that if he ever attained the summit, he intended to leave a photograph of her there.[809] Ruth had told Clare as a teenager about the story of the letter and photograph.[809] Because of erroneous information that she received, she incorrectly stated in the interview that, discovered on 1 May 1999, was a letter from her mother on Mallory’s body.[809] There was no discovery of either a letter from Ruth or a picture of her found on Mallory’s remains.[810][811]
- ^ The snow goggles discovered in Mallory’s pocket on 1 May 1999 suggest he and Irvine may have been descending in fading light or after nightfall. However, an alternative theory suggests that during what Noel Odell described as a «rather severe blizzard,» which lasted from approximately 2:00 p.m. until 4:00 p.m.,[739][738] the vents on Mallory’s goggles may have become clogged with snow, resulting in the lenses fogging up, forcing him to remove them.
- ^ Found on Mallory’s body on 1 May 1999 were three letters: one from his brother Trafford, another from his sister Mary Henrietta, and a third from Stella Cobden-Sanderson (1886–1979)—daughter of Thomas Cobden-Sanderson and Anne Cobden-Sanderson—with whom he met and developed a friendship after she had attended one of his lectures during his lecture tour of the United States and Canada in early 1923.[810][833]
References[edit]
- ^ Green 2005, p. 13.
- ^ Firstbrook 2000, p. 6.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k Gillman & Gillman 2000, p. 22.
- ^ a b c Robertson 1999, p. 15.
- ^ a b c d Gillman & Gillman 2000, p. 25.
- ^ Gillman & Gillman 2000, p. 24.
- ^ a b c Robertson 1999, p. 223.
- ^ a b Gillman & Gillman 2000, p. 21.
- ^ a b Davis 2011, p. 560.
- ^ Green 2005, p. 78.
- ^ Robertson 1999, p. 16.
- ^ a b c d Gillman & Gillman 2000, p. 19.
- ^ Robertson 1999, p. 18.
- ^ Gillman & Gillman 2000, p. 27.
- ^ a b Green 2005, p. 15.
- ^ Firstbrook 2000, p. 9.
- ^ Robertson 1999, p. 19.
- ^ a b c d Gillman & Gillman 2000, p. 28.
- ^ Green 2005, p. 16.
- ^ Robertson 1999, p. 20.
- ^ Green 2005, p. 17.
- ^ a b c d e f Gillman & Gillman 2000, p. 29.
- ^ a b c d Green 2005, p. 18.
- ^ a b c d Robertson 1999, p. 22.
- ^ «Gibson, Harry Olivier Sumner». winchestercollegeatwar.com. Winchester, UK: Winchester College. Archived from the original on 23 January 2023. Retrieved 23 January 2023.
- ^ Messner 2001, p. 106.
- ^ a b c d Gillman & Gillman 2000, p. 33.
- ^ Robertson 1999, p. 34.
- ^ Gillman & Gillman 2000, p. 35.
- ^ Green 2005, p. 23.
- ^ «Alumni & Development, Notable Members». Magdalene College Cambridge. Archived from the original on 20 October 2013. Retrieved 1 August 2013.
- ^ a b c d Robertson 1999, p. 35.
- ^ a b c Robertson 1999, p. 36.
- ^ a b c Robertson 1999, p. 49.
- ^ Robertson 1999, p. 46–47.
- ^ Green 2005, p. 31.
- ^ a b Thompson 2012, p. 173.
- ^ Gillman & Gillman 2000, p. < 65.
- ^ a b c Gillman & Gillman 2000, p. 98.
- ^ «Portrait: George Leigh-Mallory». npg.org.uk. London, UK: National Portrait Gallery. Archived from the original on 21 September 2022. Retrieved 21 September 2022.
- ^ «Duncan Grant (1885-1978) Portrait of George Mallory». christies.com. London, UK: Christie’s. Archived from the original on 21 September 2022. Retrieved 21 September 2022.
- ^ Robertson 1999, p. 50.
- ^ «Friends of Magdalene Boat Club». Magdalene Boat Club. Archived from the original on 20 October 2013. Retrieved 1 August 2013.
- ^ Robertson 1999, pp. 39 & 43.
- ^ Gillman & Gillman 2000, pp. 39 & 46.
- ^ a b c Green 2005, p. 26.
- ^ a b Robertson 1999, p. 43.
- ^ a b Gillman & Gillman 2000, p. 47.
- ^ a b Cook 1919, pp. 121–139.
- ^ «ROWING: Henley Royal Regatta». The Times Archive. No. 38687. London, UK. 1 July 1908. p. 18. Retrieved 29 September 2022.
- ^ «Henley Regatta 1908». The Times Archive. No. 38690. London, UK. 4 July 1908. p. 13. Retrieved 29 September 2022.
- ^ a b c d e Robertson 1999, p. 38.
- ^ Green 2005, p. 25.
- ^ a b c Robertson 1999, p. 39.
- ^ Gillman & Gillman 2000, pp. 41 & 46.
- ^ Gillman & Gillman 2000, p. 41.
- ^ Gillman & Gillman 2000, p. 42.
- ^ a b c d Green 2005, p. 28.
- ^ a b c d e Gillman & Gillman 2000, p. 48.
- ^ Green 2005, pp. 32–33.
- ^ Robertson 1999, pp. 44–45.
- ^ a b Gillman & Gillman 2000, pp. 48–49.
- ^ a b Green 2005, p. 32.
- ^ Robertson 1999, p. 46.
- ^ a b c d Robertson 1999, p. 61.
- ^ Gillman & Gillman 2000, p. 72.
- ^ Gillman & Gillman 2000, p. 94.
- ^ Green 2005, p. 47.
- ^ Robertson 1999, p. 257.
- ^ a b Gillman & Gillman 2000, p. 102.
- ^ Green 2005, p. 48.
- ^ Robertson 1999, p. 52.
- ^ a b Gillman & Gillman 2000, p. 61.
- ^ a b c d Green 2005, p. 33.
- ^ Robertson 1999, pp. 52–53.
- ^ Gillman & Gillman 2000, p. 61–62.
- ^ Gillman & Gillman 2000, pp. 70–71.
- ^ Green 2005, p. 39.
- ^ Gillman & Gillman 2000, p. 71.
- ^ «Portrait of George Leigh-Mallory, By Simon Bussy». npg.org.uk. London, UK: National Portrait Gallery. Archived from the original on 27 September 2022. Retrieved 27 September 2022.
- ^ a b Robertson 1999, p. 60.
- ^ Gillman & Gillman 2000, p. 73.
- ^ a b c d e f Green 2005, p. 40.
- ^ a b c Gillman & Gillman 2000, p. 74.
- ^ Gillman & Gillman 2000, pp. 74–75.
- ^ a b Robertson 1999, p. 62.
- ^ a b Gillman & Gillman 2000, p. 75.
- ^ Gillman & Gillman 2000, pp. 75–76.
- ^ a b Gillman & Gillman 2000, p. 76.
- ^ a b Green 2005, p. 41.
- ^ Robertson 1999, p. 63.
- ^ Graves 1998, p. 62.
- ^ Davis 2011, p. 182.
- ^ Robertson 1999, p. 64.
- ^ a b Gillman & Gillman 2000, p. 79.
- ^ Green 2005, p. 44.
- ^ a b c Gillman & Gillman 2000, p. 80.
- ^ a b c d e Green 2005, p. 45.
- ^ Robertson 1999, p. 66.
- ^ Gillman & Gillman 2000, pp. 80–81.
- ^ Graves 1998, p. 272.
- ^ a b c Robertson 1999, p. 121.
- ^ Gillman & Gillman 2000, p. 149.
- ^ Davis 2011, pp. 92 & 195.
- ^ Graves 1998, p. 51.
- ^ Graves 1998, p. 61.
- ^ Robertson 1999, p. 67.
- ^ Gillman & Gillman 2000, p. 83.
- ^ Green 2005, p. 54.
- ^ Robertson 1999, p. 86.
- ^ Gillman & Gillman 2000, p. 104.
- ^ a b Green 2005, p. 49.
- ^ «Christiana Ruth Turner (1891–1942)». ancestry.co.uk. Dublin, Ireland: Ancestry Ireland Unlimited Company. Archived from the original on September 2022. Retrieved 18 September 2022.
- ^ Simkin, John (ed.). «Ruth Mallory: Biography». Spartacus Educational. Worthing, West Sussex, UK: Spartacus Educational Publishers Ltd. Archived from the original on 2 September 2022. Retrieved 2 September 2022.
- ^ Gillman & Gillman 2000, p. 115.
- ^ a b Robertson 1999, pp. 92–93.
- ^ Gillman & Gillman 2000, pp. 111 & 114.
- ^ a b c d e f g Green 2005, p. 50.
- ^ Gillman & Gillman 2000, p. 116.
- ^ a b Robertson 1999, p. 93.
- ^ a b c d Gillman & Gillman 2000, p. 111.
- ^ Gillman & Gillman 2000, p. 120.
- ^ Robertson 1999, p. 92.
- ^ a b Gillman & Gillman 2000, p. 112.
- ^ a b Robertson 1999, p. 94.
- ^ a b c Davis 2011, p. 184.
- ^ a b Gillman & Gillman 2000, p. 119.
- ^ a b Robertson 1999, p. 101.
- ^ a b c Gillman & Gillman 2000, p. 124.
- ^ Green 2005, p. 66–67.
- ^ Gillman & Gillman 2000, pp. 119–120.
- ^ Gillman & Gillman 2000, pp. 265–266.
- ^ «Christiana R Leigh-Mallory (Marriage to William Arnold-Forster)». ancestry.com. San Francisco, California, U.S.: Ancestry.com Operations Inc. Archived from the original on 18 September 2022. Retrieved 18 September 2022.
- ^ Robertson 1999, p. 99.
- ^ Gillman & Gillman 2000, p. 119 & 121.
- ^ Green 2005, p. 53.
- ^ a b Robertson 1999, p. 105.
- ^ Firstbrook 2000, p. 28.
- ^ Gillman & Gillman 2000, pp. 22 & 147.
- ^ Firstbrook 2000, p. 30.
- ^ Green 2005, p. 90.
- ^ Firstbrook 2000, p. 34.
- ^ Badham, Phil (18 November 2020). «George Leigh Mallory – Godalming to Everest via the Western Front». surreyinthegreatwar.org. Woking, Surrey, UK: Surrey Heritage. Archived from the original on 4 September 2022. Retrieved 5 September 2022.
- ^ a b c Green 2005, p. 68.
- ^ Robertson 1999, pp. 101–102.
- ^ Firstbrook 2000, p. 27.
- ^ a b c d e Robertson 1999, p. 102.
- ^ a b Gillman & Gillman 2000, p. 126.
- ^ Robertson 1999, p. 79.
- ^ Gillman & Gillman 2000, p. 99.
- ^ a b Robertson 1999, pp. 103–104.
- ^ a b Gillman & Gillman 2000, pp. 126–127.
- ^ Robertson 1999, p. 98.
- ^ a b c Gillman & Gillman 2000, p. 129.
- ^ «Royal Garrison Artillery». The London Gazette. No. 29409. 21 December 1915. p. 12695.
- ^ Green 2005, p. 70.
- ^ Firstbrook 2000, pp. 28–29.
- ^ a b Davis 2011, p. 189.
- ^ a b c d e Robertson 1999, p. 106.
- ^ Gillman & Gillman 2000, pp. 130–131.
- ^ Gillman & Gillman 2000, p. 131.
- ^ Gillman & Gillman 2000, p. 132.
- ^ Green 2005, p. 71.
- ^ a b Gillman & Gillman 2000, p. 134.
- ^ Robertson 1999, p. 107.
- ^ Davis 2011, pp. 189–190.
- ^ a b c d Gillman & Gillman 2000, p. 135.
- ^ a b c d e f Davis 2011, p. 190.
- ^ Green 2005, p. 72.
- ^ a b c d Robertson 1999, p. 108.
- ^ a b c Robertson 1999, p. 112.
- ^ Davis 2011, p. 192.
- ^ Gillman & Gillman 2000, p. 136.
- ^ Gillman & Gillman 2000, pp. 136–137.
- ^ Davis 2011, pp. 190–191.
- ^ a b c d Davis 2011, p. 191.
- ^ Gillman & Gillman 2000, p. 137.
- ^ Morris, Holly (2 December 2011). «The Lure of Everest». The New York Times. New York City, U.S.: A. G. Sulzberger. Archived from the original on 11 August 2022. Retrieved 11 August 2022.
- ^ a b Robertson 1999, p. 109.
- ^ Gillman & Gillman 2000, p. 138.
- ^ Robertson 1999, p. 111.
- ^ Davis 2011, pp. 191–192.
- ^ «Peake Wood Cemetery, Fricourt». inverclydeww1.org. Greenock, Scotland: Inverclyde’s Great War. Archived from the original on 16 October 2022. Retrieved 16 October 2022.
- ^ a b Green 2005, p. 73.
- ^ a b Robertson 1999, p. 113.
- ^ Gillman & Gillman 2000, p. 140.
- ^ Robertson 1999, p. 114.
- ^ a b c d Robertson 1999, p. 115.
- ^ a b Gillman & Gillman 2000, p. 142.
- ^ a b c d Davis 2011, p. 193.
- ^ History.com, Authors (4 October 2022). «Battle of the Somme». history.com. New York City, U.S.: A&E Television Networks. Archived from the original on 17 October 2022. Retrieved 17 October 2022.
- ^ Gillman & Gillman 2000, pp. 142–143.
- ^ a b Robertson 1999, p. 117.
- ^ Gillman & Gillman 2000, p. 143.
- ^ a b Gillman & Gillman 2000, p. 144.
- ^ a b c Gillman & Gillman 2000, p. 145.
- ^ Gillman & Gillman 2000, p. 70.
- ^ Green 2005, p. 38.
- ^ Robertson 1999, p. 118.
- ^ Gillman & Gillman 2000, pp. 145–146.
- ^ Davis 2011, pp. 193–194.
- ^ a b Gillman & Gillman 2000, p. 147.
- ^ Robertson 1999, p. 119.
- ^ Green 2005, p. 75.
- ^ a b Davis 2011, p. 194.
- ^ a b c Gillman & Gillman 2000, p. 148.
- ^ «Royal Garrison Artillery: The undermentioned 2nd Lts. to be Lts». The London Gazette (Supplement). No. 30315. 1 October 1917. pp. 10139–10142.
- ^ a b c Robertson 1999, p. 120.
- ^ Gillman & Gillman 2000, pp. 147–148.
- ^ a b Davis 2011, p. 195.
- ^ Gillman & Gillman 2000, pp. 148–149.
- ^ Green 2005, p. 77.
- ^ Edmonds, Maxwell-Hyslop & Davies 1947, pp. 144–145.
- ^ a b c d e f Robertson 1999, p. 122.
- ^ a b c Davis 2011, p. 196.
- ^ Romanych & Heuer 2017, chpt. 1918: Super-Heavy Railway Guns.
- ^ History.com, Authors (25 September 2019). «Allied forces break through the Hindenburg Line». history.com. New York City, U.S.: A&E Television Networks. Archived from the original on 23 October 2022. Retrieved 23 October 2022.
- ^ Edmonds, Maxwell-Hyslop & Davies 1947, p. 144.
- ^ Gillman & Gillman 2000, p. 151.
- ^ a b Foch 1931, pp. 568–569.
- ^ Gillman & Gillman 2000, p. 152.
- ^ Firstbrook 2000, p. 31.
- ^ Gillman & Gillman 2000, pp. 152 & 154.
- ^ a b Green 2005, p. 79.
- ^ «ROYAL GARRISON ARTILLERY. The undermentioned resign their commns. 21st Feb. 1920 (Lts., and retain the rank of Lt.)». The London Gazette. No. 31789. 20 February 1920. p. 2153.
- ^ Robertson 1999, pp. 127–128.
- ^ a b c d e f Green 2005, p. 83.
- ^ Gillman & Gillman 2000, p. 154.
- ^ Robertson 1999, p. 124.
- ^ Davis 2011, p. 199.
- ^ a b Gillman & Gillman 2000, p. 160.
- ^ Robertson 1999, pp. 124–125.
- ^ Green 2005, pp. 80–81.
- ^ a b Gillman & Gillman 2000, pp. 160–161.
- ^ Robertson 1999, p. 127.
- ^ a b c d e f Gillman & Gillman 2000, p. 163.
- ^ Green 2005, pp. 83–84.
- ^ a b c d Green 2005, p. 84.
- ^ «The Construction of Dún Laoghaire Harbour» (PDF). dlharbour.ie. Dún Laoghaire, Ireland: Dún Laoghaire Harbour Company. Archived (PDF) from the original on 1 November 2022. Retrieved 1 November 2022.
- ^ Walsh 2016, p. 258.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j Gillman & Gillman 2000, p. 165.
- ^ a b Walsh 2016, p. 259.
- ^ Croston 2000, pp. 157–176.
- ^ Gillman & Gillman 2000, pp. 106, 130 & 162.
- ^ a b Robertson 1999, p. 128.
- ^ a b Robertson 1999, p. 129.
- ^ Firstbrook 2000, p. 32.
- ^ Green 2005, p. 85.
- ^ Gillman & Gillman 2000, pp. 165–166.
- ^ Walsh 2016, p. 259–260.
- ^ Firstbrook 2000, p. 33.
- ^ Davis 2011, p. 200.
- ^ Robertson 1999, pp. 147–148.
- ^ a b Howard-Bury 1922, pp. 16–20.
- ^ Howard-Bury 1922, pp. 16–17.
- ^ West 2003, p. 1708.
- ^ Howard-Bury 1922, p. 18.
- ^ a b Gillman & Gillman 2000, p. 166.
- ^ a b Gillman & Gillman 2000, p. 171.
- ^ a b c d e Green 2005, p. 102.
- ^ Robertson 1999, p. 148.
- ^ Gillman & Gillman 2000, pp. 171–172.
- ^ Gillman & Gillman 2000, p. 172.
- ^ a b Gillman & Gillman 2000, p. 174.
- ^ Green 2005, p. 106.
- ^ Robertson 1999, p. 149.
- ^ Howard-Bury 1922, p. 19.
- ^ Gillman & Gillman 2000, p. 175.
- ^ Gillman & Gillman 2000, pp. 175–176.
- ^ Gillman & Gillman 2000, pp. 174 & 177.
- ^ a b c d e Green 2005, p. 109.
- ^ Gillman & Gillman 2000, p. 177.
- ^ Gillman & Gillman 2000, p. 179.
- ^ a b c Green 2005, p. 122.
- ^ Davis 2011, p. 364.
- ^ a b c d e Robertson 1999, p. 179.
- ^ Gillman & Gillman 2000, p. 194.
- ^ Davis 2011, pp. 364 & 371.
- ^ a b c d e Gillman & Gillman 2000, p. 196.
- ^ a b c d Green 2005, p. 123.
- ^ Davis 2011, p. 371.
- ^ a b Gillman & Gillman 2000, p. 200.
- ^ Gillman & Gillman 2000, pp. 199–200.
- ^ Howard-Bury 1922, p. VII, Contents.
- ^ Davis 2011, p. 380.
- ^ Gillman & Gillman 2000, p. 201.
- ^ «Caledonia (1894)» (PDF). poheritage.com. London, UK: P&OSNCo. November 2008. Archived (PDF) from the original on 16 November 2022. Retrieved 16 November 2022.
- ^ Davis 2011, p. 379.
- ^ a b Somervell 1947, p. 50.
- ^ Green 2005, p. 127.
- ^ a b Davis 2011, p. 389.
- ^ Bruce 1923, pp. 19–20.
- ^ a b Robertson 1999, p. 184.
- ^ Davis 2011, pp. 394–395.
- ^ Bruce 1923, p. 30.
- ^ Davis 2011, p. 404.
- ^ Bruce 1923, p. 40.
- ^ Green 2005, p. 129.
- ^ Bruce 1923, pp. 49–50 & Maps: Sketch Map of Mount Everest and the Rongbuk Glaciers At end of book.
- ^ Green 2005, pp. 137 & 141.
- ^ Davis 2011, p. 457.
- ^ Davis 2011, p. 461.
- ^ Green 2005, p. 141.
- ^ Green 2005, pp. 141–142.
- ^ a b Davis 2011, p. 458.
- ^ «Can Everest Be Climbed? Story Of Gallant Failure». The Times Archive. No. 43164. London, UK. 17 October 1922. p. 7. Retrieved 20 November 2022.
- ^ Robertson 1999, p. 207.
- ^ a b Gillman & Gillman 2000, p. 216.
- ^ Davis 2011, p. 459.
- ^ a b Gillman & Gillman 2000, p. 217.
- ^ a b Green 2005, p. 142.
- ^ a b c Davis 2011, p. 464.
- ^ Gillman & Gillman 2000, pp. 218–219.
- ^ a b Gillman & Gillman 2000, p. 219.
- ^ Green 2005, p. 143.
- ^ Bruce 1923, p. VII, Contents.
- ^ Robertson 1999, p. 208.
- ^ Gillman & Gillman 2000, pp. 219–220.
- ^ Davis 2011, pp. 464–465.
- ^ Robertson 1999, p. 209.
- ^ Green 2005, p. 144.
- ^ Robertson 1999, p. 210.
- ^ a b Davis 2011, p. 465.
- ^ Green 2005, pp. 144–145.
- ^ «SAYS BRANDY AIDED MT. EVEREST PARTY; A Swig 27,000 Feet Up ‘Cheered Us All Up Wonderfully,’ Mallory Tells Audience». The New York Times. New York City, U.S.: A. G. Sulzberger. 5 February 1923. Archived from the original on 24 November 2022. Retrieved 24 November 2022.
- ^ Gillman & Gillman 2000, p. 220.
- ^ a b Robertson 1999, p. 211.
- ^ a b c Gillman & Gillman 2000, p. 221.
- ^ a b «Climbing Mount Everest is work for Supermen». The New York Times. New York City, U.S.: A. G. Sulzberger. 18 March 1923. Archived from the original on 12 August 2022. Retrieved 12 August 2022.
- ^ «HAZARDS OF THE ALPS». The New York Times. New York City, U.S.: A. G. Sulzberger. 29 August 1923. Archived from the original on 12 August 2022. Retrieved 12 August 2022.
- ^ a b Gillman & Gillman 2000, p. 222.
- ^ Holzel & Salkeld 1999, pp. 186–190.
- ^ Rees 2006, p. 309.
- ^ Robertson 1999, pp. 211–212.
- ^ Green 2005, p. 146.
- ^ a b Robertson 1999, p. 212.
- ^ Green 2005, p. 147.
- ^ Davis 2011, p. 466.
- ^ a b c d Gillman & Gillman 2000, p. 223.
- ^ Davis 2011, p. 467.
- ^ a b c Robertson 1999, p. 213.
- ^ a b c Gillman & Gillman 2000, p. 224.
- ^ a b Green 2005, p. 149.
- ^ Green 2005, p. 150.
- ^ a b Robertson 1999, p. 215.
- ^ Gillman & Gillman 2000, pp. 227–228.
- ^ a b Gillman & Gillman 2000, p. 228.
- ^ a b c Verma, Somesh (17 August 2012). «The faceless hero Nepal’s only Olympic Gold medalist in focus». The Kathmandu Post. Kathmandu, Nepal: Kantipur Publications Limited. Archived from the original on 16 December 2018. Retrieved 1 December 2022.
- ^ Bruce 1923, pp. 62, 244 & 254–257.
- ^ Firstbrook 2000, pp. 123–124.
- ^ Bruce 1923, pp. 246 & 254–257.
- ^ Bruce 1923, pp. 279–286.
- ^ Georgiou, Mark (26 March 2012). «Everest Olympic medal pledge set to be honoured». BBC News Online. London, UK: BBC. Archived from the original on 3 December 2022. Retrieved 3 December 2022.
- ^ a b c Summers 2001, p. 248.
- ^ a b Mitchell, Ian (19 May 2021). «The forgotten Scots of the first Everest expedition of 1921 — one died, the other went mad (See memorial photo for names of porters)». The Scotsman. Leeds, UK: National World Publishing Ltd. Archived from the original on 3 December 2022. Retrieved 3 December 2022.
- ^ Davis 2011, p. 481.
- ^ Robertson 1999, pp. 223–224.
- ^ a b c Davis 2011, p. 485.
- ^ Robertson 1999, p. 225.
- ^ Green 2005, p. 156.
- ^ a b Robertson 1999, p. 227.
- ^ Norton 1925, p. 19.
- ^ Norton 1925, pp. 50–53.
- ^ Summers 2001, pp. 167–168.
- ^ Elliott & Russell 1974, pp. 283–284.
- ^ a b c d e Gillman & Gillman 2000, p. 50.
- ^ Green 2005, p. 27.
- ^ a b c d Robertson 1999, p. 44.
- ^ Birkett 1989, p. 35.
- ^ a b Birkett 1989, p. 31.
- ^ Birkett et al. 1987, pp. 265–266.
- ^ Russell 1991, p. 221.
- ^ Birkett et al. 1987, p. 18.
- ^ Cram 1986, p. 34.
- ^ Russell 1989, pp. 210–211.
- ^ Puttrell 1900, pp. 102–106.
- ^ «Scafell — Keswick Brothers’ Climb». multi-pitch.com. Archived from the original on 2 January 2023. Retrieved 2 January 2023.
- ^ «Mallory’s Left-Hand Route». theCrag. Northcote, Victoria, Australia: theCrag Proprietary Limited. Archived from the original on 2 January 2023. Retrieved 2 January 2023.
- ^ «Mallory’s Right-Hand Route». theCrag. Northcote, Victoria, Australia: theCrag Proprietary Limited. Archived from the original on 2 January 2023. Retrieved 2 January 2023.
- ^ Gillman & Gillman 2000, p. 105.
- ^ Jones 1993, pp. 16–17.
- ^ «Pinnacle Traverse». UKClimbing. Sheffield, UK: UKClimbing Limited. Archived from the original on 4 January 2023. Retrieved 4 January 2023.
- ^ a b Gillman & Gillman 2000, p. 106.
- ^ Reid 2006, p. 678.
- ^ Reid 2006, pp. 678–687.
- ^ Anker & Roberts 1999, p. 153.
- ^ Gillman 2011, pp. 199–200.
- ^ Survey, Ordnance (18 March 2016). «Great Britain’s tallest mountain is taller». ordnancesurvey.co.uk. Southampton, UK: Ordnance Survey Ltd. Archived from the original on 21 December 2022. Retrieved 21 December 2022.
- ^ Nugent, Ciara (11 December 2017). «Mount Hope becomes UK’s new highest mountain after satellites reveal previous measurement was wrong». The Independent. London, UK: Independent Digital News & Media Limited. Archived from the original on 21 December 2022. Retrieved 21 December 2022.
- ^ Gillman 2011, pp. 201–202.
- ^ Gillman 2011, p. 202.
- ^ Gillman 2011, pp. 202–203.
- ^ a b Gillman 2011, p. 203.
- ^ Gillman 2011, pp. 203–204.
- ^ Crocket 1986, p. 37.
- ^ Bicknell 1975, pp. 302–303.
- ^ Gillman & Gillman 2000, pp. 149–150.
- ^ Gillman & Gillman 2000, p. 150.
- ^ Howett 2001, pp. 213–215.
- ^ Mackenzie & Williams 2005, pp. 124–125.
- ^ Howett 2001, pp. 205–210.
- ^ Mackenzie & Williams 2005, p. 150.
- ^ Pye 1919, pp. 140–145.
- ^ a b Robertson 1999, pp. 41 & 43.
- ^ Gillman & Gillman 2000, pp. 44–45.
- ^ Hankinson 1977, pp. 50–52.
- ^ a b c Gillman & Gillman 2000, p. 45.
- ^ Hankinson 1977, pp. 87–89.
- ^ Russell 1999, p. 208.
- ^ Neal 1998, p. 33.
- ^ Gillman & Gillman 2000, pp. 45–46.
- ^ Hankinson 1977, pp. 116–118 & 124–125.
- ^ Green 2005, pp. 26–27.
- ^ Hankinson 1977, pp. 116–118.
- ^ Hankinson 1977, p. 85.
- ^ Williams 1990, p. 52.
- ^ Williams 1990, p. 47.
- ^ a b c Gillman & Gillman 2000, p. 49.
- ^ Thomson & Andrews 1909, pp. 45, 49–50 & 99.
- ^ Neal 1998, pp. 39–40 & 87.
- ^ Gillman & Gillman 2000, pp. 49–50.
- ^ a b Gillman & Gillman 2000, p. 58.
- ^ Robertson 1999, p. 48.
- ^ Neal 1998, pp. 26 & 86.
- ^ Thomson & Andrews 1909, pp. 27–31 & 97.
- ^ a b c Gillman & Gillman 2000, p. 59.
- ^ Neal 1998, p. 45.
- ^ a b Thomson & Andrews 1909, p. 99.
- ^ Neal 1998, p. 42.
- ^ «The Girdle Traverse». UKClimbing. Sheffield, UK: UKClimbing Limited. Archived from the original on 14 January 2023. Retrieved 14 January 2023.
- ^ Gillman & Gillman 2000, p. 77.
- ^ a b Robertson 1999, p. 77.
- ^ Green 2005, p. 61.
- ^ a b c d Gillman & Gillman 2000, p. 91.
- ^ «Mallory’s Ridge». UKClimbing. Sheffield, UK: UKClimbing Limited. Archived from the original on 15 January 2023. Retrieved 15 January 2023.
- ^ Brockbank 2011, pp. 14–16.
- ^ Gillman & Gillman 2000, pp. 91–92.
- ^ Neal 1998, pp. 17 & 88.
- ^ a b c d e f Gillman & Gillman 2000, p. 101.
- ^ Fraser 1926, pp. 338 & 346–347.
- ^ «Pis-Aller Rib». UKClimbing. Sheffield, UK: UKClimbing Limited. Archived from the original on 18 January 2023. Retrieved 18 January 2023.
- ^ «Yellow Buttress». UKClimbing. Sheffield, UK: UKClimbing Limited. Archived from the original on 18 January 2023. Retrieved 18 January 2023.
- ^ Robertson 1999, pp. 87–88.
- ^ Gillman & Gillman 2000, pp. 107–108.
- ^ Robertson 1999, p. 88.
- ^ Gillman & Gillman 2000, p. 108.
- ^ a b c Gillman & Gillman 2000, p. 130.
- ^ Jones 2003, pp. 200–201, 204 & 282.
- ^ Neal 1998, p. 88.
- ^ Robertson 1999, p. 130.
- ^ Gillman & Gillman 2000, p. 157.
- ^ Green 2005, p. 86.
- ^ Davis 2011, p. 3.
- ^ Powell 2009, p. 334.
- ^ Robertson 1959, p. 280.
- ^ Gillman & Gillman 2000, pp. 157–158.
- ^ Robertson 1999, pp. 130–131.
- ^ Neal 1998, pp. 40–41, 84 & 88.
- ^ «Harry Olivier Sumner Gibson (1885–1917)». headington.org.uk. Headington, Oxford, UK. Archived from the original on 23 January 2023. Retrieved 23 January 2023.
- ^ Robertson 1999, pp. 21–22.
- ^ Robertson 1999, pp. 22–23.
- ^ a b Gillman & Gillman 2000, p. 30.
- ^ Robertson 1999, pp. 23–24.
- ^ Robertson 1999, p. 25.
- ^ Robertson 1999, pp. 26 & 28.
- ^ a b Robertson 1999, p. 28.
- ^ «Alpine 4000m Peaks». Mountains Of Scotland. Archived from the original on 25 January 2023. Retrieved 25 January 2023.
- ^ Robertson 1999, p. 29.
- ^ Irving 1948, pp. 386–390.
- ^ Robertson 1999, p. 30.
- ^ Robertson 1999, p. 32.
- ^ Gillman & Gillman 2000, p. 34.
- ^ Gillman & Gillman 2000, p. 64.
- ^ a b c d e Gillman & Gillman 2000, p. 66.
- ^ a b Robertson 1999, p. 55.
- ^ Young 1910, pp. 138–145.
- ^ Robertson 1999, pp. 55 & 62.
- ^ a b Robertson 1999, p. 56.
- ^ Gillman & Gillman 2000, pp. 66–67.
- ^ a b c Robertson 1999, p. 57.
- ^ Gillman & Gillman 2000, p. 67.
- ^ a b Gillman & Gillman 2000, p. 68.
- ^ Robertson 1999, p. 58.
- ^ Green 2005, pp. 41–42.
- ^ Gillman & Gillman 2000, p. 78.
- ^ Green 2005, p. 60.
- ^ Robertson 1999, p. 74.
- ^ a b c Gillman & Gillman 2000, p. 89.
- ^ a b Irving 1911, p. 748.
- ^ Irving 1911, pp. 735–736.
- ^ a b Irving 1912, pp. 340–341.
- ^ a b «Panoramic views of Gran Paradiso Area». summitpost.org. Crystal City, Missouri, U.S.: SummitPost. Archived from the original on 31 January 2023. Retrieved 1 February 2023.
- ^ a b Irving 1911, p. 749.
- ^ Mondini 1902, pp. 208–209.
- ^ Mondini 1902, p. 209.
- ^ a b «Mont Maudit». summitpost.org. Crystal City, Missouri, U.S.: SummitPost. Archived from the original on 2 February 2023. Retrieved 2 February 2023.
- ^ Gillman & Gillman 2000, pp. 89–90.
- ^ Mallory 1918, pp. 148–162.
- ^ Gillman & Gillman 2000, pp. 90–91.
- ^ «Tête Carrée» [Square Head]. camptocamp.org (in French). Grenoble, France: Camptocamp-Association. Archived from the original on 4 February 2023. Retrieved 4 February 2023.
- ^ Gillman & Gillman 2000, pp. 99–100.
- ^ Young 1912, pp. 457–458.
- ^ «Climbers’ Club — Obituaries» (PDF). The Climbers’ Club. UK: The Climbers’ Club. page 9. Archived (PDF) from the original on 5 February 2023. Retrieved 5 February 2023.
- ^ a b c Gillman & Gillman 2000, p. 100.
- ^ a b Robertson 1999, p. 83.
- ^ Yeld 1912, p. 469.
- ^ Robertson 1999, pp. 83–84.
- ^ Mallory 1912, pp. 462–463.
- ^ «Tête du Lion» [Lion’s Head]. camptocamp.org (in French). Grenoble, France: Camptocamp-Association. Archived from the original on 7 February 2023. Retrieved 7 February 2023.
- ^ Robertson 1999, pp. 84–85.
- ^ Gillman & Gillman 2000, pp. 100–101.
- ^ Young 1927, pp. 217–220.
- ^ «Col Tournanche» [Col Tournanche]. camptocamp.org (in French). Grenoble, France: Camptocamp-Association. Archived from the original on 7 February 2023. Retrieved 7 February 2023.
- ^ Robertson 1999, p. 131.
- ^ Gillman & Gillman 2000, pp. 158–159.
- ^ a b c Gillman & Gillman 2000, p. 159.
- ^ Mallory & Porter 1920, pp. 132–133.
- ^ Russell 2019, p. 242.
- ^ Mallory & Porter 1920, p. 132.
- ^ «Mallory-Porter». summitpost.org. Crystal City, Missouri, U.S.: SummitPost. Archived from the original on 9 February 2023. Retrieved 9 February 2023.
- ^ «Mallory-Porter (rectified)». Mountain Project. Missoula, Montana, U.S.: Adventure Projects Inc. Archived from the original on 9 February 2023. Retrieved 9 February 2023.
- ^ Robertson 1999, pp. 140–141.
- ^ Robertson 1999, pp. 141–142.
- ^ «Mont Blanc: Éperon de la Tournette» [Mont Blanc: Tournette Spur]. camptocamp.org (in French). Grenoble, France: Camptocamp-Association. Archived from the original on 10 February 2023. Retrieved 10 February 2023.
- ^ «Aiguille de Talèfre». summitpost.org. Crystal City, Missouri, U.S.: SummitPost. Archived from the original on 11 January 2023. Retrieved 11 February 2023.
- ^ Robertson 1999, pp. 144–145.
- ^ a b Gillman & Gillman 2000, p. 164.
- ^ a b Robertson 1999, p. 145.
- ^ Finch 1965, pp. 374–376.
- ^ Gillman & Gillman 2000, pp. 69, 74–75, 77–78, 83–92, 95–96, & 98.
- ^ Beauman, Nicola (23 September 2004). «O’Malley [née Sanders], Mary Dolling, Lady O’Malley [pseud. Ann Bridge] (1889–1974)». Oxford Dictionary of National Biography. Oxford, UK: Oxford University Press. doi:10.1093/ref:odnb/57596. Retrieved 12 February 2023.
- ^ Gillman & Gillman 2000, pp. 100–109, 112, 114, 123, & 195.
- ^ Gillman & Gillman 2000, pp. 69 & 273.
- ^ Neff 2015, pp. Everest Dream.
- ^ Robertson 1999, pp. 154–155.
- ^ Gillman & Gillman 2000, pp. 13–14.
- ^ Howard-Bury 1922, pp. 18 & 53–54.
- ^ Howard-Bury 1922, pp. 20 & 319–337.
- ^ Morshead 1923, p. 357.
- ^ Boswell, Randy (13 November 2011). «Canadian geographer conquered Mount Everest in ‘epic quest’«. National Post. Toronto, Ontario, Canada: Postmedia. Archived from the original on 13 August 2022. Retrieved 13 August 2022.
- ^ Howard-Bury 1922, pp. 179, 319, & 328.
- ^ a b c Morshead 1923, p. 363.
- ^ Howard-Bury 1922, pp. 179, 319, & 328–337.
- ^ Howard-Bury 1922, pp. 20 & 338–340.
- ^ Heron 1922, pp. 418–431.
- ^ Howard-Bury 1922, pp. 20, 281–303, & 344–350.
- ^ Robertson 1999, pp. 156–157 & 169–170.
- ^ a b c d Gillman & Gillman 2000, p. 188.
- ^ Howard-Bury 1922, p. 245.
- ^ Howard-Bury 1922, pp. 242–249.
- ^ Howard-Bury 1922, pp. 248–249.
- ^ Howard-Bury 1922, p. 258.
- ^ a b Robertson 1999, p. 175.
- ^ a b Gillman & Gillman 2000, p. 190.
- ^ Davis 2011, pp. 355–356.
- ^ Davis 2011, pp. 356–357.
- ^ Robertson 1999, pp. 175–176.
- ^ Robertson 1999, p. 176.
- ^ Davis 2011, pp. 359–360.
- ^ Davis 2011, p. 361.
- ^ Murray 1953, p. 41.
- ^ Howard-Bury 1922, pp. 260–261.
- ^ Bruce 1923, pp. 210 & 246.
- ^ a b c d e f Hemmleb et al. 1999, pp. 13 & 185.
- ^ a b c Bruce 1923, p. 246.
- ^ a b Norton 1925, pp. 108–109.
- ^ a b Hemmleb & Simonson 2002, pp. 107, 113, & 180.
- ^ Bruce 1923, pp. 3–13.
- ^ Bruce 1923, p. 17.
- ^ Firstbrook 2000, pp. 113–114.
- ^ Bruce 1923, pp. 183–185.
- ^ Firstbrook 2000, pp. 114–115.
- ^ Bruce 1923, p. 185.
- ^ Firstbrook 2000, p. 114.
- ^ Bruce 1923, pp. 184 & 191.
- ^ Bruce 1923, pp. 190–191.
- ^ a b c Gillman & Gillman 2000, p. 205.
- ^ a b Bruce 1923, pp. 193–194.
- ^ Firstbrook 2000, p. 115.
- ^ Bruce 1923, p. 196.
- ^ Bruce 1923, pp. 201 & 206.
- ^ Bruce 1923, pp. 199 & 203–204.
- ^ Bruce 1923, pp. 200 & 206.
- ^ Bruce 1923, p. 206.
- ^ Bruce 1923, pp. 206–208.
- ^ Bruce 1923, p. 208.
- ^ Bruce 1923, pp. 209–210.
- ^ a b Gillman & Gillman 2000, p. 206.
- ^ a b Bruce 1923, p. 211.
- ^ a b c Bruce 1923, p. 214.
- ^ a b Bruce 1923, pp. 214–215.
- ^ Murray 1953, p. 63.
- ^ Gillman & Gillman 2000, pp. 206–207.
- ^ Firstbrook 2000, pp. 117–118.
- ^ Bruce 1923, pp. 215–221.
- ^ Bruce 1923, pp. 237–238 & 243-244.
- ^ Bruce 1923, pp. 141 & 244.
- ^ Bruce 1923, pp. 62 & 244.
- ^ Bruce 1923, p. 244.
- ^ a b c Bruce 1923, p. 245.
- ^ Gillman & Gillman 2000, pp. 207–208.
- ^ Bruce 1923, pp. 246–248.
- ^ Bruce 1923, p. 247.
- ^ Bruce 1923, p. 248.
- ^ Bruce 1923, pp. 273–278.
- ^ Bruce 1923, pp. 275–277 & 280.
- ^ Bruce 1923, pp. 278–279.
- ^ Bruce 1923, pp. 279–280.
- ^ Bruce 1923, p. 280.
- ^ a b c d Gillman & Gillman 2000, p. 211.
- ^ Bruce 1923, p. 281.
- ^ a b Somervell 1947, p. 71.
- ^ Robertson 1999, p. 201.
- ^ Bruce 1923, p. 281–283.
- ^ Bruce 1923, pp. 282–283.
- ^ Bruce 1923, p. 283.
- ^ Bruce 1923, pp. 283–284.
- ^ a b Bruce 1923, pp. 284–285.
- ^ Somervell 1947, p. 72.
- ^ Gillman & Gillman 2000, p. 212.
- ^ Bruce 1923, pp. 285.
- ^ a b Hemmleb & Simonson 2002, p. 103.
- ^ Green 2005, pp. 152–155.
- ^ Norton 1925, pp. 13–20.
- ^ Gillman & Gillman 2000, p. 238.
- ^ Green 2005, p. 158.
- ^ Robertson 1999, p. 230.
- ^ Hemmleb & Simonson 2002, p. 104.
- ^ a b Gillman & Gillman 2000, p. 249.
- ^ Norton 1925, pp. 80, 94, & 96.
- ^ Robertson 1999, pp. 246–247.
- ^ a b Norton 1925, p. 94.
- ^ a b Norton 1925, p. 96.
- ^ Norton 1925, pp. 96–97 & 105.
- ^ a b c Norton 1925, p. 97.
- ^ Gillman & Gillman 2000, pp. 249–250.
- ^ Norton 1925, p. 102.
- ^ Norton 1925, p. 104.
- ^ a b Norton 1925, p. 105.
- ^ Norton 1925, p. 107.
- ^ Norton 1925, pp. 107–108.
- ^ Norton 1925, p. 108.
- ^ Norton 1925, pp. 107–109.
- ^ a b c Norton 1925, p. 109.
- ^ a b c Norton 1925, p. 110.
- ^ Norton 1925, pp. 110–111.
- ^ Norton 1925, pp. 110–112.
- ^ a b c d Norton 1925, p. 111.
- ^ Norton 1925, pp. 108 & 111–112.
- ^ Somervell 1947, pp. 123 & 128–131.
- ^ Norton 1925, p. 112.
- ^ a b Somervell 1947, p. 129.
- ^ Norton 1925, p. 117.
- ^ Norton 1925, pp. 111–113.
- ^ Norton 1925, p. 113.
- ^ Anker & Roberts 1999, p. 126.
- ^ Summers 2001, p. 105.
- ^ «Everest Climbed For First Time Without Oxygen». The Times Archive. No. 60297. London, UK. 10 May 1978. p. 1. Retrieved 16 March 2023.
- ^ a b c Somervell 1947, p. 131.
- ^ Norton 1925, p. 115.
- ^ Davis 2011, pp. 537–538.
- ^ Summers 2001, p. 4.
- ^ Norton 1925, pp. 64, 80, & 122.
- ^ a b Norton 1925, p. 116.
- ^ Norton 1925, pp. 116–117.
- ^ a b c Gillman & Gillman 2000, p. 254.
- ^ a b c d e Norton 1925, p. 125.
- ^ a b c d Odell 1924, p. 456.
- ^ Norton 1925, pp. 125–126.
- ^ a b Norton 1925, p. 126.
- ^ a b Hemmleb & Simonson 2002, p. 114.
- ^ Norton 1925, p. 127.
- ^ a b Noel 1927, p. 261.
- ^ Gillman & Gillman 2000, p. 255.
- ^ a b Noel 1927, p. 251.
- ^ Noel 1927, pp. 213 & 261.
- ^ a b Noel 1927, p. 262.
- ^ Norton 1925, pp. 127–129.
- ^ Noel 1927, pp. 261–262.
- ^ Norton 1925, pp. 130–131.
- ^ Norton, Edward Felix; Odell, Noel (5 July 1924). «More Light On Everest Disaster: Mr Odell’s Last View Of Lost Climbers». Aberdeen Press and Journal. Dundee, Scotland, UK: D.C. Thomson & Co. Ltd. p. 7. Archived from the original on 20 March 2023. Retrieved 20 March 2023.
- ^ Norton 1925, p. 140.
- ^ Norton 1924, pp. 160–161.
- ^ a b «Everest: Mystery of Mallory and Irvine». pbs.org. Arlington, Virginia, U.S.: PBS. 6 October 1999. Archived from the original on 17 August 2022. Retrieved 17 August 2022.
- ^ a b Norton 1925, p. 130.
- ^ a b c Norton 1925, p. 131.
- ^ a b c d Norton 1925, p. 132.
- ^ Norton 1925, p. 133.
- ^ Davis 2011, p. 547.
- ^ Norton 1925, p. 135.
- ^ Davis 2011, pp. 547–548.
- ^ Norton 1925, pp. 135–136.
- ^ Norton 1925, p. 136.
- ^ Norton 1925, pp. 136–137 & 142.
- ^ Davis 2011, p. 548.
- ^ a b c Norton 1925, p. 137.
- ^ Norton 1925, p. 138.
- ^ a b c d Gillman & Gillman 2000, p. 259.
- ^ a b c Davis 2011, p. 549.
- ^ Norton 1925, pp. 135 & 138.
- ^ Noel 1927, p. 265.
- ^ a b Noel 1927, p. 266.
- ^ Davis 2011, pp. 549–550.
- ^ Gillman & Gillman 2000, pp. 193 & 261.
- ^ Somervell 1947, p. 135.
- ^ Norton 1925, pp. 153–155.
- ^ Gillman & Gillman 2000, pp. 259–260.
- ^ «The Mount Everest Tragedy: Message From The King». The Times Archive. No. 43686. London, UK. 24 June 1924. p. 14. Retrieved 8 December 2022.
- ^ Green 2005, p. 171.
- ^ a b c «Leigh-Mallory And Irvine: Memorial Service At St Paul’s». The Times Archive. No. 43786. London, UK. 18 October 1924. p. 14. Retrieved 8 December 2022.
- ^ Hinks 1924, pp. 462–465.
- ^ UK Retail Price Index inflation figures are based on data from Clark, Gregory (2017). «The Annual RPI and Average Earnings for Britain, 1209 to Present (New Series)». MeasuringWorth. Retrieved 11 June 2022.
- ^ «Search probate records or find a will». gov.uk. London, UK: UK Government Digital Service. Archived from the original on 3 September 2022. Retrieved 3 September 2022.
- ^ Hemmleb & Simonson 2002, pp. 132 & 180.
- ^ Ruttledge 1934, pp. 135–137.
- ^ Hemmleb & Simonson 2002, pp. 14, 132, & 190.
- ^ Ruttledge 1934, p. 137.
- ^ Hemmleb & Simonson 2002, pp. 132–134 & 189.
- ^ Ruttledge 1934, pp. 138–141.
- ^ Hemmleb & Simonson 2002, p. 199, Appendix II, notes and references of chapter 8, no. 8.
- ^ Holzel & Salkeld 1999, p. 8.
- ^ a b Norton 1925, p. 114.
- ^ a b c Hemmleb et al. 1999, p. 110.
- ^ a b c d e f g h Odell 1934, p. 447.
- ^ Hemmleb & Simonson 2002, p. 134.
- ^ a b c d Unsworth 1991, p. 655, Appendix VI, notes and references of chapter 5, no. 36.
- ^ a b Hoyland 2014, pp. 128–130 & 290 notes of chapter 10, no. 10.
- ^ Smythe 2013, pp. 215–216.
- ^ a b Hoyland 2014, pp. 128–130.
- ^ Smythe 2013, pp. 11 & 215–216.
- ^ Smythe 2013, pp. 215–216 & 305.
- ^ Douglas, Ed (23 November 2013). «Lifelong secret of Everest pioneer: I discovered Mallory’s body in 1936». The Observer. London, UK: Guardian News & Media. Archived from the original on 1 April 2023. Retrieved 1 April 2023.
- ^ Holzel & Salkeld 1999, p. 4.
- ^ Holzel & Salkeld 1999, pp. 10, 322, & 360 notes on sources of chapter 1, no. 11.
- ^ Holzel & Salkeld 1999, p. 322.
- ^ a b c Holzel & Salkeld 1999, p. 323.
- ^ a b c Odell 1924, p. 458.
- ^ a b Norton 1925, pp. 131–132.
- ^ a b Hoelzgen, Joachim, ed. (29 June 1986). «Das phantastischste Rätsel des Jahrhunderts» [The most fantastic riddle of the century]. Der Spiegel (in German). Hamburg, Germany: SPIEGEL-Verlag Rudolf Augstein GmbH & Co. KG. Archived from the original on 6 April 2023. Retrieved 6 April 2023.
- ^ Holzel & Salkeld 1999, pp. 1 & 359 notes on sources of chapter 1, no. 1.
- ^ Holzel & Salkeld 1999, pp. 1–2.
- ^ a b c d e f Holzel & Salkeld 1999, pp. 2–3.
- ^ Unsworth 1991, p. 570.
- ^ Carter 1980, pp. 657–658.
- ^ a b c d Carter 1980, p. 658.
- ^ «Riddle of Everest near solution: Japanese climbers to seek Briton’s body». The Times Archive. No. 60556. London, UK. 21 February 1980. p. 9. Retrieved 2 April 2023.
- ^ a b c d e Salkeld 1991, p. 129.
- ^ Salkeld 1991, pp. 129–130.
- ^ a b c d Salkeld 1991, p. 130.
- ^ a b Holzel & Salkeld 1999, pp. 318–319.
- ^ a b c Holzel, Tom (11 February 1988). «Mallory & Irvine–The Search Continues». numa.net. Los Alamos, U.S.: National Underwater and Marine Agency. Archived from the original on 6 April 2023. Retrieved 6 April 2023.
- ^ Unsworth 1991, p. 592.
- ^ Holzel & Salkeld 1999, pp. 321 & 325.
- ^ a b Bell, George (12 October 1986). «Everest Team Finds Artifacts of ’22 Expedition». Los Angeles Times. El Segundo, California, U.S. Archived from the original on 7 April 2023. Retrieved 7 April 2023.
- ^ a b Harvard, Andrew (30 November 1986). «Look Back at Life on the Mountain: Chronicling Ups and Downs of 10 Weeks on Mt. Everest». Los Angeles Times. El Segundo, California, U.S. Archived from the original on 7 April 2023. Retrieved 7 April 2023.
- ^ Holzel & Salkeld 1999, pp. 324–325.
- ^ a b c Holzel & Salkeld 1999, p. 324.
- ^ a b c d e f g Holzel & Salkeld 1999, p. 326.
- ^ Hemmleb & Simonson 2002, pp. 89–90, 97, & 180.
- ^ Holzel & Salkeld 1999, pp. 326–327.
- ^ a b Holzel & Salkeld 1999, p. 327.
- ^ a b Hemmleb & Simonson 2002, pp. 88 & 180.
- ^ Hemmleb & Simonson 2002, p. 88.
- ^ Hemmleb et al. 1999, p. 38.
- ^ Hemmleb et al. 1999, pp. 36 & 195.
- ^ «Index of Daily North Side Dispatches». MountainZone. U.S.: Locality LLC. Archived from the original on 13 April 2023. Retrieved 13 April 2023.
- ^ a b c d Hemmleb et al. 1999, p. 195.
- ^ a b c d e f Beckwith 2000, p. 375.
- ^ Hemmleb et al. 1999, pp. 21–28, 40, & 195.
- ^ Simonson, Eric (8 May 1999). «Daily Dispatches Giving Thanks and Looking Ahead». MountainZone. U.S.: Locality LLC. Archived from the original on 13 April 2023. Retrieved 13 April 2023.
- ^ «The Mystery of George Mallory». Hartford Courant. Chicago, Illinois, U.S.: Tribune Publishing. 2 September 2021 [18 January 2000]. Archived from the original on 14 April 2023. Retrieved 14 April 2023.
- ^ Hemmleb et al. 1999, p. 111.
- ^ a b Hemmleb et al. 1999, p. 112.
- ^ a b Anker & Roberts 1999, p. 31.
- ^ Hemmleb et al. 1999, pp. 113–116 & 196–197.
- ^ Hemmleb et al. 1999, p. 116.
- ^ Hemmleb et al. 1999, pp. 119–197.
- ^ Hemmleb & Simonson 2002, p. 180.
- ^ Anker, Conrad (3 May 1999). «Daily Dispatches A Patch of White». MountainZone. U.S.: Locality LLC. Archived from the original on 16 April 2023. Retrieved 16 April 2023.
- ^ Hemmleb et al. 1999, pp. 120–122.
- ^ a b Anker & Roberts 1999, p. 34.
- ^ «Mallory’s Son Says Everest Mystery Still Unsolved». Chicago Tribune. Chicago, Illinois, U.S.: Tribune Publishing. 3 May 1999. Archived from the original on 19 April 2021. Retrieved 17 April 2023.
- ^ a b c Hemmleb et al. 1999, p. 121.
- ^ a b c Firstbrook 2000, p. 233.
- ^ Firstbrook 2000, pp. 232–233.
- ^ «Lost on Everest: Questions and Responses». pbs.org. Arlington, Virginia, U.S.: PBS. 11 May 1999. Archived from the original on 17 April 2023. Retrieved 17 April 2023.
- ^ a b c d e f g Hemmleb et al. 1999, p. 125.
- ^ a b Anker & Roberts 1999, p. 22.
- ^ a b c d Anker & Roberts 1999, p. 21.
- ^ Anker & Roberts 1999, pp. 21–22.
- ^ Hemmleb et al. 1999, pp. 118 & 121–123.
- ^ Hemmleb et al. 1999, pp. 121–123.
- ^ Hemmleb et al. 1999, p. 123.
- ^ Hemmleb et al. 1999, p. 122.
- ^ a b Hemmleb et al. 1999, pp. 108 & 122.
- ^ Hemmleb et al. 1999, pp. 122–123.
- ^ Hemmleb et al. 1999, pp. 123–125.
- ^ Anker & Roberts 1999, p. 34–35.
- ^ a b Hemmleb et al. 1999, p. 124.
- ^ History.com (25 May 2022) [24 November 2009]. «Edmund Hillary and Tenzing Norgay reach Everest summit». history.com. New York City, U.S.: A&E Television Networks. Archived from the original on 7 October 2022. Retrieved 20 April 2023.
- ^ Holzel & Salkeld 1999, p. 320.
- ^ Holzel, Tom (28 August 2010). «A127 Film: Care & Developing Suggestions (Letter from Kodak Laboratories to Tom Holzel, 9 May 1984)». velocitypress.com. Archived from the original on 17 July 2011. Retrieved 30 April 2023.
- ^ a b Firstbrook 2000, p. 260.
- ^ Kohsiek, Wim (10 January 2013). «Mallory’s altimeter revisited». everest1924.com. Archived from the original on 22 April 2023. Retrieved 22 April 2023.
- ^ Hemmleb et al. 1999, pp. 125–126.
- ^ a b Hemmleb et al. 1999, p. 126.
- ^ a b c d e Dunn, Tom Newton (8 August 1999). «Is this picture the proof that George Mallory conquered Everest first». Sunday Mirror. London, U.K: MGN Ltd. Archived from the original on 3 May 2023. Retrieved 3 May 2023.
- ^ a b Gillman & Gillman 2000, pp. 270–272.
- ^ Hemmleb et al. 1999, pp. 125–129 & 161–163.
- ^ Hemmleb et al. 1999, pp. 126–129.
- ^ Hemmleb et al. 1999, pp. 121 & 126–128.
- ^ a b Anker & Roberts 1999, p. 36.
- ^ a b Anker & Roberts 1999, p. 37.
- ^ Hemmleb et al. 1999, pp. 123 & 128.
- ^ a b c d e Hemmleb et al. 1999, p. 161.
- ^ a b c d Anker & Roberts 1999, p. 139.
- ^ Boettcher, David. «George Mallory’s Wristwatch: A Borgel on Mount Everest». Vintage Watchstraps. Archived from the original on 24 April 2023. Retrieved 24 April 2023.
- ^ Hemmleb et al. 1999, pp. 161–162 & 188 notes of chapter 8, no. 2.
- ^ Poston, Pete (26 March 2012). «Mallory’s Watch — does it really point to 12:50 PM?». everest1924.com. Archived from the original on 24 April 2023. Retrieved 24 April 2023.
- ^ Anker & Roberts 1999, p. 140.
- ^ Hemmleb et al. 1999, p. 27.
- ^ Hill, Craig (20 May 2016). «Adventurer of the Week: Mountaineer Eric Simonson». The News Tribune. Sacramento, California, U.S.: McClatchy. Archived from the original on 25 April 2023. Retrieved 25 April 2023.
- ^ Hemmleb et al. 1999, pp. 196–197, Appendix II, Mallory and Irvine Research Expedition Statistics, Diary of Events.
- ^ Hemmleb et al. 1999, pp. 142–146 & 197, Appendix II, Mallory and Irvine Research Expedition Statistics, Diary of Events.
- ^ Hemmleb et al. 1999, pp. 144–145 & 153–154.
- ^ Hemmleb et al. 1999, pp. 153–154.
- ^ a b c d Hemmleb, Jochen. «What happened to Mallory & Irvine? A Synopsis». jochenhemmleb.com. Archived from the original on 26 March 2023. Retrieved 25 April 2023.
- ^ Hemmleb et al. 1999, pp. 162–163.
- ^ «Stella Gabrielle Cobden-Sanderson (1886–1979)». ancestry.co.uk. Dublin, Ireland: Ancestry Ireland Unlimited Company. Archived from the original on 3 May 2023. Retrieved 3 May 2023.
- ^ Gentleman, Amelia (4 May 1999). «Irvine and Mallory: In hobnail boots they took on Everest». The Guardian. London, UK: Guardian News & Media. Archived from the original on 12 August 2022. Retrieved 12 August 2022.
- ^ Hemmleb & Simonson 2002, p. 195, Appendix II, 2001 Mallory and Irvine Research Expedition Statistics.
- ^ «The 2001 Mallory & Irvine Research Expedition». K2News.com. Ohio, U.S.: K2News.com. Archived from the original on 28 April 2023. Retrieved 28 April 2023.
- ^ «2001 Mallory & Irvine Research Expedition». mountainguides.com. Ashford, Washington, U.S.: International Mountain Guides, LLC. Archived from the original on 20 April 2021. Retrieved 11 September 2022.
- ^ Hemmleb & Simonson 2002, pp. 108–109, 111, 113, & 180.
- ^ Hemmleb, Jochen (29 April 2001). «2001 Mallory & Irvine Research Expedition: 1924 Camp 6 found!». mountainguides.com. Ashford, Washington, U.S.: International Mountain Guides, LLC. Archived from the original on 10 September 2022. Retrieved 30 April 2023.
- ^ Hemmleb & Simonson 2002, pp. 135–136 & 180.
- ^ «Mallory and Irvine The Final Chapter: Dispatches». EverestNews.com. Ohio, U.S.: EverestNews.com. Archived from the original on 7 September 2022. Retrieved 10 September 2022.
- ^ Norton, Jake (April 2023). «Mallory & Irvine Everest Searches, 1999-2019». jakenorton.com. Archived from the original on 30 April 2023. Retrieved 30 April 2023.
- ^ a b c Roberts, David (8 December 2010). «Conrad Anker on Everest: In the Footsteps of Mallory & Irvine». National Geographic. Washington, D.C., U.S.: NG Media. Archived from the original on 18 August 2022. Retrieved 18 August 2022.
- ^ a b c d Hemmleb & Simonson 2002, p. 123.
- ^ «Chinese Ladder Retires». crienglish.com. Beijing, China: China Radio International. 28 May 2008. Archived from the original on 23 November 2019. Retrieved 5 May 2023.
- ^ a b c d Keenlyside 1961, p. 33.
- ^ Salkeld 2003, p. 59.
- ^ «Free-climbing Everest’s Second Step update: Before Fritsche was Òscar Cadiach – the other «Mallory». MountEverest.net. Manhattan, New York City, U.S.: ExplorersWeb. 7 June 2007. Archived from the original on 14 March 2009. Retrieved 5 May 2023.
- ^ Cadiach, Òscar. «Luces y sombras del Everest» [Everest lights and shadows]. sge.org (in Spanish). Madrid, Spain: Sociedad Geográfica Española. Archived from the original on 5 May 2023. Retrieved 5 May 2023.
- ^ a b Anker & Roberts 1999, pp. 152–153.
- ^ a b Beckwith 2000, pp. 376–379.
- ^ Hemmleb 2006, pp. 468–469.
- ^ «ExWeb Special: Anker’s Everest team free-climbing the Second Step in the footprints of Mallory … Oscar Cadiach and Theo Fritsche». MountEverest.net. Manhattan, New York City, U.S.: ExplorersWeb. 7 June 2007. Archived from the original on 19 October 2007. Retrieved 7 May 2023.
- ^ «K2 West face climber Nickolay Totmjanin: «I free climbed the Everest second step to avoid the crowd». MountEverest.net. Manhattan, New York City, U.S.: ExplorersWeb. 22 June 2007. Archived from the original on 25 August 2009. Retrieved 5 May 2023.
- ^ Sharma, Gopal (14 June 2007). «Climbers staging Mallory Everest bid get cold feet». Reuters. Toronto, Ontario, Canada: Thomson Reuters. Archived from the original on 14 August 2022. Retrieved 14 August 2022.
- ^ a b Mustain, Andrea (10 August 2010). «Mysterious 1924 Everest deaths linked to storm». NBC News. New York City, U.S.: NBCUniversal Media, LLC. Archived from the original on 10 September 2022. Retrieved 10 September 2022.
- ^ a b Rincon, Paul (3 August 2010). «Everest pioneers ‘hit by storm’«. BBC News Online. London, UK: BBC. Archived from the original on 12 September 2022. Retrieved 12 September 2022.
- ^ a b Squires, Nick (4 August 2010). «Mallory and Irvine’s Everest death explained». The Telegraph. London, UK. Archived from the original on 17 September 2022. Retrieved 17 September 2022.
- ^ a b c d Moore, Semple & Sikka 2010, p. 215.
- ^ Moore, Semple & Sikka 2010, p. 216.
- ^ a b c d Moore, Semple & Sikka 2010, p. 217.
- ^ Norton 1925, p. 128.
- ^ a b c d e Moore, Semple & Sikka 2010, p. 218.
- ^ Firstbrook 2000, pp. 22–23.
- ^ Weber 2003, p. 343, chpt. Geoffrey Winthrop Young from On High Hills.
- ^ Young 1927, p. 218.
- ^ «Lost on Everest: Voices from the Past». pbs.org. Arlington, Virginia, U.S.: PBS. Archived from the original on 18 August 2022. Retrieved 18 August 2022.
- ^ Cairns, Lois (29 August 2010). «Mallory mystery no worry for Hillary». Stuff. Wellington, New Zealand: Stuff Limited. Archived from the original on 13 August 2022. Retrieved 13 August 2022.
- ^ Messner 2001, pp. 166–169.
- ^ Conrad Anker on George Mallory (Part 5). New Delhi, India: Wilderness Films India Limited. 14 September 2011. 13:38 minutes in. Archived from the original on 30 August 2022. Retrieved 30 August 2022 – via YouTube.
- ^ Graves 1998, p. 35.
- ^ Foster, Richard (2 March 2021). «The Great British Art Tour: mystery of an old boy with a head for heights». The Guardian. London, UK: Guardian News & Media. Archived from the original on 15 December 2022. Retrieved 15 December 2022.
- ^ Rushton 2017–2018, pp. 60–61.
- ^ Robertson 1999, p. 252.
- ^ Roach, John Peter Charles, ed. (1959). «The colleges and halls: Magdalene,» in A History of the County of Cambridge and the Isle of Ely: Volume 3, the City and University of Cambridge». British History Online. London, UK: Victoria County History. pp. 450–456. Archived from the original on 10 December 2022. Retrieved 10 December 2022.
- ^ Rushton 2017–2018, p. 34.
- ^ Rushton 2017–2018, p. 61.
- ^ Bogdan, Robert (2011). «Charterhouse The Heritage Tour» (PDF). resources.finalsite.net. Archived (PDF) from the original on 15 December 2022. Retrieved 15 December 2022.
- ^ a b Thornber, Craig. «Mobberley». thornber.net. Cheshire, UK. Archived from the original on 14 December 2022. Retrieved 14 December 2022.
- ^ Gillman & Gillman 2000, pp. 22–25.
- ^ Summers 2001, pp. 260–261.
- ^ «Mount Mallory». Geographic Names Information System. United States Geological Survey, United States Department of the Interior. 19 January 1981. Retrieved 12 September 2022.
- ^ «Mount Irvine». Geographic Names Information System. United States Geological Survey, United States Department of the Interior. 19 January 1981. Retrieved 12 September 2022.
- ^ «OBITUARY: PROFESSOR G.I. FINCH Distinguished scientist and mountaineer». The Times Archive. No. 58031. London, UK. 24 November 1970. p. 14. Retrieved 28 September 2022.
- ^ «Air Chief Marshal Sir Trafford Leigh-Mallory». rafweb.org. Archived from the original on 13 August 2022. Retrieved 13 August 2022.
- ^ «CRASH OF AN AVRO 685 YORK IN LE RIVIER D’ALLEMONT: 10 KILLED». baaa-acro.com. Geneva, Switzerland: The Bureau of Aircraft Accidents Archives (B3A). Archived from the original on 13 September 2022. Retrieved 13 September 2022.
- ^ Randall, Colin (18 October 2004). «Forgotten wartime hero is quietly honoured». The Telegraph. London, UK. Archived from the original on 13 September 2022. Retrieved 13 September 2022.
- ^ Beckey 1948, p. 100.
- ^ «Milestones, Jun. 9, 1947». TIME. New York City. 9 June 1947. Archived from the original on 2 September 2022. Retrieved 2 September 2022.
- ^ Anker & Roberts 1999, pp. 12–15.
- ^ Abrons 1964, pp. 47–51.
- ^ Vajpai & Kumar 2010, p. 110.
- ^ «EverestHistory.com: Everest Summits 1995». EverestHistory.com. Ohio, U.S.: EverestHistory.com. Archived from the original on 15 June 2022. Retrieved 7 September 2022.
- ^ Hutchinson, Pamela (17 October 2013). «The Epic of Everest – London film festival review». The Guardian. London, UK: Guardian News & Media. Archived from the original on 16 August 2022. Retrieved 16 August 2022.
- ^ Goldberg, Max (2014). «The Epic of Everest». silentfilm.org. San Francisco, California, U.S.: San Francisco Silent Film Festival. Archived from the original on 16 August 2022. Retrieved 14 September 2022.
- ^ Lowe, George (director) (1953). The Conquest of Everest (Motion picture). Countryman Films & Group 3 Films. Retrieved 13 September 2022 – via Internet Archive.
- ^ «Q&A with Riley Morton Producer of Found On Everest: Detectives on the Roof of the World». k2news.com. Ohio, U.S.: EverestNews.com. Archived from the original on 13 September 2022. Retrieved 13 September 2022.
- ^ «A clip from Found on Everest on Riley Morton’s web site which includes a shot of George Mallory». Rileymorton.com. Archived from the original on 14 September 2012. Retrieved 3 October 2011.
- ^ Blessed, Brian (3 May 1997). «The biggest avalanche in Everest history just missed my feet». The Independent. London, UK: Independent Digital News & Media Limited. Archived from the original on 9 September 2022. Retrieved 10 September 2022.
- ^ Honeycutt, Kirk (14 October 2010). «The Wildest Dream — Film Review». The Hollywood Reporter. California, U.S.: PMRC Holdings, LLC. Archived from the original on 11 September 2022. Retrieved 11 September 2022.
- ^ Lewis, Matt (22 October 2013). «Benedict Cumberbatch front-runner to play George Mallory in Hollywood film, Everest». The Telegraph. London, UK. Archived from the original on 13 September 2022. Retrieved 13 September 2022.
- ^ Fear, David (6 June 2014). «No ‘Tomorrow’: Doug Liman on the Blockbuster That Almost Broke Him». Rolling Stone. Los Angeles, California, U.S.: Penske Media Corporation. Archived from the original on 14 August 2022. Retrieved 14 August 2022.
- ^ Showbiz, Bang (17 June 2021). «Ewan McGregor, Sam Heughan and Mark Strong to star in Everest». Contactmusic. Leeds, UK: Contactmusic.com Ltd. Archived from the original on 5 September 2022. Retrieved 6 September 2022.
- ^ West, Michael (9 April 2015). «Michael Sheen to Play George Mallory in Everest Movie ‘In High Places’«. Contactmusic. Leeds, UK: Contactmusic.com Ltd. Archived from the original on 14 August 2022. Retrieved 14 August 2022.
- ^ «Feature Film & Television Projects». James McEachen. Archived from the original on 9 May 2023. Retrieved 9 May 2023.
- ^ a b c Wilson, James (28 September 2009). «Exhibition tells the story of two Everest explorers». Northwich & Winsford Guardian. London, UK: Newsquest Media Group. Archived from the original on 11 May 2023. Retrieved 11 May 2023.
- ^ Summers 2001, p. 15.
- ^ «Northwich Salt Museum looks back to the future». Northwich & Winsford Guardian. London, UK: Newsquest Media Group. 20 May 2010. Archived from the original on 11 May 2023. Retrieved 11 May 2023.
- ^ Gillman & Gillman 2000, pp. 221–223.
- ^ Pack, Mark (24 April 2020). «One of the greatest political speeches, mixing the visionary and the pragmatic». markpack.org.uk. London, UK: Mark Pack. Archived from the original on 10 May 2023. Retrieved 10 May 2023.
- ^ Girls in Hawaii (Lionel Vancauwenberghe, Antoine Wielemans) (11 April 2019). Mallory’s Height (Album, Everest). Braine-le-Comte, Belgium: 62TV / GOLDO (published 2 September 2013). 3:35 minutes in. Archived from the original on 21 September 2022. Retrieved 22 September 2022 – via YouTube.
His body appears to be mummified. There’s rope around his waist … Oh, still some socks. Can see a boot …
— Dave Hahn, 1 May 1999.
Bibliography[edit]
Books[edit]
- Anker, Conrad; Roberts, David (1999). The Lost Explorer: Finding Mallory on Mount Everest. New York City, U.S.: Simon & Schuster. ISBN 978-0-684-87151-6.
- Birkett, Thomas William (1989). Classic Rock Climbs in the Lake District. Oxford, UK: Oxford Illustrated Press. ISBN 978-0-946609-56-7.
- Birkett, Thomas William; Cram, Geoff; Eilbeck, Chris; Roper, Ian (1987). Rock Climbing in the Lake District: An Illustrated Guide to Selected Climbs in the Lake District (3rd ed.). London, UK: Constable. ISBN 978-0-09-467640-4.
- Bruce, Charles Granville (1923). The Assault on Mount Everest: 1922. Introduction by Sir Francis Younghusband; Contributions from G.H. Leigh-Mallory, G.I. Finch, T.H. Somervell, and T. G. Longstaff. New York City, U.S.: Longmans, Green & Co.
- Cook, Theodore Andrea (1919). Henley Races: With Details of Regattas from 1903 to 1914 Inclusive and a Complete Index of Competitors and Crews Since 1839. Oxford, UK: Oxford University Press; Humphrey Milford.
- Cram, Alan Geoffrey, ed. (1986). 100 Years of Rock Climbing in the Lake District. Vol. 24 (2) #70. UK: The Fell And Rock Climbing Club of the English Lake District. ISBN 978-0-85028-023-4.
- Crocket, Ken (1986). Ben Nevis: Britain’s Highest Mountain. Edinburgh, UK: Scottish Mountaineering Trust. ISBN 978-0-907521-16-7.
- Davis, Wade (2011). Into the Silence: The Great War, Mallory, and the Conquest of Everest. London, UK: The Bodley Head. ISBN 978-1-847-92184-0.
- Murray, William Hutchison (1953). The Story of Everest. Illustrated by Robert Anderson. New York City, U.S.: E.P Dutton & Co. Inc.
- Edmonds, J.E. (Compiled by); Maxwell-Hyslop, R. (Compiled by); Davies, H.R. (Compiled by) (1947). Military Operations France and Belgium, 1918. Volume V: 26th September – 11th November The Advance to Victory. History of the Great War Based on Official Documents by Direction of the Historical Section of the Committee of Imperial Defence. UK: His Majesty’s Stationery Office.
- Firstbrook, Peter (2000). Lost on Everest: The Search for Mallory & Irvine. Oxford, UK: ISIS Publishing Limited. ISBN 978-0-7531-5480-9.
- Foch, Ferdinand (1931). The Memoirs of Marshal Foch. Translated by Mott, Colonel Thomas Bentley. London, UK: William Heinemann Ltd.
- Gillman, Peter; Gillman, Leni (2000). The Wildest Dream: The Biography of George Mallory (1st North American ed.). Seattle, Washington, U.S.: The Mountaineers Books. ISBN 978-0-89886-741-1.
- Graves, Robert (1998). Good-Bye to All That: An Autobiography. Introduction by Paul Fussell (New Revised ed.). New York City, U.S: Anchor Books. ISBN 978-0-385-09330-9.
- Green, Dudley (2005). Because It’s There: The Life of George Mallory. Foreword by John Mallory (George Mallory’s son). Stroud, Gloucestershire, UK: Tempus Publishing Limited. ISBN 978-0-7524-3399-8.
- Hankinson, Alan (1977). The Mountain Men: An Early History of Rock Climbing in North Wales. London, UK: Heinemann Educational Books Limited. ISBN 978-0-435-86002-8.
- Hemmleb, Jochen; Johnson, Larry; Simonson, Eric; Nothdurft, William E. (1999). Fulsaas, Kris (ed.). Ghosts of Everest: The Search for Mallory & Irvine. Foreword by Clare Millikan (George Mallory’s daughter) (1st ed.). Seattle, Washington, U.S.: The Mountaineers Books. ISBN 978-0-89886-699-5.
- Hemmleb, Jochen; Simonson, Eric (2002). Graydon, Don (ed.). Detectives on Everest: The 2001 Mallory and Irvine Research Expedition. Contributions from Dave Hahn, Larry Johnson, Riley Morton, Jake Norton, Brent Okita, Andy Politz, John Race, Tap Richards, and Jason Tanguay (1st ed.). Seattle, Washington, U.S.: The Mountaineers Books. ISBN 978-0-89886-913-2.
- Holroyd, Michael (1995). Lytton Strachey: The New Biography. New York City, U.S: Farrar, Straus and Giroux. ISBN 978-0-374-52465-4.
- Holzel, Tom; Salkeld, Audrey (1999). The Mystery of Mallory and Irvine. Foreword by Eric Simonson (2nd Revised ed.). London, UK: Pimlico. ISBN 978-0-7126-6488-2.
- Howard-Bury, Charles Kenneth (1922). Mount Everest: The Reconnaissance, 1921. Introduction by Sir Francis Younghusband; Contributions from G.H. Leigh-Mallory, A.F.R.Wollaston, J.N. Collie, H.T. Morsehead, E.O. Wheeler, A.M. Heron, and A.R. Hinks. London, UK: Edward Arnold & Co.
- Howett, Kevin (2001). Rock climbing in Scotland (2nd ed.). London, UK: Constable Publishers, an imprint of Constable & Robinson Limited. ISBN 978-0-09-479610-2.
- Jones, David (1993). Rock Climbing in Britain. London, UK: Diamond Books. ISBN 978-0-261-66030-4.
- Hoyland, Graham (2014). Last Hours on Everest: The Gripping Story of Mallory & Irvine’s Fatal Ascent. Glasgow, UK: William Collins, an imprint of HarperCollins. ISBN 978-0-00-745574-4.
- Jones, Iwan Arfon (2003). Moulton, Bob (ed.). Llanberis (5th ed.). UK: The Climbers’ Club. ISBN 978-0-901601-76-6.
- Mackenzie, John Ruaridh Grant; Williams, Noel (2005). Everett, Roger (ed.). Skye: Rock and Ice Climbs. Location: Edinburgh, UK: Scottish Mountaineering Trust. ISBN 978-0-907521-87-7.
- Messner, Reinhold (2001). The Second Death of George Mallory: The Enigma and Spirit of Mount Everest. Translated by Carruthers, Tim (1st U.S. ed.). New York City, U.S.: St. Martin’s Press. ISBN 978-0-312-26806-0.
- Neal, Kelvin (1998). Smith, Ian (ed.). Lliwedd (4th ed.). UK: The Climbers’ Club. ISBN 978-0-901601-61-2.
- Neale, Jonathan (2002). Tigers of the Snow: How One Fateful Climb Made The Sherpas Mountaineering Legends (1st ed.). New York City, U.S: Thomas Dunne Books, an imprint of St. Martin’s Press. ISBN 978-0-312-26623-3.
- Neff, Kelly Joyce (2015). Everest Dream: A Novel of Friendship — George Mallory and Mary Anne O’Malley. North Charleston, SC, U.S.: Createspace Independent Publishing Platform. ISBN 978-1-5152-2103-6. Archived from the original on 5 September 2022. Retrieved 5 September 2022.
- Noel, John Baptist Lucius (1927). Through Tibet to Everest. London, UK: Edward Arnold & Co.
- Norton, Edward Felix (1925). The Fight for Everest: 1924. Introduction by Sir Francis Younghusband; Contributions from C.G. Bruce, J.G. Bruce, N.E. Odell, Bentley Beetham, R.W.G. Hingston, T.H. Somervell, and E.O. Shebbeare. London, UK: Edward Arnold & Co.
- Powell, Anne, ed. (2009). Women in the War Zone: Hospital Service in the First World War. Cheltenham, UK: The History Press. ISBN 978-0-7509-5059-6.
- Rees, Nigel (2006). Brewer’s Famous Quotations: 5000 Quotations and the Stories Behind Them. London, UK: Weidenfeld & Nicolson. ISBN 978-0-304-367993.
- Robertson, David Allan (1999). George Mallory. Foreword by Joe Simpson (1st Paperback ed.). London, UK: Faber and Faber Limited. ISBN 978-0-571-20314-7.
- Romanych, Marc; Heuer, Greg (2017). Railway Guns of World War I. New Vanguard. Illustrated by Steve Noon (1st Paperback ed.). Oxford, UK: Osprey Publishing, an imprint of Bloomsbury Publishing Plc. ISBN 978-1-4728-1639-9. Archived from the original on 24 October 2022. Retrieved 24 October 2022.
- Ruttledge, Hugh (1934). Everest 1933. Foreword by Sir Francis Younghusband; Contributions from Dr C.R. Greene, E.O. Shebbeare, J.L. Longland, L.R. Wager, Dr S.N. Sen, and N.P. Chatterjee. London, UK: Hodder & Stoughton.
- Salkeld, Audrey (1991). People in High Places: Approaches to Tibet. London, UK: Jonathan Cape. ISBN 978-0-224-02883-7.
- Salkeld, Audrey (2003). Climbing Everest: Tales of Triumph and Tragedy on the World’s Highest Mountain. Washington D.C., U.S.: National Geographic Society. ISBN 978-0-7922-5105-7.
- Smythe, Tony (2013). My Father, Frank: Unresting Spirit of Everest. Foreword by Doug Scott (1st ed.). Sheffield, UK: Bâton Wicks Publications. ISBN 978-1-898573-87-6. Archived from the original on 31 March 2023. Retrieved 31 March 2023.
- Somervell, Theodore Howard (1947). After Everest: The Experiences of a Mountaineer and Medical Missionary. Foreword by Sir Francis Younghusband (4th ed.). London, UK: Hodder & Stoughton.
- Summers, Julie (2001). Fearless on Everest: The Quest for Sandy Irvine. Seattle, Washington, U.S.: The Mountaineers Books. ISBN 978-0-89886-796-1.
- Thompson, Simon (2012). Unjustifiable Risk?: The Story of British Climbing (1st Paperback ed.). Cumbria, UK: Cicerone Press Limited. ISBN 978-1-85284-679-4.
- Thomson, James Merriman Archer; Andrews, Arthur Westlake (1909). The Climbs on Lliwedd. London, UK: Edward Arnold.
- Unsworth, Walt (1991). Everest: The Ultimate Book of the Ultimate Mountain (2nd ed.). London, UK: GraftonBooks. ISBN 978-0-586-20626-3.
- Vajpai, Arjun; Kumar, Anu (2010). On Top of the World: My Everest Adventure. New Delhi, India: Penguin Books, India. ISBN 978-0-143-33172-8. Archived from the original on 13 December 2022. Retrieved 13 December 2022.
- Walsh, Maurice (2016). Bitter Freedom: Ireland in a Revolutionary World 1918-1923. London, UK: Faber and Faber Limited. ISBN 978-0-571-24301-3.
- Weber, Alan, ed. (2003). Because It’s There: A Celebration of Mountaineering from 200 B.C. to Today. Translated by Weber, Alan. Lanham, Maryland, U.S.: Taylor Trade Publishing. ISBN 978-0-87833-303-5.
- Williams, Paul (1990). Rock Climbing in Snowdonia. London, UK: Constable and Company Limited. ISBN 978-0-09-468410-2.
- Young, Geoffrey Winthrop (1927). On High Hills: Memories of the Alps (2nd ed.). London, UK: Methuen & Co. Limited.
Journals[edit]
- Abrons, Henry L. (1964). Carter, H. Adams (ed.). «A New Route on The Wickersham Wall (Mount McKinley, North Face Direct)». The American Alpine Journal. New York City, U.S.: American Alpine Club. 14 #1 (38): 47–51. Retrieved 17 December 2022.
- Beckey, Fred (April 1948). Bates, Robert H.; Robertson, David Allan (eds.). «Appalachian Mountains». The American Alpine Journal. New York City, U.S.: American Alpine Club. 7 #1 (21): 100. Retrieved 19 December 2022.
- Beckwith, Christian, ed. (2000). «Climbs And Expeditions: Tibet». The American Alpine Journal. Golden, Colorado, U.S.: American Alpine Club. 42 (74): 375–379. ISBN 978-0-930410-87-2. Retrieved 11 April 2023.
- Bicknell, Peter (1975). Pyatt, Edward (ed.). «In Memoriam (Leslie Garnet Shadbolt 1883–1973)» (PDF). The Alpine Journal. 80 (1975 #324): 294–304. Archived from the original on 26 December 2022. Retrieved 26 December 2022.
- Brockbank, Philip (2011). Prepared for publication in 2011 by Mike Dent, Roger Booth, and John Payne. «The Beginning: 1902–1918» (PDF). A Short History of The Rucksack Club 1902–1939. Manchester, UK: The Rucksack Club: 3–22. Archived from the original on 15 January 2023. Retrieved 15 January 2023.
- Carter, H. Adams, ed. (1980). «Climbs And Expeditions» (PDF). The American Alpine Journal. New York City, U.S.: American Alpine Club. 22 #2 (53): 657–658. ISBN 978-0-930410-76-6. Archived (PDF) from the original on 11 April 2023. Retrieved 11 April 2023.
- Croston, Roger (1 October 2000). Douglas, Ed (ed.). «The Letter: A newly-discovered letter written by George Leigh Mallory» (PDF). The Alpine Journal. Glasgow, UK: Ernest Press. 105 #349 (2000): 157–176. ISBN 978-0-948153-62-4. Archived (PDF) from the original on 3 November 2022. Retrieved 3 November 2022.
- Elliott, Claude; Russell, Robert Scott (1974). Pyatt, Edward (ed.). «In Memoriam (H.E.L. Porter 1886–1973)» (PDF). The Alpine Journal. London, UK: Alpine Club (UK). 79 #323 (1974): 279–286. ISBN 978-0-900523-11-3. Archived (PDF) from the original on 8 February 2023. Retrieved 8 February 2023.
- Finch, George Ingle (1965). Cox, Anthony David Machell (ed.). «In Memoriam (Thomas Guy Burton Forster Smith-Barry 1886–1962)» (PDF). The Alpine Journal. London, UK: Alpine Club (UK). 70 #310 & 311 (1965): 359–381. Archived (PDF) from the original on 17 July 2020. Retrieved 11 February 2023.
- Fraser, Duncan Cumming (November 1926). «Obituary. Mr. Ralph Todhunter». Journal of the Institute of Actuaries. Cambridge, UK: Cambridge University Press. 57 #3 (291): 338–347. JSTOR 41137170. Retrieved 16 January 2023.
- Gillman, Peter (10 September 2011). Goodwin, Stephen (ed.). «Mallory on The Ben». The Alpine Journal. London, UK: Alpine Club (UK). 115 #359 (2010–2011): 199–205. ISBN 978-0-9569309-0-3. Retrieved 20 December 2022.
- Hemmleb, Jochen (2006). Cordes, Kelly (ed.). «Climbs And Expeditions: Tibet». The American Alpine Journal. Seattle, Washington, U.S.: The Mountaineers Books. 48 (80): 468–469. ISBN 978-1-933056-01-2. Retrieved 7 May 2023.
- Heron, Alexander Macmillan (June 1922). «Geological Results of the Mount Everest Expedition, 1921». The Geographical Journal. London, UK: The Royal Geographical Society. 59 #6 (1922): 418–431. JSTOR 1780634. Retrieved 18 February 2023.
- Hinks, Arthur Robert, ed. (December 1924). «Memorial Service at St. Paul’s Cathedral». The Geographical Journal. London, UK: The Royal Geographical Society. 64 (6): 462–465. JSTOR 1781920. Retrieved 9 December 2022.
- Irving, Robert Lock Graham (1911). Yeld, George (ed.). «The Alpine Journal: February 1910 to November 1911». The Alpine Journal. London, UK: Longmans, Green & Co. 25 #187–194 (1910–1911). Retrieved 31 January 2023.
- Irving, Robert Lock Graham (1912). Yeld, George (ed.). «The Alpine Journal: February 1912 to November 1912». The Alpine Journal. London, UK: Longmans, Green & Co. 26 #195–198 (1912). Retrieved 31 January 2023.
- Irving, Robert Lock Graham (November 1948). «In Memoriam Harry Edmund Guise Tyndale (1888–1948)» (PDF). The Alpine Journal. London, UK: Alpine Club (UK). 56 #277 (1948): 386–402. Archived (PDF) from the original on 20 July 2020. Retrieved 25 January 2023.
- Keenlyside, Francis Hugh, ed. (1961). «The Conquest of Everest by the Chinese Mountaineering Team» (PDF). The Alpine Journal. London, UK: Alpine Club (UK). 66 # 302 & 303 (1961): 28–41. Archived (PDF) from the original on 6 May 2023. Retrieved 6 May 2023.
- Mallory, George Herbert Leigh (1912). Yeld, George (ed.). «The Alpine Journal: February 1912 to November 1912». The Alpine Journal. London, UK: Longmans, Green & Co. 26 #195–198 (1912). Retrieved 6 February 2023.
- Mallory, George Herbert Leigh (September 1918). Yeld, George (ed.). «Mont Blanc from the Col du Géant by the Eastern Buttress of Mont Maudit». The Alpine Journal. London, UK: Longmans, Green & Co. 32 #218 (1918): 148–162. Retrieved 3 February 2023.
- Mallory, George Herbert Leigh; Porter, Harold Edward Lionel (March 1920). Yeld, George; Farrar, John Percy (eds.). «New Expeditions In 1919» (PDF). The Alpine Journal. London, UK: Longmans, Green & Co. 33 #220 (1920): 129–134. Archived (PDF) from the original on 8 February 2023. Retrieved 8 February 2023.
- Mallory, George Herbert Leigh (February 1922). «Mount Everest: The Reconnaissance» . The Geographical Journal. 59 (2): 100–09. doi:10.2307/1781387. JSTOR 1781387.
- Mallory, George Herbert Leigh (December 1922). «The First High Climb» . The Geographical Journal. 60 (6): 400–12. doi:10.2307/1781077. JSTOR 1781077.
- Mondini, Felice (1902). «Il versante Italiano del Monte Bianco: 1. Storia alpinistica» [The Italian side of Mont Blanc: 1. Mountaineering history] (PDF). Bollettino Del Club Alpino Italiano (in Italian). Turin, Italy: Club Alpino Italiano. 35 #68 (1902): 171–222. Archived from the original on 2 February 2023. Retrieved 2 February 2023.
- Moore, George William Kent; Semple, John; Sikka, Dev (2 August 2010). Graham, Eddy; Lee, Simon (eds.). «Mallory and Irvine on Mount Everest: Did extreme weather play a role in their disappearance?». Weather Journal: (Royal Meteorological Society). Hoboken, New Jersey, U.S.: John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 65 (8): 215–218. doi:10.1002/wea.590. Archived (PDF) from the original on 9 September 2022. Retrieved 9 September 2022.
- Morshead, Henry Treise (September 1923). «MOUNT EVEREST: By MAJOR H.T. MORSHEAD, D.S.O., R.E.» The Royal Engineers Journal. Chatham, UK: The Institution of Royal Engineers. 37 #3 (1923): 353–368. Retrieved 18 February 2023.
- Norton, Edward Felix (August 1924). Contributions from George Herbert Leigh-Mallory, Howard Somervell, and Noel Odell. «The Mount Everest Dispatches». The Geographical Journal. London, UK: The Royal Geographical Society. 64 #2 (1924): 145–165. JSTOR 1780694. Retrieved 21 March 2023.
- Odell, Noel Ewart (December 1924). «The Last Climb of Mallory and Irvine». The Geographical Journal. London, UK: The Royal Geographical Society. 64 #6 (1924): 455–461. JSTOR 1781919. Retrieved 16 September 2022.
- Odell, Noel Ewart (November 1934). Strutt, Edward Lisle (ed.). «Correspondence: The Ice Axe Found on Everest» (PDF). The Alpine Journal. London, UK: Alpine Club (UK). 46 #249 (1934): 442–452. Archived (PDF) from the original on 30 March 2023. Retrieved 30 March 2023.
- Puttrell, James William (1900). Gray, Thomas (ed.). «The Keswicks Brothers’ Climb, Scafell» (PDF). The Yorkshire Ramblers’ Club Journal. Leeds, UK: Yorkshire Ramblers’ Club. 1 #2 (1900): 102–106. Archived from the original on 31 December 2022. Retrieved 31 December 2022.
- Pye, David Randall (1919). Goggs, Frank Sidney (ed.). «A Fortnite In Skye» (PDF). The Scottish Mountaineering Club Journal. Scotland, UK: Scottish Mountaineering Club. 15 #87–88 (1919): 132–149. Archived (PDF) from the original on 27 December 2022. Retrieved 27 December 2022.
- Reid, Stephen (2006). Elliott, Doug; Holden, John (eds.). «Mallory’s Route or North-West by West» (PDF). The Fell and Rock Centenary Journal 2006. UK: The Fell And Rock Climbing Club of the English Lake District. 27 (3) #80 (2006): 678–687. ISBN 978-0-85028-047-0. Archived from the original on 4 January 2023. Retrieved 4 January 2023.
- Robertson, David Allan (1959). Farquhar, Francis Peloubet (ed.). «In Memoriam: Geoffrey Winthrop Young 1876–1958». The American Alpine Journal. New York City, U.S.: American Alpine Club. 11 #2 (33): 278–282. Retrieved 21 January 2023.
- Russell, Chris A. (1 July 1989). Sondheimer, Ernst (ed.). «One Hundred Years Ago» (PDF). The Alpine Journal. London, UK: Frederick Muller, an imprint of Century Hutchinson Limited. 93 #337 (1988–1989): 207–212. ISBN 978-0-09-173659-0. Archived (PDF) from the original on 31 December 2022. Retrieved 31 December 2022.
- Russell, Chris A. (19 September 1991). Sondheimer, Ernst (ed.). «One Hundred Years Ago». The Alpine Journal. London, UK: Frederick Muller, an imprint of Random Century Group Limited. 96 #340 (1991–1992): 215–222. ISBN 978-0-09-174841-8. Retrieved 30 December 2022.
- Russell, Chris A. (1 September 1999). Douglas, Ed (ed.). «One Hundred Years Ago» (PDF). The Alpine Journal. Glasgow, UK. 104 #348 (1999): 202–209. ISBN 978-0-948153-59-4. Archived (PDF) from the original on 7 January 2023. Retrieved 7 January 2023.
- Russell, Chris A. (2019). Douglas, Ed (ed.). «One Hundred Years Ago» (PDF). The Alpine Journal. Hinckley, UK: Cordee Limited. 123 #367 (2019): 241–243. ISBN 978-0-9569309-8-9. Archived (PDF) from the original on 9 February 2023. Retrieved 9 February 2023.
- West, John Burnard (1 May 2003). Bodine, Sue (ed.). «George I. Finch and his pioneering use of oxygen for climbing at extreme altitudes». Journal of Applied Physiology. Rockville, Maryland. U.S.: American Physiological Society. 94 (5): 1702–1713. doi:10.1152/japplphysiol.00950.2002. PMID 12679344. Archived (PDF) from the original on 7 November 2022. Retrieved 7 November 2022.
- Yeld, George, ed. (1912). «The Alpine Journal: February 1912 to November 1912». The Alpine Journal. London, UK: Longmans, Green & Co. 26 #195–198 (1912). Retrieved 6 February 2023.
- Young, Geoffrey Winthrop (May 1910). Yeld, George (ed.). «In Memoriam Charles Donald Robertson (1879–1910)» (PDF). The Alpine Journal. London, UK: Longmans, Green & Co. 25 #188 (1910): 138–145. Archived (PDF) from the original on 26 January 2023. Retrieved 26 January 2023.
- Young, Geoffrey Winthrop (November 1912). Yeld, George (ed.). «Alpine Accidents In 1912: The Accident on the Pic du Midi d’Ossau» (PDF). The Alpine Journal. London, UK: Longmans, Green & Co. 26 #198 (1912): 452–458. Archived (PDF) from the original on 5 February 2023. Retrieved 5 February 2023.
Magazines[edit]
- Rushton, Neil, ed. (2017–2018). «Magdalene College Magazine». Magdalene College Magazine. No. 62. Aude Valluy-Fitzsimons (Deputy Editor), Jo Hornsby, and Louise Foster. Cambridge, UK: Alumni Publications, Magdalene College (published 1 October 2018). Archived from the original on 11 December 2022. Retrieved 11 December 2022.
Further reading[edit]
- Archer, Jeffrey (2009). Paths of Glory (1st U.S. ed.). New York City, U.S.: St. Martin’s Press. ISBN 978-0-312-53951-1.
External links[edit]
- Expedition to rewrite Everest history – BBC World News.
- Ghosts of Everest – Outside Magazine.
- Lost on Everest: The Search for Mallory and Irvine – NOVA Online.
- Peter H. Hansen: Mallory, George Herbert Leigh (1886–1924) – Oxford Dictionary of National Biography.
- Interactive Panorama of Everest’s Northeast Ridge! – The MountainWorld™ Blog.
- Mallory and Irvine The Final Chapter: The retrieval of the camera – Everest News.
- Mount Everest 1924 – The John Noel Photographic Collection.
- Replica clothes pass Everest test – BBC News.
- An account of Mallory’s rowing at Magdalene College and a photo taken in 1908 – History, George Mallory.
- Magdalene Boat Club: The First Hundred Years – Magdalene College.
- Tracking truth-in-evidence on Mount Everest: Tom Holzel’s conclusion about Mallory and Irvine’s final climb – MountEverest.net.
- Mike Parsons and Mary B. Rose. Mallory Myths and Mysteries: The Mallory Replica Project – Mallory Myths.
- Mallory and Irvine Memorials – Mount Everest The British Story.
- The George Mallory Award – Wasatch Mountain Film Festival.
- Everest Dream – Kelly Joyce Neff.
- The Epic of Everest at the Internet Archive
- Boswell, the Biographer at the Internet Archive
- George Mallory at Olympedia
- Works by George Mallory at LibriVox (public domain audiobooks)
- Works by George Mallory at Project Gutenberg
- George Herbert Leigh-Mallory on Lives of the First World War
Перенесемся в 1924 год. Немногим ранее Джордж Мэллори произнес свою самую известную сентенцию, свой единственный афоризм. Вращаясь в обществе друзей, которые говорили крылатыми фразами, изрекая их за едой, на прогулках, в поездках, даже в туалетах, Мэллори никогда не был многословен. Но одной своей фразой он заткнул всех этих Стрейчи, Бруков, Кейнсов, всю интеллектуальную элиту. Их красивые слова были и остаются абстракциями, голословием, измышлениями разума, которому больше нечем заняться, кроме как мыслить.
Почему вы хотите забраться на вершину, спросил у Мэллори журналист.
Потому что она существует, ответил великий альпинист.
Эти слова – «Because it’s there» – сегодня называют самыми знаменитыми тремя словами альпинизма. Единственным и важнейшим альпинистским принципом и причиной. Хотя слова там не три, а четыре. Но это не важно.
Журналист, который задал Мэллори этот вопрос, работал в New York Times. Впоследствии его обвиняли в том, что он сам придумал ответ, который приписал англичанину. Журналист отмолчался. Но даже если он и придумал эти слова, они в полной мере отражают характер Мэллори. Скажу даже более. Если фраза «потому что она существует» принадлежит нью-йоркскому щелкоперу, то он гений в своем деле. Такой же, как Мэллори, – в своем.
Но наверх Мэллори шел не один. В его тени остался второй участник экспедиции – юный Эндрю Комин Ирвин по кличке Сэнди. В момент смерти ему было всего двадцать два года. Как вообще этот мальчик оказался в экспедиции, средний возраст участников которой был тридцать пять – тридцать семь лет? Почему именно он пошел с Мэллори наверх, хотя о горе грезили значительно более опытные альпинисты?
Эндрю Комин Ирвин родился в городе Биркенхед, Чешир, и был третьим из шести детей в семье Уильяма Фергюсона Ирвина и Лилиан Дэвис-Колли. Он был очень умен, этот мальчишка. В 1916 году он отправил в штаб армии чертежи собственноручно разработанного пулеметного синхронизатора, отличавшегося от уже существовавших систем Фоккера и Биркигта. Это произвело переполох, потому что мальчик честно написал в сопроводительном письме: мне четырнадцать лет, и я хочу сделать что-нибудь для своей страны. Он любил работать руками. Любая механическая штука, попадавшая к Эндрю, тут же оказывалась разобранной, усовершенствованной и собранной обратно. Он бы стал новым Эдисоном, если бы не гора.
Он был очень силен и ловок, этот молодой человек. В 1919 году он произвел фурор на Хенлейской Королевской регате, вытянув свой экипаж к победе за несколько футов до финиша. И конечно, он поступил в Оксфорд, в Мертон-колледж, чтобы стать инженером. Блестящим инженером, подобным Изамбарду Кингдому Брюнелю, которого считал своим кумиром.
Вернемся в 1829 год. Нет, я не ошибся в столетии. Действительно, я хочу заглянуть в те времена, когда никто и не помышлял о горе.
Чарльз Мэривейл из Кембриджа и Чарльз Уодсворт из Оксфорда поспорили, кто быстрее проплывет по Темзе через городок Хенли-он-Темз. Они собрали команды, и Оксфорд легко выиграл, преодолев заданную дистанцию за четырнадцать минут три секунды. Это была первая из знаменитых регат «Оксфорд – Кембридж», которые ныне устраивают ежегодно при примерно равном счете побед. Кембридж выигрывал восемьдесят один раз, Оксфорд – семьдесят семь. Гонки не проводились во время войн, иногда им мешали иные обстоятельства, но в целом регата стала престижнейшим соревнованием по академической гребле в мире. Ну, по крайней мере, – в Англии.
Когда я покидал страну, было время Кембриджа. Его команда одержала победу в последней предвоенной гонке 1914 года, затем – в первой послевоенной, затем продолжала побеждать вплоть до 1936 года. До этой серии Оксфорд вел на девять побед, после – проигрывал на семь.
Серия прервалась лишь один раз – 24 марта 1923 года, когда Оксфорд вырвал победу у непогрешимых кембриджцев. В составе той команды был Эндрю Комин Ирвин. Они опередили соперников совсем чуть-чуть – на три четверти длины лодки, но победа есть победа.
Все это сухие факты биографии, призванные сформировать образ идеального человека. Ирвин – сильный, умный, красивый – пользовался огромной популярностью у девушек. После того как он пропал без вести, сразу шесть дам заявили о том, что он собирался на них жениться. Возможно, на словах и собирался – Ирвин был горазд на обещания.
Но какое бы блестящее будущее ни ожидало Ирвина, оно так и не наступило. Началом конца стал Оксфордский альпинистский клуб, а человеком, который убил Ирвина, оказался Ноэль Оделл. Оделл, друг и почти ровесник Мэллори, должен был идти в экспедицию двадцать четвертого года в качестве специалиста по дополнительному кислороду. В его обязанности входил контроль емкостей, проверка (и, кстати, разработка) их креплений, инструктаж альпинистов, прежде никогда не работавших с кислородом.
Оделл и Ирвин познакомились в 1919 году. Оделл с супругой поднимались на 977-метровую гору Фоэл Грэч в Уэльсе. Они добрались до вершины – и в этот миг раздался рев мотоцикла. Это наверх – без дороги, прямо по камням – ехал молодой и наглый Ирвин. Он усовершенствовал своего двухколесного коня, сделав его «внедорожным», и хотел испытать машину в боевых условиях.
Впоследствии Оделл работал с Ирвином в оксфордской экспедиции на Шпицберген 1923 года и был поражен силой, ловкостью и выносливостью молодого британца. Кроме того, Оделлу нравился характер Ирвина – спокойный, покладистый, надежный и упрямый. Именно такой, какой нужен в горах. Когда команда уже была сформирована, Мэллори писал своему другу Джеффри Янгу: «Ирвин – это наша попытка заполучить в команду хотя бы одного супермена, даже несмотря на то, что недостаток опыта выступает аргументом против его кандидатуры».
Ирвин был прямой противоположностью остальным альпинистам группы. Они были интеллектуалами, цитировали наизусть Чосера и Шекспира, рассуждали о философии Канта и калокагатии в античном искусстве, Ирвин же прочел в жизни полторы художественные книги и едва ли помнил их названия. Он не умел писать стихи и петь серенады. Зато он мог голыми руками из мотка проволоки, обрывков рубашки и обломков рюкзачной рамы смастерить планер. Он был блестящим практиком, инженером от Бога, и это стало решающим фактором в его пользу. Свой дар Ирвин проявил в самом начале экспедиции, когда придумал новый способ крепления кислородных баллонов, что позволило равномернее распределить нагрузку на мышцы и связки. Ирвин совершенствовал, чинил и видоизменял все, что видел, – экспедиционные примусы, палатки, фотокамеры. Он все делал с прибауткой, весело и легко, чем заслужил любовь и уважение старших коллег.
Но почему Мэллори выбрал именно Ирвина для последнего, самого важного рывка? Ведь у Ирвина вообще не было опыта – раньше он поднимался лишь на две крошечные горы: один раз на Шпицбергене и один раз в Швейцарии! Почему Мэллори не позвал с собой Оделла, значительно более опытного альпиниста? Чаще всего на этот вопрос отвечают так: Мэллори хотел, чтобы рядом с ним был гениальный механик, который способен починить кислородный аппарат, если тот откажет, и придумать решение любой задачи, требующей математического мышления. Например, как вытащить альпиниста из расщелины. Или как перебраться через пропасть. Из своей последней экспедиции Мэллори писал матери: «Ирвин – отличный парень, все схватывает на лету и будет наилучшим из возможных компаньонов при восхождении. Я полагаю, „Биркенхедским новостям“ будет что написать, если мы доберемся до вершины вместе».
Я преодолел нечеловеческую дистанцию. Четыре тысячи триста пятьдесят миль за семнадцать дней – без карт, без официальных разрешений, с минимумом топлива и практически полным отсутствием летных навыков. Меня арестовал не консул, не летный инспектор, а простой констебль – Британия не оставляет своих подданных в покое. Меня ждали на аэродроме и объявили об аресте, как только я выбрался из самолета.
Я не сдался. Я нанял машину и проехал сто восемьдесят шесть миль в сторону непальской границы, откуда попытался связаться непосредственно с Трибхуваном, королем Непала. Я был уверен, что добьюсь этого. Я два с лишним часа уговаривал местных бюрократов выдать мне разрешение на пересечение границы, на полет над территорией Непала, звонил и просил соединить меня с королем – впустую. Я видел непонимающие глаза.
Я вернулся в Лалбалу и там за сущие гроши продал самолет – от него все равно уже не было никакого толку. Я поехал в Дарджилинг, где прожил всю зиму, – это позволило мне немного акклиматизироваться. Там я и познакомился с шерпами – случайно, в местном кабаке, не знаю, как правильно называются такие заведения. Когда я узнал, что за год до меня они поднимались наверх с Ратледжем, я сразу заплатил им аванс как проводникам и носильщикам. Будь я поопытнее, то нашел бы Карма Пола, организатора альпинистских партий и «поставщика» шерпов, незаменимого участника британских экспедиций, – но тогда я ничего о нем не знал.
Границу мы пересекли тайно, переодевшись в буддийских монахов. Весь переход занял десять дней, Теванг хорошо знал дорогу. В пути произошло одно комическое происшествие. Утром после одной из ночевок я выбрался из палатки и увидел местного старика. Он был уверен, что около деревни в палатке тайно ночует путешествующий инкогнито Далай-лама. Я сильно его разочаровал.
А потом мы добрались до Ронгбука.
Попытаемся проанализировать положение мертвого Джорджа Мэллори на горе. Сперва кажется, что, как и Цеванг Палжор, погибший семьюдесятью годами позже, Мэллори обут в зеленые ботинки. Но это заблуждение – зеленоватый оттенок коже придало время и суровые погодные условия. На самом деле ботинки коричневого цвета. На подошвах – самопальные металлические трикони. Никаких множественных слоев, как в современной гималайской обуви, никаких вам Scarpa Phantom 8000 или La Sportiva Olimpus Mons Evo. Просто тяжелые утепленные ботинки со скобами на жесткой подошве. Под ботинками – три слоя шерстяных носков.
Перчатки практически истлели, но можно догадаться, как они выглядели: кожаные, на меховой подкладке. Поверх – шерстяные перчатки без пальцев. Кожа на руках, полупогруженных в гравий, желтая, обтягивающая кости. Рукава куртки сохранились, потому что руки полузасыпаны. Куртка и нижняя одежда сорваны, хорошо видна отбеленная ветрами спина. При этом понятно, что на Мэллори – всего пять слоев одежды, не более. Шерстяное нижнее белье, нижняя шелковая рубашка с этикеткой Junior Army & Navy Stores, фланелевая рубашка в синюю и белую полоску, коричневый шерстяной свитер и хлопковая ветрозащитная куртка зеленой армейской расцветки. Никто из современных альпинистов не дошел бы в подобной амуниции даже до семи тысяч.
Штаны практически целиком истлели и содраны ветром и непогодой. Они охватывают тело только вокруг пояса и под коленями. Кожа ниже ягодиц белая, на голенях она желтеет. На ягодицах и верхней части ног – серьезные повреждения кожного покрова, можно сказать, дыры, хорошо видны кости. Голени немного «проедены», в разрывах кожи также заметны внутренние ткани и кости, и одна из костей правой ноги сломана. Ботинок с левой ноги отсутствует. Судя по всему, перед смертью Мэллори положил правую ногу на левую – в такой позе сломанная кость «сходилась», несколько облегчая боль. Скорее всего, Мэллори сорвался, будучи значительно выше, сломал от удара ногу, а затем съехал по горе, цепляясь руками, сорвав кожу с пальцев.
Голова почти не видна – она уходит в гравий. Мэллори лежит лицом вниз, его руки и лицо вмерзли в смесь льда и камней. Перевернуть его невозможно. Члены экспедиции, нашедшей тело, опознали его по бирке на воротнике куртки. В кармане они обнаружили очки Мэллори.
Потом альпинисты обложили тело камнями и ушли.
Что на самом деле увидели Ричардс, Анкер, Хан и остальные на 8155 метрах? Они увидели мертвого человека в куртке Мэллори. Человека в экипировке двадцатых годов двадцатого века. Очень сильного, стройного человека – его мускулатура сохранилась даже спустя столько лет после смерти. Но был ли это Мэллори? Действительно ли он погиб на спуске? Ответов на эти вопросы не было и нет до сих пор.
В официальном сообщении Симонсон, руководитель поисковой группы 1999 года, безапелляционно заявляет: мы нашли тело Мэллори и осмотрели все окрестности. Других тел не найдено. Мэллори надежно идентифицирован, группа провела погребальную церемонию и похоронила великого альпиниста в камнях.
Но что значит слово «надежно»? Можно ли считать доказательством нашитый на куртке ярлык? Могли ли Мэллори и Ирвин по какой-то причине поменяться куртками? И если тело Мэллори нашли на высоте 8155 метров, то где же Ирвин? Выше? Может, он сорвался в расщелину? Веревка, обвивающая тело Мэллори, перетерта, порвана. Что это значит? Никто не перерезал веревку – ни Ирвин, чтобы отпустить друга, ни Мэллори, чтобы малодушно спасти свою шкуру. Их разделила гора.
Симонсон знал, где искать, по двум причинам. В 1933 году Перси Вин-Харрис, участник четвертой британской экспедиции, нашел на высоте 8460 метров, примерно в 230 метрах от Первой ступени[6], ледоруб Ирвина. Почему именно Ирвина? Дело в том, что все свое оборудование Сэнди помечал тремя параллельными линиями-зарубками, оставляя нечто вроде автографа. Этот вывод исследователи сделали спустя почти сорок лет после трагедии, в 1963 году, изучая личные вещи Ирвина. Оставалась одна загадка – крестообразная зарубка, явно сделанная другим инструментом и в другое время. Но эту загадку разрешил сам Вин-Харрис. Он попросил одного из шерпов, Кусанга Паглу, пометить ледоруб, чтобы не перепутать его с другим оборудованием экспедиции. Пагла вырезал на рукояти крест. Горное снаряжение обычно индивидуализировано, и вряд ли Мэллори поменялся ледорубами со своим напарником. Исходя из местоположения ледоруба, можно было высчитать, как спускались альпинисты (точнее, один из них).
Вторая наводка оказалась более значимой. Член китайской экспедиции 1975 года Ванг Хонг-бао через четыре года участвовал в совместном с японцами восхождении. Он упоминал, что на маршруте китайская группа наткнулась на очень старый труп, причем явно англичанина. Он описал его местоположение так: «Высоко на Северном склоне, в нескольких минутах ходьбы от лагеря». Больше он ничего не сказал – а на следующий день его смело лавиной. В той лавине 12 октября 1979 года погибли трое участников экспедиции – все китайцы.
К слову, их смерть осталась в тени трагедии, случившейся десятью днями ранее, когда погибли американец Рей Дженет и немка Ханнелора Шматц. Она стала первой женщиной, нашедшей свою смерть на горе. Казалось бы – их двое, а китайцев трое. Но китайцев просто смело лавиной – это была мгновенная и относительно безболезненная смерть. Дженет и Шматц умирали долго и страшно – от гипотермии, сидя в палатке и будучи не в силах из нее выбраться. Через некоторое время палатку сдуло ветром, снесло и тело Рея Дженета, останки же Ханнелоры Шматц в течение еще шести лет можно было рассмотреть с маршрута. Она полусидела с открытыми глазами, а ее волосы развевались на ветру. Потом ветер отполировал ее череп, и труп стал бесполым. В 1984-м два альпиниста погибли во время попытки эвакуировать тело, а годом позже англичанин Крис Бонингтон столкнул его вниз, дальше от тропы. Еще позже труп сдуло ветром в ту же расщелину, куда некогда затянуло Рэя Дженета.
Но это было отступление от темы. Главное, что Симонсон и другие участники поисковой группы знали, что тело находится неподалеку от китайского лагеря 1975 года, местоположение которого было известно точно. Это сильно сужало область поисков.
Конрад Анкер, первым нашедший тело Мэллори, ходил зигзагами. Первого мая 1999 года группа покинула лагерь V на высоте 7830 метров, достигла лагеря VI и разделилась, чтобы расширить территорию поисков. Анкер пошел на запад и почти сразу наткнулся на мертвеца в современном снаряжении – тот лежал неподалеку от остатков китайского лагеря. Затем он начал спускаться по пологому склону и на одной из скальных полок увидел другого мертвеца – тоже погибшего недавно. Дойдя до нижней точки западного ребра, Анкер отправился назад – по другой стороне. Он шел зигзагами и, выбравшись на достаточно высокую точку, осмотрелся. На западе что-то белело – и это был не снег. По снаряжению и состоянию мумии было ясно, что тело пролежало тут несколько десятков лет – и Анкер вызвал по рации остальных.
Другие члены экспедиции тоже не дремали. За тот день, обходя зигзагами зону поисков, они нашли несколько десятков мертвецов – почти все погибли относительно недавно, после 1980-го. Остальным участникам экспедиции казалось, что Энди Политц и Конрад Анкер отправились в неверных направлениях, причем Анкер ушел слишком далеко – за него уже начали волноваться.
В том, что найденное Анкером тело лежит с 1924 года, сомнений не было. Одежда и ботинки не могли быть более поздними. Участники экспедиции были уверены: это – Ирвин, и никто иной. Они знали, где нашли ледоруб Ирвина. Если бы тот спускался, то на девяносто пять процентов шел этой самой дорогой. Поэтому, когда кто-то из экспедиции отвернул воротник куртки и увидел метку G. Leigh Mallory, он воскликнул: «Oh my God!» И еще раз, и еще. Потому что трудно было поверить в то, что экспедиция нашла величайшего альпиниста двадцатого столетия. Человека, который три четверти века пролежал здесь, на безумной и безымянной высоте, вмороженный в камень. О Боже, восклицали они, о Боже!
Потом они нашли ряд дополнительных доказательств. Еще несколько нашивок с фамилией Мэллори на свитере и подкладке штанов, разбитый альтиметр, очки, наручные часы (с разбитым стеклом, без стрелок), почти полный коробок спичек Swan Vestas, жестяную коробку с бульонными кубиками, маникюрные ножнички в кожаном чехольчике, карманный нож в ножнах, смятый тюбик с какой-то мазью, карандаш, бумажку со списком необходимого оборудования, шейный платок, один хорошо сохранившийся ботинок и фрагмент второго. Кислородных баллонов не было – видимо, Мэллори использовал весь запас и выбросил тяжелое снаряжение. К слову, один из баллонов – трудно сказать, кому он принадлежал, – обнаружили в мае 1991 года на высоте 8480 метров – выше и ближе к Первой ступени, чем ледоруб.
И еще у Мэллори нашли три письма, которые альпинист хранил у сердца. В этом месте одежда не примерзла к камням, и удалось засунуть руку в нагрудный карман. На всех письмах была фамилия Мэллори в обрамлении почтовых марок.
Первое письмо было от его сестры Виктории. Второе – от его брата Траффорда, будущего главного маршала авиации Великобритании.
И третье письмо – от Рут. Оно не подписано, но почерк – явно женский, и автор письма обращается к Джорджу Мэллори с искренней дружбой и любовью, без сексуального подтекста, но в некотором роде чрезмерно откровенно, нежно. Члены поисковой группы не сомневались, что такое письмо могла написать только Рут Тернер, женщина, чью фотографию Мэллори обещал оставить на вершине в случае успешного восхождения.
Но когда они спустились вниз, и письмо было отправлено на анализ, оказалось, что Рут не имела к этим строкам никакого отношения. У нее был другой почерк.
В последние минуты своей жизни Джордж Мэллори прижимал к сердцу письмо неизвестной женщины.
Эту женщину звали Стелла Габриэлла Кобден-Сандерсон. Она родилась в 1886 году в семье знаменитого барристера, переплетчика и художника Томаса Джеймса Сандерсона, одного из основателей и идеолога «Движения искусств и ремесел», и Анны Кобден, британской социалистки и политической активистки. После замужества родители Стеллы взяли двойные фамилии. Сандерсон был очень эксцентричным человеком. Закрыв в 1916 году свою лондонскую типографию, он выбросил в Темзу все оборудование, в том числе уникальные литеры специально для него разработанного шрифта, восстановить который удалось лишь спустя много лет, уже в компьютерную эпоху. Дед Стеллы по материнской линии, Ричард Кобден, был членом палаты общин и лидером движения фритредеров, боровшихся за невмешательство государства в частное предпринимательство. Анна Кобден сражалась за права женщин, права детей, права, права, права – всю свою жизнь.
Какая девочка могла вырасти в подобной семье? Сильная, волевая, умная и интересная, суфражистка по убеждениям и железная леди по характеру. В Стелле не было ни капли присущей Рут Тернер нежности, Стелла была прямой противоположностью супруги Мэллори и, возможно, той женщиной, которую он искал, но не успел найти.
Они познакомились всего за год до смерти альпиниста, во время его визита в США в 1923 году, как раз когда он произнес свой знаменитый афоризм. В том году брак Джорджа и Рут начал постепенно давать трещину. Их детям было восемь лет, шесть лет и три года соответственно. В семье часто скандалили, но ни один из биографов Мэллори даже не заикается о том, что тот мог уйти из семьи. Скорее всего, они с Рут перевалили бы через этот кризис и продолжали бы жить дальше в мире и согласии. В какой-то мере роковая экспедиция Мэллори стала его реакцией на семейный раскол.
О дружеской переписке между Джорджем Мэллори и Стеллой Кобден-Сандерсон было известно. После смерти альпиниста все письма забрал себе Траффорд Мэллори – и унес их содержание в могилу. Он погиб в авиакатастрофе близ Гренобля 14 ноября 1944-го в возрасте пятидесяти двух лет.
Более загадочно исчезновение всех датированных 1924 годом писем от Рут Тернер к мужу. Письма Джорджа к Рут, которые он писал в начале года из Азии, а затем в каждом лагере на пути к вершине, сохранились, обратные – нет. Их местонахождение до сих пор остается тайной. Тем не менее Рут, несомненно, писала мужу – этому есть устные подтверждения Фрэнсис Клэр, старшей дочери альпиниста. Что такого содержали эти письма, что владелец предпочел их спрятать или уничтожить? Траффорд ли это был или кто-то иной? Еще одна загадка.
До наших дней дошли переплетные и художественные работы Стеллы – она унаследовала способности и интересы отца. Но эти работы никак не связаны с Джорджем Мэллори. Ничего, кроме письма, которое мертвец прижимал к сердцу, не связывает этих двоих.
Вернемся к Джону Келли. Он шел наверх уверенно, точно зная маршрут, иногда сверяясь с пометками, в суть которых он Матильду не посвящал. Идти было непросто, высота чувствовалась сильно, они уже перевалили за 8000 метров. Французы уже, вероятно, разбивали штурмовой лагерь, а Келли все шел в сторону от вершины, не пытаясь подняться выше, чем 8200. Он не собирался брать гору.
Матильда спросила у него: ты точно знаешь, что ищешь? И откуда у тебя информация? Целая поисковая экспедиция пришла сюда, чтобы найти Ирвина, и не нашла. Зато они нашли Мэллори, ответил Келли. И что? Они потратили море времени, тело нашли случайно, а второе вообще может оказаться совершенно в другом месте, может, оно на триста метров выше, ты думал об этом? Нет, ответил Келли, я знаю, где тело.
Погода стояла превосходная. Ветра почти – по меркам высокогорья – не было. Светило яркое солнце. Снег лежал участками, под ногами пересыпались мелкие камни. Кислорода хватало, усталость была, но легкая, естественная. Идеальные условия для поисков.
Они шли медленно, потому что Келли не хотел сбиться с дороги. Потом они разделились. Он что-то нашептал своим шерпам, и один пошел направо, второй – налево. Матильда молчала. Она ждала, что Келли приведет ее куда-то. Между ними был невидимый поводок.
Потом у Келли затрещала рация, и раздался голос шерпа. Келли повернулся к Матильде и сказал: есть. Нашли.
На склоне лежали тяжелые плоские камни, образуя бугор в форме человеческого тела. Могила была свободна от снежного покрова. Никаких надписей рядом не было – просто камни, обозначающие, что здесь лежит человек.
Матильда вспомнила этот вид. Он сильно изменился, но сомнений не было – это было то самое место, которое фигурировало в популярном фильме National Geographic.
Это же могила Мэллори, сказала она. Зачем мы пришли сюда?
Келли обернулся. Нет, покачал он головой. Здесь лежит не Джордж Мэллори. Здесь лежит Сэнди Ирвин.
Но ведь у него были письма Мэллори, и ярлыки на одежде, и личные вещи! – удивилась Матильда.
Да, кивнул Келли. Это я объясню тебе чуть позже.
Без малого сто лет назад альпинисты Сэнди Ирвин и Джордж Мэллори погибли на самом высоком пике планеты. Удалось ли им добраться до его вершины?
«Не надо, – услышал я. –Ты слишком устал. Оно того не стоит».
Джейми Макгиннесс, наш проводник и руководитель экспедиции, сдвинул кислородную маску, снял солнечные очки и теперь смотрел на меня запавшими, налитыми кровью глазами. Подбородок его покрывала многодневная седая щетина, а кожа приобрела землистый оттенок.
Мы сидели на груде камней на высоте 8440 метров на северо-восточном гребне Эвереста, с китайской стороны, вдали от непальских толп. Отмеченная GPS‑маркером точка на сотню метров ниже могла бы разрешить одну из величайших загадок в истории альпинизма. По новым данным, именно там мог погибнуть легендарный британский альпинист Эндрю Ирвин (Ирвайн) по прозвищу Сэнди. Вдруг останки все еще там?
Без малого 100 лет назад, спускаясь по этому гребню, Ирвин и его напарник Джордж Мэллори исчезли. С тех пор весь мир задается
вопросом, добрались ли они до вершины – на 29 лет раньше, чем Эдмунд Хиллари и Тенцинг Норгей, которые были признаны первыми людьми, покорившими Эверест. Предположительно, у Ирвина была с собой камера Kodak Vest Pocket. Если бы она нашлась, а на пленке оказались снимки с вершины, историю высочайшей горы мира пришлось бы переписывать.
На раскрашенной вручную фотографии улыбающийся Ирвин (крайний слева) стоит рядом с Мэллори, который опирается ботинком на Э. О. Шеббира, ответственного за транспорт. Команда крепких, опытных альпинистов в 1924-м предприняла третью за четыре года попытку Великобритании покорить Эверест.
Я осматривал местность. Из покрытых снегом и осыпью уступов торчали гряды невысоких крутых утесов; этот участок, сформированный более светлыми породами, называют Желтым поясом. В четырех тысячах метров ниже, словно мираж, мерцала засушливая равнина – Тибетское плато.
Последние 48 часов я почти не спал, а экстремальная высота вызывала тошноту и слабость. Три дня назад мы покинули Передовой базовый лагерь на отметке 6400 метров, и с тех пор я смог запихнуть в себя лишь несколько ложек сублимированного карри, горсть кешью, да еще укусил шоколадный батончик на вершине Эвереста – позже им меня и стошнило. Я был изможден, а изголодавшийся по кислороду мозг умолял прилечь и закрыть глаза. Но остатки здравого смысла говорили, что, сделав так, можно больше не проснуться.
Сверху с грохотом скатилось несколько камней. Я поднял голову и увидел фотографа Ренана Озтюрка, спускавшегося к нам по склону. Одной рукой он обхватил веревку, закрепленную на склоне; словно пуповина, она соединяла нас с вершиной, покинутой несколько часов назад. Озтюрк съехал, тормозя ногами, и плюхнулся рядом со мной.
Я повернулся к нему: «Что думаешь?».
Ренан ответил не сразу, только грудь его вздымалась и опадала. Когда он наконец отдышался, я услышал приглушенный кислородной маской голос: «Попробуй».
Я кивнул, отстегнулся от веревки и сделал несколько осторожных шагов вниз по каменистому утесу. В тот же момент раздался крик: «Нет-нет-нет!». Кричал Лакпа Шерпа.
Я махнул ему: «Нужно кое-что проверить. Я недалеко». Но он умолял остановиться: «Очень опасно, очень опасно!».
Один неверный шаг по осыпи – и будешь падать 2000 метров до ледника Ронгбук. Я прекрасно понимал это, и меня, конечно, тянуло пойти на попятную. Десятилетия альпинистского опыта во всех уголках света научили главному: я обещал себе никогда не пересекать черту, за которой объективный риск становится слишком высоким. В конце концов, дома меня ждала любимая семья.
Но в этот раз я проигнорировал предостережения проводников и данное себе обещание: загадка исчезновения Ирвина не давала покоя.
В лучах восходящего над Тибетским плато солнца Пасанг Каджи Шерпа (впереди) и Лакпа Тенджи Шерпа преодолевают отметку в 8750 метров на Эвересте. Главный вопрос: добрались ли сюда – а может, и на вершину – Джордж Мэллори и Сэнди Ирвин в 1924 году?
О том, что Мэллори и Ирвин могли быть первыми покорителями Эвереста, я слышал давно.
Но одержимость идеей отыскать Ирвина пришла лишь пару лет назад, после лекции моего друга Тома Полларда, исследователя Эвереста, живущего в нескольких километрах от меня.
«Ты же не думаешь, что его взаправду можно отыскать?», – спросил я Тома после выступления.
Он усмехнулся: «А что, если у меня есть крайне важная информация, неизвестная другим?».
«Например?», – я сразу схватил быка за рога.
Том выдержал паузу в несколько секунд и продолжил: «Например, точное местонахождение тела».
Я обещал себе никогда не переступать черту, за которой объективный риск становится слишком высоким.Но в этот раз я проигнорировал собственное обещание.
…Поллард был оператором поисковой экспедиции «Мэллори и Ирвин» 1999 года, во время которой американский альпинист Конрад Анкер обнаружил останки Джорджа Мэллори на той части северного склона Эвереста, куда мало кто из скалолазов отваживался забраться. Погибший лежал лицом вниз, со всех сторон засыпанный гравием.
Одежда на спине Мэллори была разодрана, а сохранившаяся кожа поражала чистотой и белизной – он напоминал мраморную статую. Обвязанная вокруг пояса веревка оставила отметины на торсе – это могло указывать на резкое и жесткое падение. Правая нога оказалась сломана чуть выше ботинка, левая была сплетена с правой, словно прикрывая ее. Что бы там ни произошло, видимо, после падения какое-то время Мэллори оставался жив.
Анкер и члены его команды подумали было, что это тело Сэнди Ирвина – лежало оно прямо под тем местом на гребне, где через десять лет после пропажи альпинистов нашли ледоруб Ирвина. Был ли на момент падения Мэллори привязан к напарнику? Если да, то каким образом веревка порвалась и почему тела Ирвина нет рядом?
Находки породили еще больше вопросов. Отсвечивающие зеленым очки Мэллори обнаружили у него в нагрудном кармане. Означало ли это, что он спускался ночью, когда очки были не нужны? Наручные часы остановились между часом и двумя – но дня или ночи? Мэллори говорил, что если он поднимется на вершину, то оставит там фотографию своей жены. Снимка при нем не было.
Не осталось и следа камеры; многие историки Эвереста заключили, что ее нес Ирвин. Это вполне логично: он лучше фотографировал.
Последним человеком, видевшим эту пару, был их компаньон Ноэль Оделл, который, как явствует из его записей, 8 июня 1924 года остановился на высоте около 8000 метров. Запрокинув голову, Ноэль наблюдал за вершиной. В 12:50 клубящиеся облака на мгновение расступились, открыв взору Мэллори и Ирвина, быстро продвигавшихся к вершине, до которой оставалось метров 250.
«Я следил за крохотной черной точкой на небольшом снежном гребне, – писал Оделл в своем отчете от 14 июня. – Первый человек приблизился к скальному выступу и вскоре показался наверху; второй последовал за ним. Затем завораживающее видение исчезло, снова окутанное облаком».
Поднявшись на Северное седло, альпинисты обычно проводят одну-две ночи на 7000 метрах, чтобы акклиматизироваться перед подъемом на вершину. Хоть и менее людный, чем непальская сторона Эвереста, китайский склон все равно бывает опасно загруженным.
До сих пор идея восхождения на Эверест меня не грела: я был наслышан о людских толпах, о новичках, которым на такой горе делать нечего, а также о перекладывании риска на плечи команд поддержки. Люди из этих команд, преимущественно этнические шерпы, носят на своих спинах тяжесть чужого эго и порой расплачиваются за других собственными жизнями.
Это была одна из причин, по которой я никогда не понимал одержимости Полларда Эверестом. Но, по мере того как мы продолжали общаться после его лекции, история Ирвина и Мэллори интриговала меня все больше. А однажды от Полларда я услышал о Томе Холзеле, 79-летнем писателе и поклоннике Эвереста, который более 40 лет пытался разгадать загадку погибших.
В 1986 году Холзел отправился в первую поисковую экспедицию вместе с коллегой, сценаристкой и исследовательницей Одри Солкелд. Необычайно сильные снегопады не позволили им подняться достаточно высоко по китайскому склону – при другой погоде они вполне могли бы обнаружить тело Мэллори, которое впоследствии было найдено в 35 метрах от точки, намеченной Холзелом.
Тогда Том решил использовать материалы фотосъемки, сделанной в рамках проводившегося при поддержке National Geographic проекта по картированию Эвереста. Идея заключалась в том, чтобы постараться отметить точное место на горе, где тело Ирвина якобы видел китайский альпинист Сюй Цзин. Сюй был заместителем руководителя экспедиции, совершившей первое восхождение по северной стороне Эвереста в мае 1960 года.
По словам Сюй Цзина, отказавшись от попытки штурмовать вершину и спускаясь вниз коротким путем через Желтый пояс, он заметил труп в расселине примерно на 8300 метрах. На тот момент единственными людьми, погибшими на такой высоте на северном склоне, были Мэллори и Ирвин. (Когда Сюй об этом рассказал, в 2001 году, останки Мэллори уже обнаружили ниже по склону.)
Мы с Поллардом навестили Холзела в декабре 2018-го: он продемонстрировал нам на увеличенном в ширину до 2,5 метра снимке, что существовал один-единственный маршрут, которым Сюй мог срезать дорогу. Подробно анализируя и исключая различные элементы рельефа, Холзел сузил регион поисков до конкретной расселины, в которой, по его мнению, следовало искать Ирвина, и определил точные координаты этого места.
Я указал на красный кружок на огромной фотографии: «Каковы шансы, что он действительно здесь?»
«Его не может там не быть», – последовал ответ.
Ирвин попал на Эверест во многом благодаря случайному стечению обстоятельств.
Застенчивый спортивный 21-летний парень еще учился в Мертон-Колледже Оксфорда, когда Комитет по Эвересту пригласил его присоединиться к экспедиции в 1923 году. В отличие от более опытных членов британской команды, Сэнди имел в послужном списке лишь скромные пики на Шпицбергене, в Уэльсе и Альпах – не чета гималайским гигантам.
Тем не менее к тому моменту, как группа добралась до горы, самый молодой член команды уже снискал уважение товарищей: талантливый и умелый инженер, Ирвин разобрал и заново собрал кислородные аппараты, облегчив их и защитив от поломок.
…За пару месяцев до нашей собственной экспедиции в 2019 году я изучил архив Сэнди Ирвина в Мертон-Колледже. Меня интересовал дневник с Эвереста, привезенный сюда после исчезновения хозяина.
Архивариус Джулиан Рид вынес мне книжечку 20 на 13 сантиметров в черном тканевом переплете и, долистав до последней записи, сказал: «Когда я это прочел, у меня волосы на затылке зашевелились».
Ирвин нацарапал свою последнюю запись вечером 5 июня, когда они с Мэллори стояли лагерем на 7000 метрах на Северном седле, – этот узкий заснеженный перевал соединяет северный склон Эвереста с малым пиком Чангзе. Оттуда альпинисты наутро намеревались начать штурм вершины. В дневнике парень жаловался, что его светлая кожа вся потрескалась и до волдырей обгорела на солнце.
«Мое лицо – совершеннейшая агония. Подготовил два кислородных аппарата для выхода завтра утром», – писал Ирвин.
Я испытал те же чувства, что и Рид: когда Сэнди пропал, ему было ровно столько же, сколько сейчас моему старшему сыну.
До самых последних дней на горе Ирвин занимался усовершенствованием кислородного оборудования команды, пытаясь облегчить его и защитить от повреждений и протекания.
Прежде чем начать поиски Ирвина, мы должны были акклиматизироваться и опробовать наше секретное оружие – небольшой флот дронов.
Ренан Озтюрк надеялся использовать эти беспилотные летательные аппараты не только для поисков так называемой расселины Ирвина, но и для осмотра всего северного склона горы.
1 мая 2019 года в Передовом базовом лагере на высоте 6400 метров наша команда сидела за складным столиком в палатке-столовой, разбитой на каменной платформе на краю ледника Восточный Ронгбук. День стоял теплый, и вход в палатку был подвязан, что открывало прекрасный вид на северо-восточный склон Эвереста. Словно хвост белого дракона, протянувшийся на несколько километров, с вершины развевался снежный плюмаж.
«Это циклон четвертой категории, – сказал Макгиннесс, указывая на яркий завиток в районе Бенгальского залива на экране ноутбука. – В ближайшие пару дней он может вывалить на нас добрый фут снега (30 сантиметров. – Ред.)».
На следующий день мы планировали выпустить дроны в Северное седло: не терпелось проверить их возможности на большой высоте. Но Макгиннесс не разделял нашего оптимизма: «Ветер наверху может быть слишком сильным».
Он был прав: через полтора дня порывы ветра на перевале стали столь резкими, что Озтюрк даже не смог вернуть дрон на базу. Пришлось посадить аппарат неподалеку и идти за ним.
После суматохи за ужином поварская команда отдыхает и принимает гостей. Непальский повар Бире Таманг (сзади справа) и его тибетский помощник Чумби (справа) каждый день готовят полезную еду – рис, чечевицу, суп и лапшу на 30–40 человек, включая начальника команды поддержки Дава Шерпа (сзади слева) и частного гида Пасанг Гомба Шерпа.
Той ночью мы сгрудились в палатке и слушали, как буря набирает силу. Наша команда уже стояла на 600 метров выше Передового базового лагеря; я чувствовал страшную вялость, меня раздирал кашель и немного подташнивало – по ощущениям как грипп в жестоком похмелье. Голова болела, ветер усиливался, и тканевая палатка ходила ходуном. Незадолго до полуночи раздался такой шум, словно над головой взлетал 747-й «Боинг». Через пару секунд палатка сложилась; шквал длился несколько мгновений, после чего палатка приняла прежнюю форму, но я знал, что этим дело не кончится.
Следующие пару часов ураган набирал силу, и около двух ночи, когда порывом ветра меня придавило к земле, я щекой почувствовал лед под палаткой. Гора дрожала, словно вулкан перед извержением. Это длилось секунд 20 или 30, и я, помню, подумал: «Должно быть, так чувствует себя человек перед смертью». Дуги треснули, их острые обломки разорвали ткань в лоскуты, и меня замотало в заиндевевший нейлон, куски ткани стали хлестать по лицу. Я молился, чтобы выдержали бамбуковые колышки, которыми мы закрепились на горе.
В ураган на высоте 7000 метров Ник Кейлис цепляется за палатку, разломанную за ночь ужасным штормом. Член съемочной команды, Ник позже будет эвакуирован в Катманду с диагнозом «легочная эмболия».
Когда солнце наконец взошло, я сел; рядом, свернувшись калачиком, лежали два моих товарища, и я потыкал их ноги, чтобы убедиться, что они еще живы. Когда я выбрался наружу, от увиденного перехватило дыхание. Все палатки были раздавлены и порваны, а одна, взлетев как воздушный змей, парила в 150 метрах над нашими головами.
Бросив взгляд на гребень, я увидел группу индийских альпинистов, спускавшихся к нашему лагерю. Но тут неожиданно налетел новый вихрь, все разом закричали: четыре человека повисли на 300-метровой ледяной стене, словно рождественская гирлянда. Парень из нашей команды кинулся к крюку, на котором держался ближайший к нам конец их веревки, и вбил рядом свой ледоруб, тем самым укрепив конструкцию, остальные схватились за другую веревку, чтобы вытащить альпинистов на безопасное место.
«Надо выбираться к чертям отсюда», – сказал я.
Более удачный запуск дрона состоялся через неделю. Предприняв последнюю попытку обыскать Желтый пояс с воздуха, мы снова взобрались на Северное седло и напряженно наблюдали за летящим к вершине дроном. Пока аппарат поднимался в разреженном воздухе, я, нависая над плечом Озтюрка, подсказывал, куда лететь и что фотографировать. К обеду, когда ветер стал крепчать, он уже сделал 400 снимков поисковой зоны с высоким разрешением, включая точку Холзела крупным планом.
На одной фотографии я заметил расселину, но ракурс не позволял заглянуть внутрь. Могло ли тело Ирвина оказаться там? Время, отпущенное на поиск ответа, подходило к концу.
Вершина мира и Млечный Путь кажутся равноудаленными от Передового базового лагеря, где более 200 человек разместились на полукилометровой морене. Вершина находится за заснеженным Северным седлом, справа – на фото ее практически не видно.
Первое окно для восхождений на вершину с китайской стороны открылось 22 мая, застав нас в Передовом базовом лагере на высоте 6400 метров. После двух вылазок на перевал мы уже полностью акклиматизировались и были готовы отправиться в поисковую зону в верхней части Северо-восточного гребня. Но на горе мы были далеко не одни: более 450 человек намеревались совершить восхождение по непальскому склону, Базовый лагерь которого уже приобрел репутацию коммерциализированного шапито. Еще порядка 200 человек ждали вместе с нами на китайской стороне. Макгиннесс, едва бросив взгляд на эту алчущую вершины толпу, сказал: «Нет. Подождем другого окна».
За несколько следующих дней на Эвересте расстались с жизнью девять человек: семеро на южной стороне и двое на северной (еще двое погибли на южной стороне неделей ранее, так что всего жертв было 11). Я никогда не забуду то ощущение беспомощности, которое возникает, когда разглядываешь в мощный бинокль паровозик из пары сотен полных надежд альпинистов, продвигающихся к вершине, а стоящее рядом радио выплевывает отчеты о бедолагах, которые уже никогда не вернутся домой к семьям.
Член съемочной команды Мэтью Ирвинг снимает кусок фольги с «кошки» Ренана Озтюрка в Штурмовом лагере, заваленном мусором. На спуске многие альпинисты настолько истощены, что у них не остается сил забрать из лагерей палатки, газ и прочее снаряжение.
Под звон колокольчиков яки тащат пропан и припасы до Передового базового лагеря, расположенного на высоте 6400 метров. Это выше, чем они могут подняться по непальской стороне Эвереста.
Чтобы сделать лагеря более комфортными для клиентов, шерпы и другие члены команд поддержки тащат пенные коврики и постельные принадлежности вверх по крутому склону на Северное седло. Всё, начиная от палаток и баллонов с кислородом и заканчивая плитками, едой и топливом, после Передового базового лагеря нужно нести на себе. «Вес любой экспедиции ложится на плечи шерпов», – говорит Марк Синнот.
Фотограф Ренан Озтюрк приветствует альпиниста, возвращающегося в Передовой базовый лагерь.
23 мая после полудня мы уселись вместе с командой поддержки, чтобы обсудить предстоявшие поиски. Макгиннесс заверял, что команда была в курсе нашего плана, но, видимо, все же не до конца. Когда я объяснил, как мы собираемся разыскивать тело Ирвина на Желтом поясе, кто-то лишь всплеснул руками, остальные заспорили на непальском.
«Мы не идем на вершину? – спросил Лакпа Шерпа. – Большая проблема».
Озтюрк переводил для остальных. Во-первых, команда поддержки не хотела, чтобы мы отходили от веревок, провешенных китайцами, – это было бы слишком опасно и против официальных правил. Во-вторых, вершина была важна для них: в нашей команде были новички, еще не успевшие побывать на Эвересте. В-третьих, все хотели провести как можно меньше времени в Штурмовом лагере, расположенном на высоте 8200 метров, далеко в Зоне смерти, где воздух слишком разрежен. «Очень опасно для всех», – повторяли они.
Я повернулся к Макгиннессу: «В чем дело? Я думал, ты рассказал им о поисках».
Джейми пожал плечами: из-за ларингита разговаривать он практически не мог. Но дал понять, что правда обсуждал наш план по крайней мере с некоторыми сопровождающими еще в Катманду.
Тяжело дыша через кислородные маски в разреженном воздухе Зоны смерти, Ирвинг (слева) и Синнот продвигаются к Северо-восточному гребню на высоте примерно 8300 метров – выше них сейчас всего пять пиков в мире.
Оставалось признать, что отныне у нас были натянутые отношения с командой поддержки, в которую входило 12 человек. Впрочем, никто не питал иллюзий, что мы смогли бы подняться на гору без их помощи. Как и любая другая группа, мы зависели от их поддержки.
«Если мы пойдем на вершину, я смогу, по дороге туда или обратно, свернуть с проложенного пути, чтобы обыскать расселину Ирвина?» – спросил я Макгиннесса.
«Лучше тогда на обратном пути», – ответил он. Меня этот вариант привлекал еще и тем, что он позволит увидеть ландшафт с того ракурса, с которого его, вероятно, видел Сюй Цзин в 1960-м, когда, по его словам, он заметил тело.
Я позвал Лакпу в столовую палатку сообщить, что мы собираемся на вершину. Он кивнул и пробормотал «ладно» по-непальски. Никто прямым текстом не сказал, что я могу свернуть с маршрута во время спуска, но, предположил я, Лакпа это понял, ведь несколькими минутами ранее мы объяснили ему: главной нашей целью были поиски. Сами мы воспринимали этот план – подняться на вершину, а затем поискать останки Ирвина на пути вниз – как разумный компромисс.
Через восемь дней наша команда достигла вершины мира и двинулась в обратный путь. Лакпа, замыкавший группу, не спускал с меня глаз, пока я внимательно изучал рельеф и часто сверялся с GPS. И вот, стоило мне отстегнуться от веревки на 8440 метрах, он закричал: «Нет-нет-нет!»
Я замер, пытаясь решить, что же делать. В глубине души я понимал: будет неправильно поступить наперекор шерпу, я поведу себя как очередной эгоистичный западный турист. Если бы я упал или пропал, Лакпа был бы обязан отправиться на поиски. В случае моей гибели ему пришлось бы объяснять китайским чиновникам, что произошло. Но еще более важным было ощущение: к тому моменту он по-настоящему ко мне привязался. Более того, привязанность была взаимной. Тут-то и крылся подвох: я знал, что выходка сойдет мне с рук. И что Лакпа простит мне это безрассудство.
Согласно GPS, до расселины Ирвина было рукой подать. Под пристальными взглядами Лакпы и остальных я пошел по узкому уступу, покрытому пластами известняка, укрывавшего землю словно брусчатка. Буквально через метр камень выскользнул у меня из-под ноги, и я пошатнулся.
«Осторожней!» – закричал Озтюрк.
Пройдя траверсом метров 30, я посмотрел вниз и увидел узкий овраг, прорезавший крутой скальный пояс до следующего заснеженного уступа. Мне смутно вспоминался этот рельеф – мы его видели на фотографиях с дрона. Здесь ли Сюй пытался срезать путь через Желтый пояс?
Ледоруб Ирвина, найденный на Северо-восточном гребне в 1933 году, опознали по засечкам на деревянном черенке.
Крепкую карманную камеру Vest Pocket Kodak, которую Ирвин предположительно взял с собой в 1924 году, так и не нашли.
Я повернулся лицом к склону, принял такое положение тела, как если бы собрался спускаться по стремянке, и всадил ледоруб в твердый как камень лед. Стальное лезвие лязгнуло, пробив утрамбованную ветрами корку. Глядя вниз, я спускался в пьянящую бездну, отделявшую меня от лежащего далеко внизу ледника. В нескольких сотнях метров раскинулось снежное плато, где нашли Мэллори. Теперь я был примерно над местом его гибели, на той части горы, куда люди не забираются, если хотят вернуться домой живыми. Я еще раз проверил GPS. Стрелка на компасе указывала на северо-запад. Еще 15 метров.
Спустившись чуть ниже, я остановился на расколотом блоке бледно-коричневого известняка. Скала была около двух с половиной метров высотой, покатая, словно горка на детской площадке. Со стороны это могло показаться непоследовательным, но в тот момент, изнуренный, одинокий и без веревки, я испугался. Глядя вверх, я гнал от себя мысль вернуться назад тем же способом, каким спустился сюда.
Осторожность требовала отступить, но любопытство было сильнее. Не вынимая острия ледоруба из снега, я ступил на скалу. «Кошки» проскользнули со скрежетом – словно ногти по гладкой классной доске.
У подножья скалы я сделал несколько глубоких выдохов. Справа была небольшая ниша, окаймленная скалистой стеной – чуть более крутой и высокой, чем та, с которой я только что спустился. Посередине ее рассекала жила темно-коричневой породы с узкой трещиной посередине. GPS сообщил о прибытии в место назначения. И тут я осознал: полоса темной породы и есть та самая «расселина», которую мы видели с дрона. Видимо, оптическая иллюзия. Трещина в камне была всего 23 сантиметра шириной – слишком узко, чтобы человек мог оказаться внутри. Вокруг было пусто.
Его здесь нет.
Парой скрещенных на льду спальников участники экспедиции 1924 года сообщили товарищам, что найти Мэллори или Ирвина больше нет никакой надежды.
Я прильнул к кислородной маске, пытаясь развеять туман в голове. Высоко надо мной на фоне бледно-голубого неба сияла вершина, как всегда непоколебимая и равнодушная.
Мы исследовали все зацепки, прочесали горные склоны при помощи дронов; я рискнул жизнью, чтобы разгадать одну из главных тайн Эвереста. У нас осталось больше вопросов, чем ответов. Что случилось с Ирвином в тот день? Где он нашел последнее пристанище? Кто-то снял его тело с горы? А может, его смыло струйным течением или лавиной?
На все эти вопросы ответов у меня не было. Но я узнал нечто очень важное о притяжении Эвереста, притяжении, заставляющем людей прилагать столько усилий: не пойди я по следам Ирвина, я бы никогда не прочувствовал этого. Теперь с полной уверенностью я могу заявить только одно: тайна Мэллори и Ирвина пока – а возможно, навсегда – останется неразгаданной. И я принял это.
Поделитесь в социальных сетях
Комментарии 0
<!— —>
Оригинал earth-chronicles.ru
По теме: