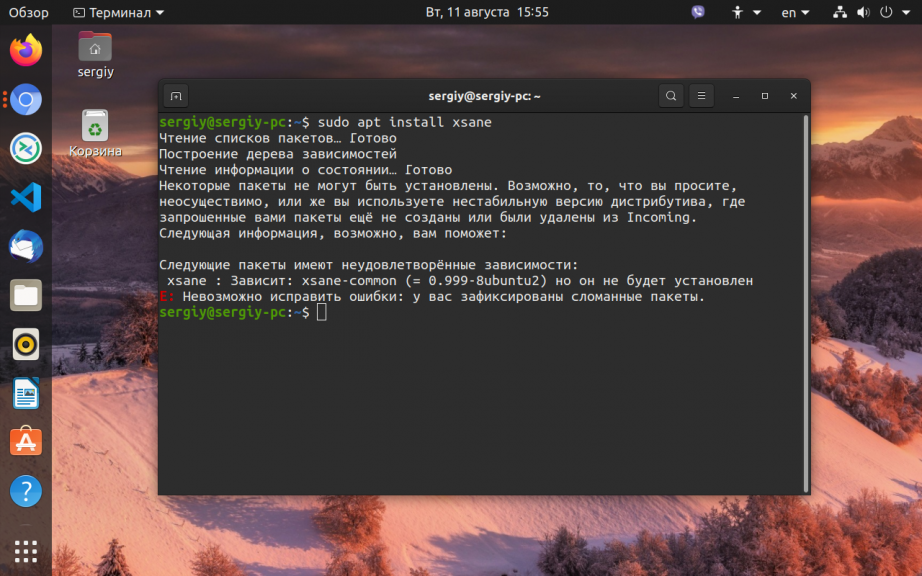
Во время установки программ с помощью пакетного менеджера apt в любом из дистрибутивов, использующих этот пакетный менеджер, вы можете столкнуться с ошибкой, что у вас зафиксированы сломанные пакеты. Это пакеты, которые не установились полностью потому что им не хватает зависимостей или процесс установки был по какой-либо причине прерван.
В этой статье мы рассмотрим что делать с такой ошибкой, как её исправить, а также я дам ссылки на другие материалы на сайте, которые помогут справится с проблемой.
Как исправить у вас зафиксированы сломанные пакеты?
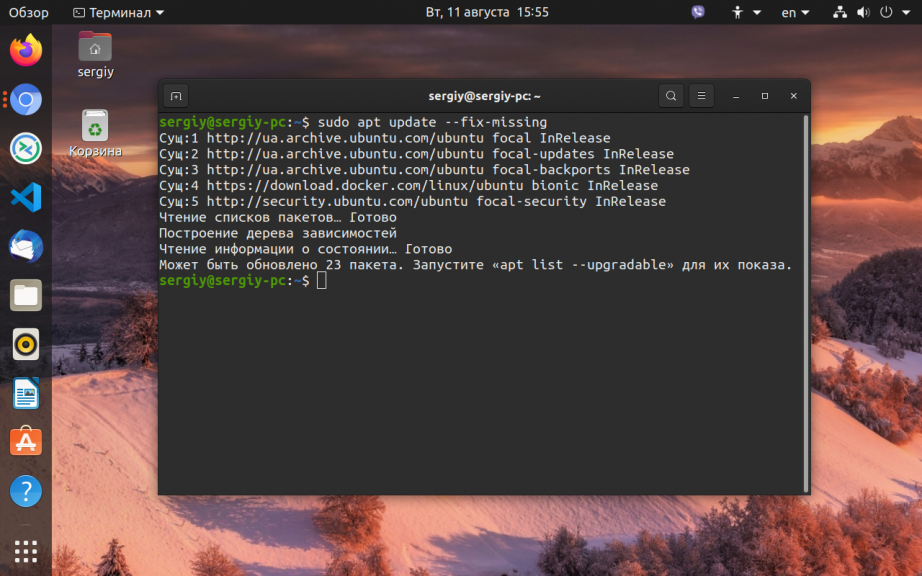
1. Обновите списки пакетов
Возможно вам не удалось установить нужные пакеты потому что списки репозиториев устарели, и там ещё не было нужных пакетов. Для обновления списка пакетов выполните:
sudo apt update --fix-missing
2. Установите битые пакеты
После обновления списка пакетов из репозиториев может помочь установка битых пакетов. Этот шаг поможет особенно если вы устанавливали пакет с помощью dpkg и теперь нужно доустановить его зависимости с помощью пакетного менеджера. Для этого есть специальная команда:
sudo apt install -f
3. Очистите лишние пакеты
Установке могут мешать лишние пакеты, которые больше не нужны в системе. Для их удаления выполните:
sudo apt clean
Затем:
sudo apt autoremove
Утилита отобразит список всех битых пакетов, которые не установлены, вы можете попытаться их удалить с помощью команды:
sudo dpkg --remove -force --force-remove-reinstreq имя_пакета
4. Используйте dpkg
Вместо apt вы можете использовать команду dpkg чтобы посмотреть какие пакеты вызывают проблему. Просто выполните:
sudo dpkg --configure -a
Команда покажет проблемные пакеты, а потом вы сможете их удалить той же командой:
sudo dpkg --remove -force --force-remove-reinstreq имя_пакета
5. Разрешите зависимости
Битые пакеты чаще всего появляются из-за того, что пакетный менеджер не может найти для них нужные зависимости. Если вам всё же очень нужно установить такой пакет, просто разрешите эти зависимости. Для этого можно скачать и установить их вручную или если вы уверенны, что зависимости в пакете указаны неверно, можно скачать его распаковать и удалить мешающие зависимости. Подробнее об этом читайте в этой статье.
Выводы
В этой небольшой статье мы рассмотрели что делать если в вашей системе появились битые пакеты и как их исправить. Здесь решение проблемы очень сильно зависит от вашей ситуации, но здесь приведены основные варианты решения, которые должны помочь вернуть пакетный менеджер к работе. Иногда рекомендуют удалить пакет вручную из базы данных dpkg /var/lib/dpkg/status, однако лучше этого не делать и найти путь решить проблему по другому, ручное редактирование подобных файлов может создать ещё больше проблем.
Обнаружили ошибку в тексте? Сообщите мне об этом. Выделите текст с ошибкой и нажмите Ctrl+Enter.
Статья распространяется под лицензией Creative Commons ShareAlike 4.0 при копировании материала ссылка на источник обязательна .
Об авторе
Основатель и администратор сайта losst.ru, увлекаюсь открытым программным обеспечением и операционной системой Linux. В качестве основной ОС сейчас использую Ubuntu. Кроме Linux, интересуюсь всем, что связано с информационными технологиями и современной наукой.
При попытке установить libreoffice-core (или другие пакеты), выскакивает ошибка:
Пакеты, имеющие неудовлетворённые зависимости:
libreoffice-core : Зависит: libreoffice-common (> 1:4.3.3) но он не будет установлен
Зависит: ure (>= 4.2~) но он не будет установлен
Зависит: libboost-date-time1.55.0 но он не будет установлен
Зависит: libclucene-contribs1 (>= 2.3.3.4) но он не будет установлен
Зависит: libclucene-core1 (>= 2.3.3.4) но он не будет установлен
Зависит: libcmis-0.4-4 (>= 0.4.0) но он не будет установлен
Зависит: libgltf-0.0-0 (>= 0.0.2) но он не будет установлен
Зависит: libglu1-mesa но он не будет установлен или
libglu1
Зависит: libharfbuzz-icu0 (>= 0.9.18) но он не будет установлен
Зависит: libhunspell-1.3-0 (>= 1.3.3) но он не будет установлен
Зависит: libicu52 (>= 52~m1-1~) но он не будет установлен
Зависит: libmythes-1.2-0 но он не будет установлен
Зависит: libodfgen-0.1-1 но он не будет установлен
Зависит: librevenge-0.0-0 но он не будет установлен
Зависит: libstdc++6 (>= 4.9) но он не будет установлен
Зависит: uno-libs3 (>= 4.3.0~alpha) но он не будет установлен
E: Невозможно исправить ошибки, у вас отложены (held) битые пакеты.
Как это можно попытаться вылечить? У меня Debian 8 Jessie x64.
UPD_0: Удалил все из репозиториев, осталось только:
deb http://mirror.yandex.ru/debian/ jessie main
deb-src http://mirror.yandex.ru/debian/ jessie main
deb http://security.debian.org/ jessie/updates main
deb-src http://security.debian.org/ jessie/updates main
sources.list.d тоже чист.
Для «лечения» пытался выполнить:
sudo dpkg --configure -a
sudo apt-get install -f
sudo apt-get --fix-broken install
sudo rm /var/lib/apt/lists/* -vf //Не удалилась какая-то папка
sudo apt-get clean
sudo apt-get autoclean
sudo apt-get autoremove
Вывод apt-cache policy libreoffice-common libreoffice-core:
libreoffice-common:
Установлен: (отсутствует)
Кандидат: 1:4.3.3-2+deb8u2
Таблица версий:
1:5.1.3~rc2-3 0
100 /var/lib/dpkg/status
1:4.3.3-2+deb8u2 500
500 http://ftp.ru.debian.org/debian jessie/main amd64 Packages
500 http://ftp.ru.debian.org/debian jessie/main i386 Packages
libreoffice-core:
Установлен: (отсутствует)
Кандидат: 1:4.3.3-2+deb8u2
Таблица версий:
1:4.3.3-2+deb8u3 0
100 /var/lib/dpkg/status
1:4.3.3-2+deb8u2 500
500 http://ftp.ru.debian.org/debian jessie/main amd64 Packages
Если вы активный пользователь Linux, то наверняка встречались с тем, что некоторые пакеты так сказать ломаются. Это может быть вызвано по разным причинам, некорректно установленный пакет, какие-то ошибки во время установки и многое другое. Что в свою очередь может сказаться и на самом менеджере пакетов “apt-get”, и как итог, возможно что дойдет даже то того, что вы не сможете обновляться или устанавливать программное обеспечения. Данная статья поможет вам решить вопрос со сломанными пакетами в Debian / Ubuntu, а так же их производными. Так как сломанные пакеты могут возникать по разным причинам, существует несколько способов для решения этой задачи, но, не все они могут сработать, тут все зависит от конкретного случая.
P.S. Желательно точно знать какой пакет у вас сломан, так как это поможет вам выбрать один из способом решения задачи.
Чиним сломанные пакеты с apt-get
Первый вариант, который может помочь починить сломанные пакеты имеется в самом менеджере пакетов apt, и для починки сломанных пакетов достаточно ввести две команды:
sudo apt-get update --fix-missing sudo apt-get install -f
Этот способ поможет для решения уже установленных в вашей системе пакетов, который по каким то причинам сломались. После выполнения первой команды необходимо убедиться, что она исправила ошибки, а затем переходить к введению второй команды. Возможно, что для исправления сломанных пакетов понадобиться несколько минут:
Чиним сломанные пакеты с apt-get и dpkg
Но, что делать если пакет сломался во время установки? Можно попробовать выполнить команды из первого примера, если они не сработают, переходим к использованию apt-get и dpkg, для этого первым делом используем dpkg для настройки пакетов. А затем выполняем очистку apt-get:
sudo dpkg --configure -a sudo apt-get clean sudo apt-get update
В некоторых ситуациях может понадобиться удалить файл блокировки, после удаления файла блокировки, снова выполните предыдущие команды:
sudo rm /var/lib/apt/lists/lock
Принудительное удаление пакета с помощью apt-get и dpkg
В редких ситуациях может случиться и такое, что ни один из выше указанных методов не сработает и вам понадобиться вручную удалить сломанный пакет. Для этого разумеется вы должны точно знать что это за пакет, и первый вариант удаление пакета с помощью apt-get, для этого вводим команду:
sudo apt-get remove и название пакета
Если же вам не удалось удалить пакет, переходим к кардинальным мерам, для принудительного пакеты введите команду:
sudo dpkg --remove --force-remove-reinstreq и название пакеты
Затем выполните очистку и обновление пакетов:
sudo apt-get clean && sudo apt-get update
Заключение
Если вы не знаете про менеджеры пакетов apt-get и dpkg, на WIKI имеется статьи, первая про apt, вторая статья про dpkg. В редких ситуациях, выше приведенных мер может быть недостаточно для исправления сломанных пакетов. В этом случае, может понадобиться ручная сборка и удаление сломанных пакетов, правда, имеется риск повредить работоспособность всей системы, что в свою очередь может вывести ее из строя. В этом случае, если вы делали резервные копии вашей системы можно откатиться работоспособной версии системы. Сделать резервную копию вашей системы можно при помощи Timeshift или Deja Dup, последняя имеется в дистрибутиве Ubuntu. Но, чаще всего удается отделаться малой кровью когда появляются сломанные пакеты, и выше приведенных мер достаточно для исправления сломанных пактов.
А на этом сегодня все. Надеюсь данная статья будет вам полезна.
Журнал Cyber-X
In this article, I will take you through the steps to fix broken packages in Debian 10/11. Sometimes you might have noticed that whenever you try to run any update or try to install a new package then you always encountering broken package error. While this error could occur due to various number of reasons depending on server to server but here we will cover all the possible solutions that can help you solve this error with the current set of utilities you will have in your Debian based systems. So without any further delay, Let’s dive in !!
Also Read: How to Install curl on Debian 10/11 in 6 Easy Steps
In a typical Debian System, you will always find package managers like apt, apt-get and dpkg. So it is important that we try to use these tools only to solve our error. It is because even if you want to use any other utility to find and fix the broken package issue then you cannot do it as this error stops you to install any new package.
Method 1: Using apt or apt-get command
In this method first you can use apt utility to install any missing update using apt --fix-missing update command and ensure that there are no further update remains to be installed.
root@debian:~# apt --fix-missing update
Hit:1 http://deb.debian.org/debian bullseye InRelease
Get:2 http://security.debian.org/debian-security bullseye-security InRelease [44.1 kB]
Get:3 http://deb.debian.org/debian bullseye-updates InRelease [39.4 kB]
Get:4 http://security.debian.org/debian-security bullseye-security/main Sources [38.9 kB]
Get:5 http://security.debian.org/debian-security bullseye-security/main amd64 Packages [48.0 kB]
Fetched 170 kB in 2s (90.5 kB/s)
Reading package lists... Done
Building dependency tree... Done
Reading state information... Done
Now you can simply run apt update command to see if it works.
root@debian:~# apt update
Hit:1 http://security.debian.org/debian-security bullseye-security InRelease
Hit:2 http://deb.debian.org/debian bullseye InRelease
Hit:3 http://deb.debian.org/debian bullseye-updates InRelease
Reading package lists... Done
Building dependency tree... Done
Reading state information... Done
If it does not work then you can attempt fixing all broken packages by using apt install -f command as shown below.
root@debian:~# apt install -f
Reading package lists... Done
Building dependency tree... Done
Reading state information... Done
The following packages were automatically installed and are no longer required:
libjq1 libonig5
Use 'apt autoremove' to remove them.
0 upgraded, 0 newly installed, 0 to remove and 1 not upgraded.
As you can see from above output, there are few packages installed which are no longer required in the System. So to remove those packages you need to run apt autoremove -y command as shown below.
root@debian:~# apt autoremove -y
Reading package lists... Done
Building dependency tree... Done
Reading state information... Done
The following packages will be REMOVED:
libjq1 libonig5
0 upgraded, 0 newly installed, 2 to remove and 1 not upgraded.
After this operation, 1,035 kB disk space will be freed.
(Reading database ... 141510 files and directories currently installed.)
Removing libjq1:amd64 (1.6-2.1) ...
Removing libonig5:amd64 (6.9.6-1.1) ...
Processing triggers for libc-bin (2.31-13) ...
If you find any packages that needs to be upgraded then you can upgrade it by using apt upgrade -y command as shown below.
root@debian:~# apt upgrade -y
Reading package lists... Done
Building dependency tree... Done
Reading state information... Done
Calculating upgrade... Done
The following NEW packages will be installed:
linux-image-5.10.0-9-amd64
The following packages will be upgraded:
base-files gir1.2-mutter-7 gnome-maps gnome-shell gnome-shell-common gnome-shell-extension-prefs krb5-locales libapr1 libatk-wrapper-java
libatk-wrapper-java-jni libbluray2 libc-bin libc-dev-bin libc-devtools libc-l10n libc6 libc6-dev libflatpak0 libgssapi-krb5-2 libk5crypto3 libkrb5-3
libkrb5support0 libmutter-7-0 libnautilus-extension1a libpam-modules libpam-modules-bin libpam-runtime libpam0g libperl5.32 libspeechd2 linux-image-amd64
linux-libc-dev locales mutter-common nautilus nautilus-data perl perl-base perl-modules-5.32 python3-reportbug python3-speechd reportbug
speech-dispatcher speech-dispatcher-audio-plugins speech-dispatcher-espeak-ng
45 upgraded, 1 newly installed, 0 to remove and 0 not upgraded.
If you are still facing the same error then you can try doing some cleanups using below mentioned commands.
root@debian:~# rm -rf /var/lib/apt/lists/* root@debian:~# rm /var/cache/apt/*.bin root@debian:~# apt clean
Method 2: Using dpkg command
Another method that you can use is through dpkg command. In this method first you need reconfigure all the partially installed packages by using dpkg --configure -a command as shown in the below output.
root@debian:~# dpkg --configure -a
If the above command does not solve your problem then in the next step first you need to find all the broken packages using dpkg -l | grep ^..r command as shown below.
root@debian:~# dpkg -l | grep ^..r
If you see any broken packages then you can remove it by using dpkg --force-all --remove package-name command.
root@debian:~# dpkg --force-all --remove package-name
You can also remove all the files from /var/lib/dpkg/updates directory using rm -rf /var/lib/dpkg/updates/* command as shown below. More about dpkg command.
root@debian:~# rm -rf /var/lib/dpkg/updates/*
You can also use both apt and dpkg command together to fix broken package issues. Hopefully all the above shown steps are enough to solve your error.
One of the best things about Linux is the apt command which lets you install applications and software effortlessly. Using apt, you don’t have to go through downloading the software, then going through the installer and clicking ‘Next’ a dozen times. It makes sure that every software is installed with just one terminal command.
But, just like any other program, things can go wrong. The error that we will be talking about in this write-up looks something like the following:
E: Unable to correct problems, you have held broken packages.This error may occur when you are trying to install something via the apt utility. Let us look into the error in detail and try to solve the problem.
What causes this error?
Some of the software (mostly third-party ones) do not come with compatible dependencies and apt expects that your system already has those components. In case the required components aren’t found on your system, apt throws an error related to broken packages which means that the package you are trying to install is incomplete.
Outdated repositories, problems with the ‘sources.list‘ file, or an old/unsupported version of Linux might be the cause of this problem.
Methods to fix this problem
Before moving to the advanced methods, let us try a few quick tricks that can potentially help:
Method 1: Update the repositories
The apt update is a well-known command which instantly updates the list of packages and their dependencies. As the problem we are facing is due to missing dependencies, there is a good chance that this command will fix the error.
If the problem persists, try this command:
This will update the existing packages on your system to the latest version.
Method 2: Use aptitude instead of apt
Aptitude is also a package manager like apt and it surprisingly works in some situations where apt doesn’t! all you need to do is use aptitude instead of apt.
For example, suppose you want to install BIND9 using aptitude, you will have to enter the following command:
sudo aptitude install bind9
If you don’t have aptitude installed, run the following commands:
sudo apt-get update sudo apt-get install aptitude
Method 3: Use autoremove to get rid of unnecessary packages
Sometimes, unnecessary packages stay behind even after uninstalling their parent application. These residual packages might interfere with installation of new applications or libraries. To get rid of these unnecessary residual packages, just enter the following command into the terminal:
There’s no need to worry as autoremove will only handle the leftover packages and dependencies.
Now with the basics out of the way, we will look at some more advanced methods to solve this problem.
Method 4: Look for held packages and unhold them
As the error message suggests, the problem is caused by packages on hold. The term ‘held package’ means that it can’t be upgraded, removed, or modified in any way.
To get a list of held packages, you need to enter the following command:
To unhold a specific package, enter:
sudo apt-mark unhold <package-name>
To unhold all held packages, enter:
sudo apt-mark unhold $(sudo apt-mark showhold)
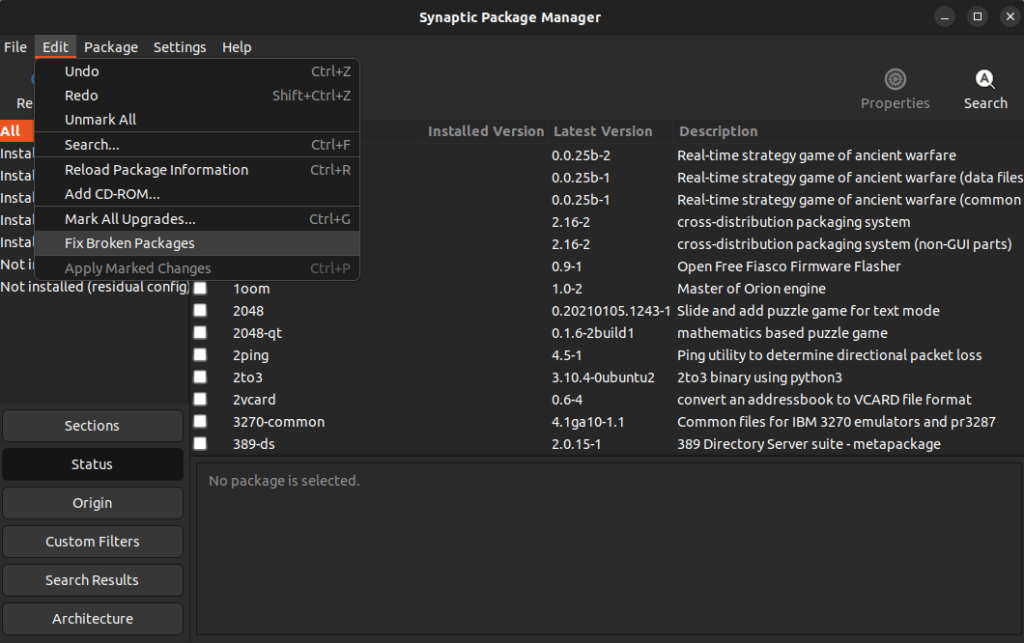
Method 5: Use the synaptic package manager to fix broken packages
Originally, Linux doesn’t have an inbuilt graphical package manager like Windows. This is why the synaptic package manager became immensely popular on Debian-based distributions made for personal computers as it provided a lightweight and robust GUI package manager.
One of the key features of this utility is that you can fix broken packages very easily. Follow the steps below:
1. First, install the synaptic package manager:
sudo apt update sudo apt install synaptic
2. Run synaptic with superuser privileges:
3. Go to Edit > Fix Broken Packages
It will take some time if there are broken packages present. Check if the problem is resolved.
References
- Ask Ubuntu – Unhold a package
- Ask Ubuntu thread on the same problem
Summary
In this article, we saw five different methods to fix the error “Unable to correct problems, you have held broken packages.” All the methods discussed were easy to execute and I hope you were able to fix the problem on your system. If you are still facing the same issue even after trying all the above methods, it can be because of using an unsupported Linux distribution, in which case, you will have to consider upgrading to a newer version of it.