Когда вы объявляете переменную ссылочного типа, на самом деле вы создаете ссылку на объект данного типа. Рассмотрим следующий код для объявления переменной типа int:
int x;
x = 10;
В этом примере переменная x имеет тип int и Java инициализирует её как 0. Когда вы присвоите переменной значение 10 (вторая строка), это значение сохранится в ячейке памяти, на которую ссылается x.
Но когда вы объявляете ссылочный тип, процесс выглядит иначе. Посмотрим на следующий код:
Integer num;
num = new Integer(10);
В первой строке объявлена переменная num, ее тип не относится к встроенному, следовательно, значением является ссылка (тип этой переменной, Integer, является ссылочным типом). Поскольку вы еще не указали, на что собираетесь ссылаться, Java присвоит переменной значение Null, подразумевая «Я ни на что не ссылаюсь».
Во второй строке, ключевое слово new используется для создания объекта типа Integer. Этот объект имеет адрес в памяти, который присваивается переменной num. Теперь, с помощью переменной num вы можете обратиться к объекту используя оператора разыменования ..
Исключение, о котором вы говорите в вопросе, возникает, если вы объявили переменную, но не создали объект, то есть если вы попытаетесь разыменовать num до того, как создали объект, вы получите NullPointerException. В самом простом случае, компилятор обнаружит проблему и сообщит, что
nummay not have been initialized
Что говорит: «возможно, переменная num не инициализирована».
Иногда исключение вызвано именно тем, что объект действительно не был создан. К примеру, у вас может быть следующая функция:
public void doSomething(Integer num){
// Работаем с num
}
В этом случае создание объекта (переменная num) лежит на вызывающем коде, то есть вы предполагаете, что он был создан ранее – до вызова метода doSomething. К сожалению, следующий вызов метода вполне возможен:
doSomething(null);
В этом случае значение переменной num будет null. Лучшим способом избежать данного исключения будет проверка на равенство нулю. Как результат, функция doSomething должна быть переписана следующим образом:
public void doSomething(Integer num){
if (num != null) {
// Работаем с num
}
}
Как альтернативный вариант предыдущему примеру вы можете сообщить вызывающему коду, что метод был вызван с неверными параметрами, например, с помощью IllegalArgumentException.
public void doSomething(Integer num){
if (num == null)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Num не должен быть null");
// Работаем с num
}
Также, обратите внимание на вопрос «Что такое stack trace и как с его помощью находить ошибки при разработке приложений?».
Перевод ответа «What is a Null Pointer Exception, and how do I fix it?» @Vincent Ramdhanie.
Ряд пользователей (да и разработчиков) программных продуктов на языке Java могут столкнуться с ошибкой java.lang.nullpointerexception (сокращённо NPE), при возникновении которой запущенная программа прекращает свою работу. Обычно это связано с некорректно написанным телом какой-либо программы на Java, требуя от разработчиков соответствующих действий для исправления проблемы. В этом материале я расскажу, что это за ошибка, какова её специфика, а также поясню, как исправить ошибку java.lang.nullpointerexception.
Содержание
- Что это за ошибка java.lang.nullpointerexception
- Как исправить ошибку java.lang.nullpointerexception
- Для пользователей
- Для разработчиков
- Заключение
Что это за ошибка java.lang.nullpointerexception
Появление данной ошибки знаменует собой ситуацию, при которой разработчик программы пытается вызвать метод по нулевой ссылке на объект. В тексте сообщения об ошибке система обычно указывает stack trace и номер строки, в которой возникла ошибка, по которым проблему будет легко отследить.
Что в отношении обычных пользователей, то появление ошибки java.lang.nullpointerexception у вас на ПК сигнализирует, что у вас что-то не так с функционалом пакетом Java на вашем компьютере, или что программа (или онлайн-приложение), работающие на Java, функционируют не совсем корректно. Если у вас возникает проблема, при которой Java апплет не загружен, рекомендую изучить материал по ссылке.
Как исправить ошибку java.lang.nullpointerexception
Как избавиться от ошибки java.lang.nullpointerexception? Способы борьбы с проблемой можно разделить на две основные группы – для пользователей и для разработчиков.
Для пользователей
Если вы встретились с данной ошибкой во время запуска (или работы) какой-либо программы (особенно это касается minecraft), то рекомендую выполнить следующее:
- Переустановите пакет Java на своём компьютере. Скачать пакет можно, к примеру, вот отсюда;
- Переустановите саму проблемную программу (или удалите проблемное обновление, если ошибка начала появляться после такового);
- Напишите письмо в техническую поддержку программы (или ресурса) с подробным описанием проблемы и ждите ответа, возможно, разработчики скоро пофиксят баг.
- Также, в случае проблем в работе игры Майнкрафт, некоторым пользователям помогло создание новой учётной записи с административными правами, и запуск игры от её имени.
Для разработчиков
Разработчикам стоит обратить внимание на следующее:
- Вызывайте методы equals(), а также equalsIgnoreCase() в известной строке литерала, и избегайте вызова данных методов у неизвестного объекта;
- Вместо toString() используйте valueOf() в ситуации, когда результат равнозначен;
- Применяйте null-безопасные библиотеки и методы;
- Старайтесь избегать возвращения null из метода, лучше возвращайте пустую коллекцию;
- Применяйте аннотации @Nullable и @NotNull;
- Не нужно лишней автоупаковки и автораспаковки в создаваемом вами коде, что приводит к созданию ненужных временных объектов;
- Регламентируйте границы на уровне СУБД;
- Правильно объявляйте соглашения о кодировании и выполняйте их.
Заключение
При устранении ошибки java.lang.nullpointerexception важно понимать, что данная проблема имеет программную основу, и мало коррелирует с ошибками ПК у обычного пользователя. В большинстве случаев необходимо непосредственное вмешательство разработчиков, способное исправить возникшую проблему и наладить работу программного продукта (или ресурса, на котором запущен сам продукт). В случае же, если ошибка возникла у обычного пользователя (довольно часто касается сбоев в работе игры Minecraft), рекомендуется установить свежий пакет Java на ПК, а также переустановить проблемную программу.
Опубликовано 21.02.2017 Обновлено 03.09.2022
Довольно часто при разработке на Java программисты сталкиваются с NullPointerException, появляющимся в самых неожиданных местах. В этой статье мы разберёмся, как это исправить и как стараться избегать появления NPE в будущем.
NullPointerException (оно же NPE) это исключение, которое выбрасывается каждый раз, когда вы обращаетесь к методу или полю объекта по ссылке, которая равна null. Разберём простой пример:
Integer n1 = null; System.out.println(n1.toString());
Здесь на первой строке мы объявили переменную типа Integer и присвоили ей значение null (то есть переменная не указывает ни на какой существующий объект).
На второй строке мы обращаемся к методу toString переменной n1. Так как переменная равна null, метод не может выполниться (переменная не указывает ни на какой реальный объект), генерируется исключение NullPointerException:
Exception in thread "main" java.lang.NullPointerException at ru.javalessons.errors.NPEExample.main(NPEExample.java:6)
Как исправить NullPointerException
В нашем простейшем примере мы можем исправить NPE, присвоив переменной n1 какой-либо объект (то есть не null):
Integer n1 = 16; System.out.println(n1.toString());
Теперь не будет исключения при доступе к методу toString и наша программа отработает корректно.
Если ваша программа упала из-за исключение NullPointerException (или вы перехватили его где-либо), вам нужно определить по стектрейсу, какая строка исходного кода стала причиной появления этого исключения. Иногда причина локализуется и исправляется очень быстро, в нетривиальных случаях вам нужно определять, где ранее по коду присваивается значение null.
Иногда вам требуется использовать отладку и пошагово проходить программу, чтобы определить источник NPE.
Как избегать исключения NullPointerException
Существует множество техник и инструментов для того, чтобы избегать появления NullPointerException. Рассмотрим наиболее популярные из них.
Проверяйте на null все объекты, которые создаются не вами
Если объект создаётся не вами, иногда его стоит проверять на null, чтобы избегать ситуаций с NullPinterException. Здесь главное определить для себя рамки, в которых объект считается «корректным» и ещё «некорректным» (то есть невалидированным).
Не верьте входящим данным
Если вы получаете на вход данные из чужого источника (ответ из какого-то внешнего сервиса, чтение из файла, ввод данных пользователем), не верьте этим данным. Этот принцип применяется более широко, чем просто выявление ошибок NPE, но выявлять NPE на этом этапе можно и нужно. Проверяйте объекты на null. В более широком смысле проверяйте данные на корректность, и консистентность.
Возвращайте существующие объекты, а не null
Если вы создаёте метод, который возвращает коллекцию объектов – не возвращайте null, возвращайте пустую коллекцию. Если вы возвращаете один объект – иногда удобно пользоваться классом Optional (появился в Java 8).
Заключение
В этой статье мы рассказали, как исправлять ситуации с NullPointerException и как эффективно предотвращать такие ситуации при разработке программ.
You have just finished creating an Android-based application and attempt to execute it. As far as you know, the application is fine, there are no syntax errors and the code should just work fine. But when you run it now, your application quits saying an uncaught RuntimeException was thrown. Attempting to dig up the cause, you find something that gives you a clue: a NullPointerException has occurred.
With this, you begin your journey into the world of exception handling with Android, in particular, handling NullPointerException. In this post, we’ll discuss how to fix NullPointerExceptions in Android apps.
Jump ahead:
- What is a
NullPointerException?- Why do
NullPointerExceptions occur?
- Why do
- Avoiding
NullPointerExceptions in Java- Using SmartCast
- Using the Elvis operator
- Avoiding
NullPointerExceptions in Kotlin - Using
logcatto detect and fix aNullPointerExceptionin Android Studio - Setting breakpoints to debug
NullPointerExceptions
What is a NullPointerException?
First, let’s quickly refresh ourselves on exceptions. They are events or abnormal conditions in a program that occur during execution and disrupt the normal flow of the program.
An exception can occur for different reasons, such as:
- A user enters invalid data to a field
- A file that must be opened cannot be found
- A network connection is lost in the middle of communication
- The JVM has run out of memory
When an error occurs inside a method, it throws an exception. A NullPointerException is one of the most common runtime exceptions.
In Java, null is a special value that represents the absence of a value. When you try to use a null value, you get a NullPointerException because the operation you are trying to perform cannot be completed on a null value.
In Kotlin, null is not a value, but a type of its own called nullable. By default, every object in Kotlin is non-null, which means it cannot have a null value.
Why do NullPointerExceptions occur?
You might encounter a NullPointerException when trying to access a view, resource, or data that hasn’t been properly initialized or loaded yet. Some of the situations in which a NullPointerException can occur in Java, according to the Java Language Specification, include:
- Attempting to access elements of a
nullarray - Using
switchwith a null expression - Accessing instance fields of
nullreferences - Invoking instance methods of a
nullreference - Using an integer or floating point operator that has one of its operands as a boxed
nullreference - Attempting an unboxing conversion with the boxed value as
null - Calling
superon anullreference
Avoiding NullPointerExceptions in Java
Below are some best practices to avoid NullPointerExceptions in Java:
- String comparison with literals
- Avoid returning null from your methods
- Keep checking arguments of methods
- Use
String.valueOf()rather thantoString() - Using primitives data types as much as possible
- Avoid chained method calls
- Use ternary operator
By contrast, Kotlin is a smarter, more modern language that has been designed to avoid NullPointerExceptions through several mechanisms, such as:
- Using nullable and non-nullable types
- Using the SmartCast feature
- Safe calls
- The Elvis operator
In Kotlin, all regular types are non-nullable unless you explicitly mark them as nullable with a question mark ?, e.g., String?.
Consider the below Kotlin code:
fun getlen(name: String) = name.length
The parameter name has a type of String, which means it must always contain a String instance and cannot contain null. This code ensures that a NullPointerException at runtime is unlikely to occur.
Instead, any attempt to pass a null value to the getlen(name: String) function will cause a compile-time error: Null cannot be a value of a non-null type String. This is because the compiler has enforced the rule that arguments of getlen() cannot be null.
Consider the below snippet, in which the code is obvious to us but may not be immediately obvious to the compiler:
class TestNPE {
companion object {
@JvmStatic
fun main(args: Array<String>) {
var m : String? // here, m is declared as nullable
println("m is : $m")
var x: Int
x = 150
if (x == 150)
println("Value of m is : $m")
}
}
}
The compiler raises a compiler error because m is not initialized:
Thus, instead of proceeding to runtime and then raising an exception, it stops at the compilation stage with a compiler error.
Using SmartCast
In order to use nullable types, Kotlin has an option called safe cast, or smart cast. Through this feature, the Kotlin compiler will trace situations inside if and other conditional expressions. So, if the compiler finds a variable belonging to a non-null type, it will allow you to access this variable safely.
In certain cases, it is not possible for the compiler to cast types, in which case it will throw an exception; this is called unsafe casting. Consider a nullable string (String?) which cannot be cast to a non-nullable string (String). It will throw an exception.
Kotlin addresses this by providing a safe cast operator as? to cast safely to another type. If casting is not possible, it returns a null rather than throwing a ClassCastException.
Example:
val aInt: Int? = a as? Int
Using the Elvis operator ?:
Kotlin also has an advanced operator called the Elvis operator (?:) that returns either a non-null value or the default value, even if the conditional expression is null. It also checks the null safety of values.
Consider an example:
val count = attendance?.length ?: -1
This means:
val count: Int = if (attendance != null) attendance.length else -1
Despite this, an NullPointerException could still occur in Kotlin-based Android applications.
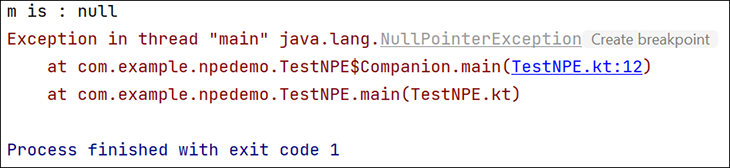
Consider the earlier example of class TestNPE. Now, the code is modified such that m is initialized but is used with a non-null assertion operator (!!), which converts a given value to a non-null type and throws an exception if the value is null.
class TestNPE {
companion object {
@JvmStatic
fun main(args: Array<String>) {
var m: String?=null // here, m is declared
//as nullable
var x: Int
x = 150
if (x == 150)
println("m is : $m")
var mlen = m!!.length
println("length of m is : $mlen")
}
}
}
In this case, a NullPointerException will be thrown, as shown here:
Avoiding NullPointerExceptions in Kotlin
A few causes of a NullPointerException in Kotlin are:
- Explicitly calling
throw NullPointerException() - Using the
!!operator - Data inconsistency with regard to initialization
- Java interoperation
To prevent NullPointerExceptions, you should always ensure that your variables and objects are properly initialized before you use them. You can also use null checks or try … catch blocks to handle possible null values and prevent your app from crashing.
An extremely simplified example of using try … catch is given below:
class TestNPE {
companion object {
@JvmStatic
fun main(args: Array<String>) {
var m: String?=null // here, m is declared
//as nullable
try {
var x: Int
x = 150
if (x == 150)
println("m is : $m")
var mlen = m!!.length
println("length of m is : $mlen")
}catch( ne: NullPointerException)
{
println("Null Pointer Exception has
occurred. ")
}
}
}
}
The code that is likely to cause a NullPointerException is enclosed in a try … catch block.
The advantage here is that the developer has control over what must be done when the exception is thrown. Here, a simple message is displayed. In practical scenarios, one can close any currently open resources, such as files, before terminating the program.
Using logcat to detect and fix a NullPointerException in Android Studio
Whenever an Android application crashes, a stack trace is written to the console that contains vital information that can help identify and solve the issue. There are two ways to get to this stack trace:
-
- Using Google’s
adbshell utility to obtain alogcatfile, which can help explain why the application crashed:adb logcat > logcat.txt
Open
logcat.txtand search for the application name. It will have information on why the application failed along with other details such as line number, class name, and so on - In Android Studio, either press
Alt + 6, or click the Logcat button in the status bar. Make sure your emulator or device is selected in the Devices panel, then locate the stack trace.
- Using Google’s
There may be a lot of stuff logged into logcat, so you may need to scroll a bit, or you can clear the logcat through the Recycle Bin option and let the app crash again to bring the most recent stack trace in the log to the top.
An important point of note is that if your app is already live, then you cannot use logcat.
Android Studio Electric Eel’s latest version has an updated logcat, which facilitates easier parsing, querying, and tracking of logs. The new logcat also:
- Formats logs for easy scanning for tags, messages, and other useful information
- Identifies various types of logs, such as warnings and errors.
- Makes it easier to track logs from your app across app crashes and restarts
When logcat notices that your app process has stopped and restarted. you’ll see a message in the output similar to below:
PROCESS ENDED
Or:
PROCESS STARTED
Developers can fine tune the command to give the message timestamp, for example:
adb logcat -v time
Using logcat, you can determine whether a widget or component is declared but not defined yet, or a variable is null and being used. Sometimes, it could happen that a context is null during navigation between screens, and you are attempting to use that context without realizing it’s null.
Setting breakpoints to debug NullPointerException
If you have a large application, it can be quite cumbersome to debug it. You can set breakpoints in your code that let you debug your code block by block.
A breakpoint serves as a stop sign for the marked piece of code. When a breakpoint is encountered during application debugging, it will pause execution, thus enabling allowing developers to examine in detail what’s happening and use other debugging tools as required.
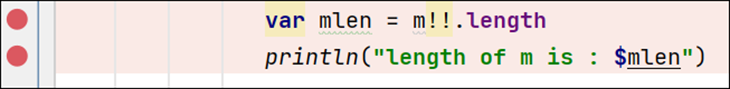
To use breakpoints, add a breakpoint by clicking the gutter in the code editor next to the line number where you want execution to pause. A dot will appear next to the line number, and the line will be highlighted. See below; two breakpoints are added:
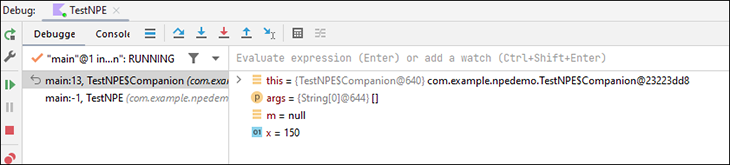
Click Run > Debug ‘app’. The program halts at the first breakpoint and you can examine the values in the Debug window at the bottom of Android Studio:
There are various buttons such as Step Over and Step Into that can help you navigate further:
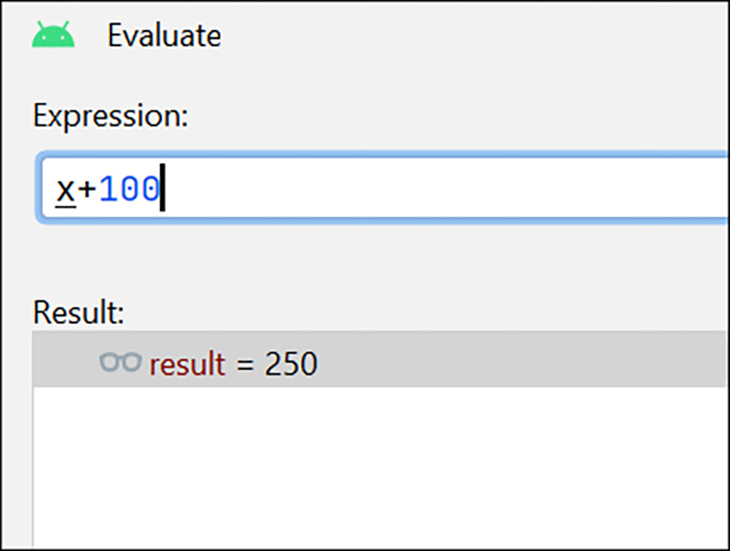
Besides examining the current values of certain operands and expressions, you can also evaluate expressions using the Evaluate option.
In the below example, I wanted to know what the value of x added to 100 would be. The window shows me the result based on the current value of x:
Here is a detailed explanation of various terms related to debugging in Android Studio.
Conclusion
To conclude, in Android development, there are various mechanisms available with Java and Kotlin that are designed to aid developers in avoiding NullPointerExceptions. In the cases these exceptions still occur, you should now have a variety of tools that help identify the cause and debug code.
LogRocket: Instantly recreate issues in your Android apps.
LogRocket is an Android monitoring solution that helps you reproduce issues instantly, prioritize bugs, and understand performance in your Android apps.
LogRocket also helps you increase conversion rates and product usage by showing you exactly how users are interacting with your app. LogRocket’s product analytics features surface the reasons why users don’t complete a particular flow or don’t adopt a new feature.
Start proactively monitoring your Android apps — try LogRocket for free.
The java.lang.NullPointerException is a runtime exception in Java that occurs when a variable is accessed which is not pointing to any object and refers to nothing or null.
Since the NullPointerException is a runtime exception, it doesn’t need to be caught and handled explicitly in application code.
Why NullPointerException Occurs in Java
The NullPointerException occurs due to a situation in application code where an uninitialized object is attempted to be accessed or modified. Essentially, this means the object reference does not point anywhere and has a null value.
Some of the most common scenarios for a NullPointerException are:
- Calling methods on a null object
- Accessing a null object’s properties
- Accessing an index element (like in an array) of a null object
- Passing null parameters to a method
- Incorrect configuration for dependency injection frameworks like Spring
- Using
synchronizedon a null object - Throwing null from a method that throws an exception
NullPointerException Example
Here is an example of a NullPointerException thrown when the length() method of a null String object is called:
public class NullPointerExceptionExample {
private static void printLength(String str) {
System.out.println(str.length());
}
public static void main(String args[]) {
String myString = null;
printLength(myString);
}
}In this example, the printLength() method calls the length() method of a String without performing a null check prior to calling the method. Since the value of the string passed from the main() method is null, running the above code causes a NullPointerException:
Exception in thread "main" java.lang.NullPointerException
at NullPointerExceptionExample.printLength(NullPointerExceptionExample.java:3)
at NullPointerExceptionExample.main(NullPointerExceptionExample.java:8)How to Fix NullPointerException
To fix the NullPointerException in the above example, the string should be checked for null or empty values before it is used any further:
import org.apache.commons.lang3.StringUtils;
public class NullPointerExceptionExample {
private static void printLength(String str) {
if (StringUtils.isNotEmpty(str)) {
System.out.println(str.length());
} else {
System.out.println("Empty string");
}
}
public static void main(String args[]) {
String myString = null;
printLength(myString);
}
}
The code is updated with a check in the printLength() method that makes sure the string is not empty using the apache commons StringUtils.isNotEmpty() method. Only if the string is not empty the length() method of the string is called, else it prints the message Empty string to console.
How to Avoid NullPointerException
The NullPointerException can be avoided using checks and preventive techniques like the following:
- Making sure an object is initialized properly by adding a null check before referencing its methods or properties.
- Using Apache Commons
StringUtilsfor String operations e.g. usingStringUtils.isNotEmpty()for verifying if a string is empty before using it further. - Using primitives rather than objects where possible, since they cannot have null references e.g. using
intinstead ofIntegerandbooleaninstead ofBoolean.
Track, Analyze and Manage Java Errors With Rollbar
Managing errors and exceptions in your code is challenging. It can make deploying production code an unnerving experience. Being able to track, analyze, and manage errors in real-time can help you to proceed with more confidence. Rollbar automates Java error monitoring and triaging, making fixing errors easier than ever. Try it today!