Default sources.list file on 14.04:
# deb http://be.archive.ubuntu.com:80/ubuntu/ trusty main restricted
# deb http://be.archive.ubuntu.com:80/ubuntu/ trusty-updates main restricted
# deb http://security.ubuntu.com/ubuntu trusty-security main restricted
# See http://help.ubuntu.com/community/UpgradeNotes for how to upgrade to
# newer versions of the distribution.
deb http://be.archive.ubuntu.com:80/ubuntu/ trusty main restricted
deb-src http://be.archive.ubuntu.com:80/ubuntu/ trusty main restricted
## Major bug fix updates produced after the final release of the
## distribution.
deb http://be.archive.ubuntu.com:80/ubuntu/ trusty-updates main restricted
deb-src http://be.archive.ubuntu.com:80/ubuntu/ trusty-updates main restricted
## N.B. software from this repository is ENTIRELY UNSUPPORTED by the Ubuntu
## team. Also, please note that software in universe WILL NOT receive any
## review or updates from the Ubuntu security team.
deb http://be.archive.ubuntu.com:80/ubuntu/ trusty universe
deb-src http://be.archive.ubuntu.com:80/ubuntu/ trusty universe
deb http://be.archive.ubuntu.com:80/ubuntu/ trusty-updates universe
deb-src http://be.archive.ubuntu.com:80/ubuntu/ trusty-updates universe
## N.B. software from this repository is ENTIRELY UNSUPPORTED by the Ubuntu
## team, and may not be under a free licence. Please satisfy yourself as to
## your rights to use the software. Also, please note that software in
## multiverse WILL NOT receive any review or updates from the Ubuntu
## security team.
deb http://be.archive.ubuntu.com:80/ubuntu/ trusty multiverse
deb-src http://be.archive.ubuntu.com:80/ubuntu/ trusty multiverse
deb http://be.archive.ubuntu.com:80/ubuntu/ trusty-updates multiverse
deb-src http://be.archive.ubuntu.com:80/ubuntu/ trusty-updates multiverse
## N.B. software from this repository may not have been tested as
## extensively as that contained in the main release, although it includes
## newer versions of some applications which may provide useful features.
## Also, please note that software in backports WILL NOT receive any review
## or updates from the Ubuntu security team.
deb http://be.archive.ubuntu.com:80/ubuntu/ trusty-backports main restricted universe multiverse
deb-src http://be.archive.ubuntu.com:80/ubuntu/ trusty-backports main restricted universe multiverse
deb http://security.ubuntu.com/ubuntu trusty-security main restricted
deb-src http://security.ubuntu.com/ubuntu trusty-security main restricted
deb http://security.ubuntu.com/ubuntu trusty-security universe
deb-src http://security.ubuntu.com/ubuntu trusty-security universe
deb http://security.ubuntu.com/ubuntu trusty-security multiverse
deb-src http://security.ubuntu.com/ubuntu trusty-security multiverse
## Uncomment the following two lines to add software from Canonical's
## 'partner' repository.
## This software is not part of Ubuntu, but is offered by Canonical and the
## respective vendors as a service to Ubuntu users.
# deb http://archive.canonical.com/ubuntu trusty partner
# deb-src http://archive.canonical.com/ubuntu trusty partner
## Uncomment the following two lines to add software from Ubuntu's
## 'extras' repository.
## This software is not part of Ubuntu, but is offered by third-party
## developers who want to ship their latest software.
# deb http://extras.ubuntu.com/ubuntu trusty main
# deb-src http://extras.ubuntu.com/ubuntu trusty main
The location of the file is: /etc/apt/source.list
You can edit it by issuing sudo vi /etc/apt/source.list or sudo nano /etc/apt/source.list (nano might be easier for you).
If you want to add those repositories mentioned, you should add these lines to the bottom of the file:
# Tor Project Repositories
deb http://deb.torproject.org/torproject.org trusty main
deb-src http://deb.torproject.org/torproject.org trusty main
14 января, 2023 12:33 пп
563 views
| Комментариев нет
Linux, Ubuntu
У вас возникла ошибка при обновлении системных репозиториев или установке нового программного обеспечения? Такое случается, если поврежден файл /etc/apt/source.list, который содержит информацию о репозиториях. В этой статье мы покажем, как восстановить репозитории по умолчанию в Ubuntu.
В системе Ubuntu есть четыре стандартных вида репозиториев:
- Main
- Universe
- Restricted
- Multiverse
Восстановление репозиториев по умолчанию в Ubuntu
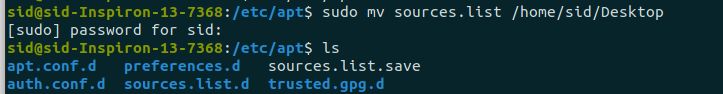
Во-первых, нам нужно сделать резервную копию поврежденного исходного файла, переместив его в другое место. Откройте терминал, нажав Ctrl+Alt+T, и введите следующую команду, чтобы перейти в каталог, в котором находится исходный файл:
cd /etc/apt
Теперь переместите поврежденный файл в другое место:
sudo mv sources.list
Например:
sudo mv sources.list /sid/home/Desktop
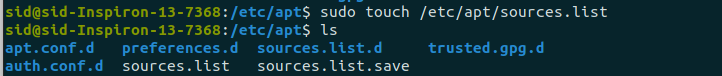
Создайте новый файл при помощи команды:
sudo touch /etc/apt/sources.list
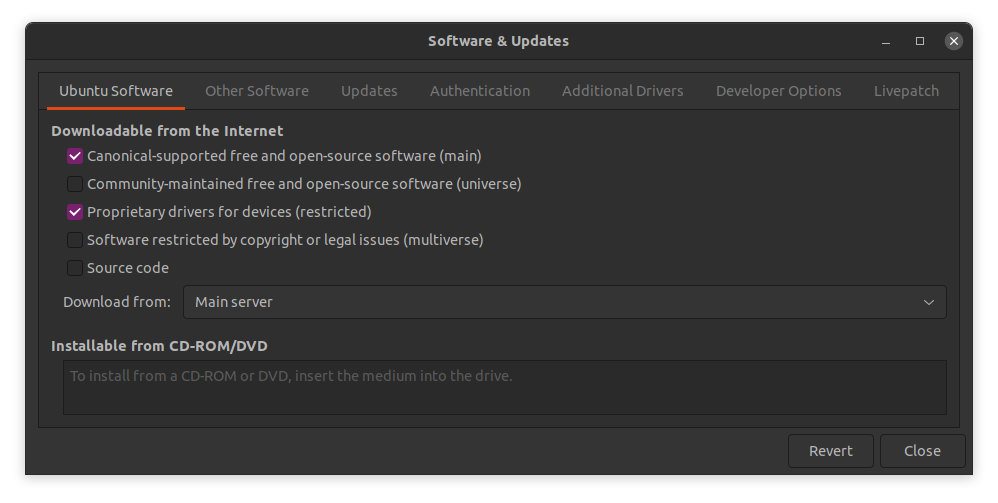
Теперь откройте приложение Software & Updates с помощью поиска или панели приложений. Перейдите на основной сервер и включите restricted репозиторий. Вы также можете включить репозитории universe и multiverse, если это необходимо.
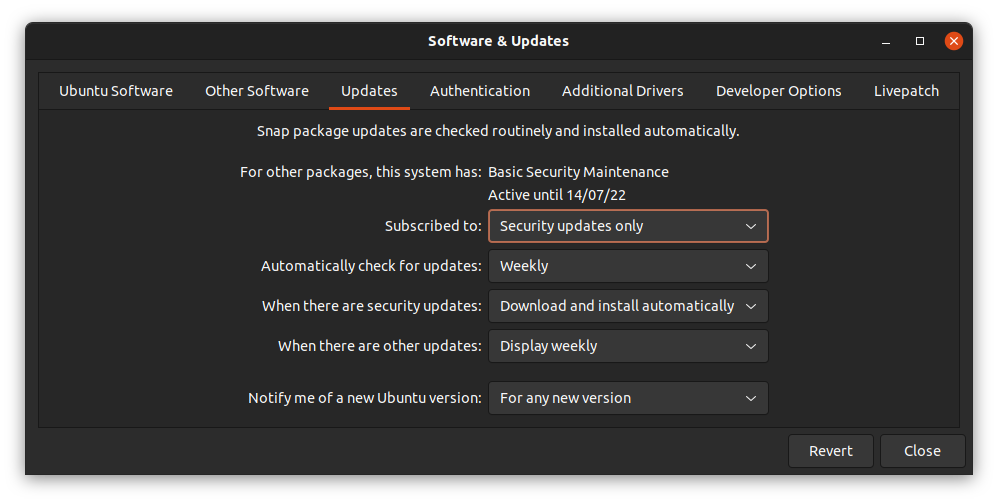
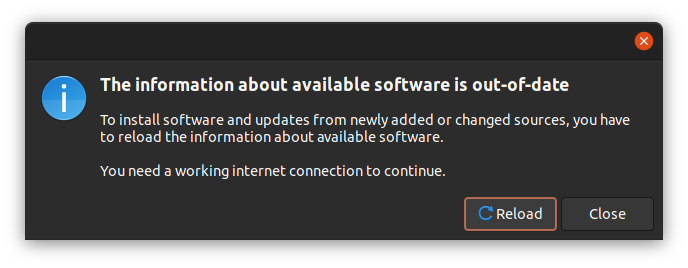
Чтобы включить обновления, откройте вкладку Updates и в раскрывающемся меню Subscribed выберите All updates или, по крайней мере, обновления security, а затем закройте окно.
Нажмите на кнопку Reload. После этого программные репозитории будут обновлены.
Проверка репозиториев
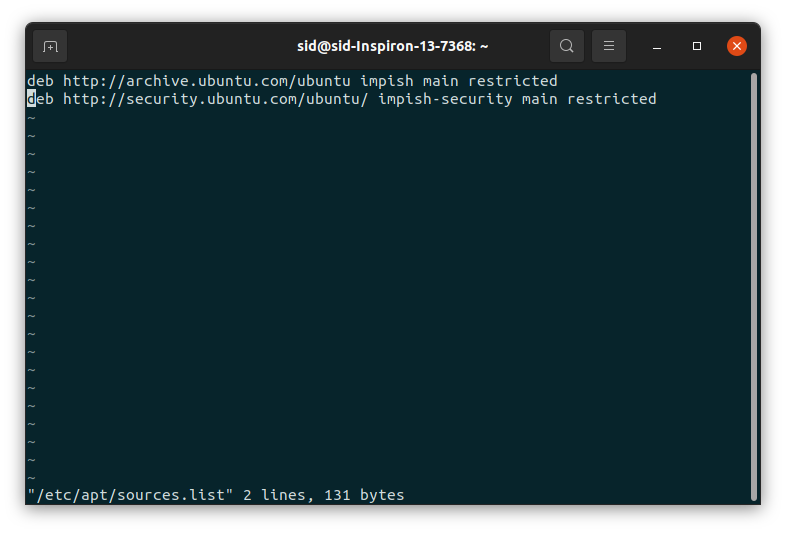
ЧТобы убедиться, что репозитории были восстановлены, откройте терминал, нажав Ctrl+Alt+T. Затем откройте файл /etc/apt/sources.list, запустив эту команду:
sudo vi /etc/apt/sources.list
Если в файле есть записи без #, как показано на картинке ниже, значит, репозитории были добавлены верно.
Осталось только обновить репозитории при помощи команды:
sudo apt update
Итак, вы научились восстанавливать репозитории по умолчанию в Ubuntu.
Читайте также: Выполнение команд через shell-скрипты в Linux
Как востановить sources.list (а это важный файл!), если вы отличаетесь редким «везением», и смогли его сломать.
Итак, мы как-то умудрились накрыть медным тазом файл sources.list, в котором хранится информация о репозиториях. Результат — мы не можем обновиться. А если при этом мы еще и ковыряли своими корявками в системных файлах , то …. ну, вы поняли.
Есть замечательный проект по созданию файла источников (ака sources.list)
Поступаем так:
-
- Заходим на сайт repogen.simplylinux.ch;
- Выбираем страну (надо только для выбора сервера, поэтому можно и не выбирать);
- Выбираем свой дистрибутив (а вот это надо);
- Ставим галочки на все, что хотим. Тут рекомендую отметить все, что не «3rd Parties Repos«;
- Посмотреть на список «3rd Parties Repos«, и выбрать свои любимые программы;
- Нажать на «Generate List».
Вам будет сгенерирован файл sources.list для вашего дистрибутива со всеми необходимыми репами.
Копируем всю информацию в наш sources.list.
Если кто-то не знает, то файл sources.list хранится тут:
/etc/apt/sources.list
Берем строки, начинающиеся с «## Run this command:» и вбиваем их в терминале. Это надо для «принятия» ключей шифрования. Т.е. для AWN (из примера выше) надо запустить в терминале команду:
sudo apt-key adv —keyserver keyserver.ubuntu.com —recv-keys BF810CD5
Все!
15342-23cookie-checkЧиним sources.list в любой Ubuntu
I installed Debian 11 (Bullseye) onto a device with no internet. I used the «firmware CD» version of the ISO. I have configured the network, so I can do ping 8.8.8.8. I tried to run sudo apt update, but I discovered that there weren’t any sources in the sources.list file (e.g., it was empty).
I found this question, but it is for Debian Jessie, not Bullseye.
I would also like non-free packages. How can I restore the default repositories, as if I had installed Debian with an internet connection?
asked Oct 3, 2021 at 15:12
You can find all the information about sources.list in the official Debian wiki site, specifically about your question under Example sources.list:
deb http://deb.debian.org/debian bullseye main contrib non-free
deb-src http://deb.debian.org/debian bullseye main contrib non-free
deb http://deb.debian.org/debian-security/ bullseye-security main contrib non-free
deb-src http://deb.debian.org/debian-security/ bullseye-security main contrib non-free
deb http://deb.debian.org/debian bullseye-updates main contrib non-free
deb-src http://deb.debian.org/debian bullseye-updates main contrib non-free
You can comment or delete the cdrom lines, since they are not useful anymore, and when executing apt update an error will be thrown.
Also comment out the deb-src lines unless you actually intend to download and compile source packages in the near future. Commenting them out halves the download time for apt update. Uncomment them if and when you want to recompile a package or examine its source code.
answered Oct 3, 2021 at 15:32
1
The original list already there just copy it
$ sudo cp /usr/share/doc/apt/examples/sources.list /etc/apt/sources.list
$ sudo apt update
answered Oct 10, 2022 at 19:51
0xFK0xFK
1312 bronze badges
Repositories in Ubuntu are servers that contain software packaged into nice .deb or .rpm files containing the programs and libraries you need to set up of packages. A repository or repo is basically a software archive that makes it easy to install new software in your machine. In Linux, systems software is packaged into nice .deb or .rpm files which contain the programs and libraries needed by you.
Software in Ubuntu’s repository is divided into four components or categories:-
- Main – this component contains software that is free and open-source and is maintained by the Ubuntu team(Canonical).
- Universe – this component contains software that is free and open-source software but maintained by the community all around the world.
- Restricted – a small set of tools and proprietary drivers which make Ubuntu run correctly, these are maintained by the actual authors.
- Multiverse – restricted software due to copyright or legal issues.
We have to follow these four steps in order to Restore Default Repositories in Ubuntu:
1. Deleting source.list file
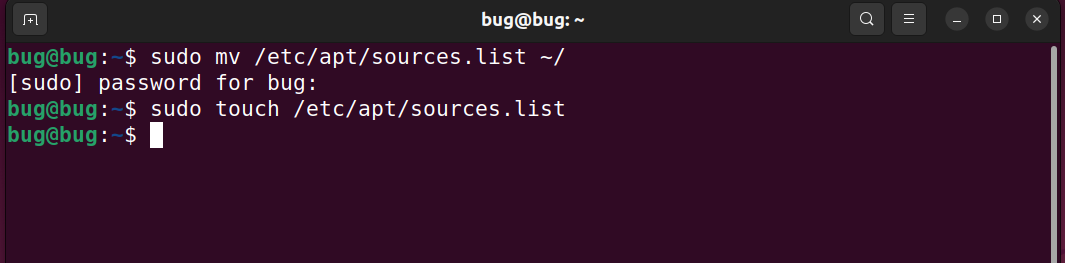
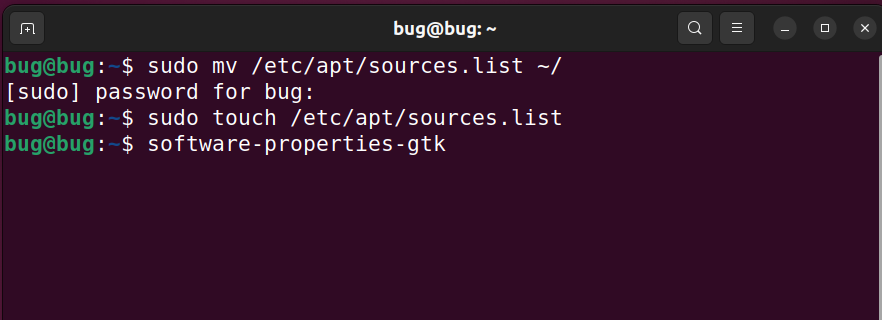
Step 1: Open the terminal in your machine. Use shortcut Ctrl + Alt + T to open the terminal. Move the corrupted sources.list file to a safe location using the command below and enter your password when prompted.
sudo mv /etc/apt/sources.list ~/
Step 2: Now create the new sources.list file in the directory /etc/apt using the touch command.
sudo touch /etc/apt/sources.list
2. Enable Default Repositories
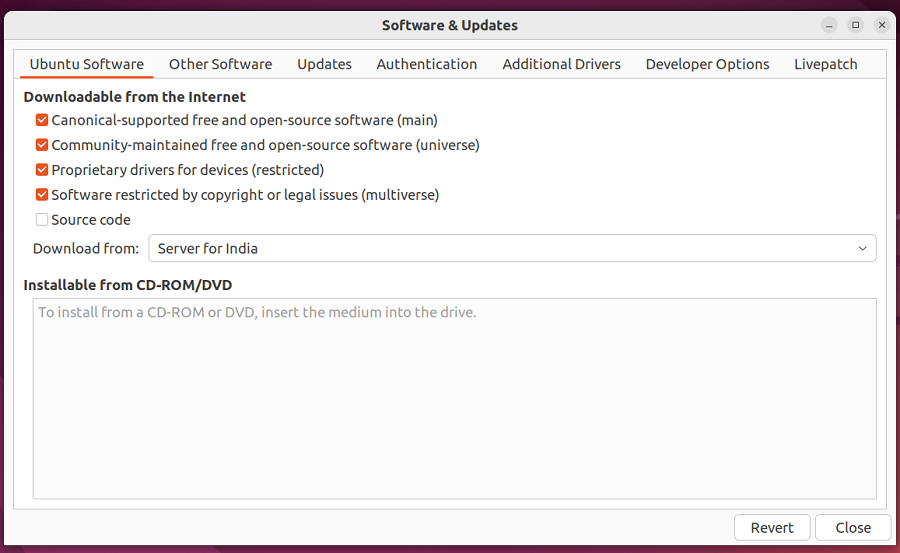
Step 1: Now open Software and Updates by searching in the menu or by typing the below command in the terminal
software-properties-gtk
Step 2: Then, change the server to the Main server or to any other server of your choice from the option Download from the Internet. We must enable some repositories from the new window to create new sources.list file in /etc/apt/ directory.
3. Remove Unwanted PPAs
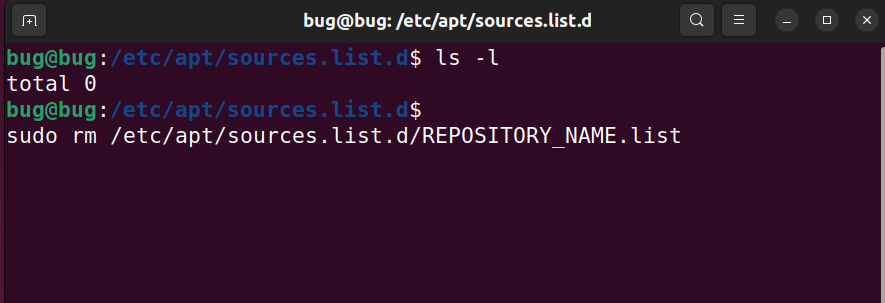
Step 1: If you have too many PPAs installed in your system, they often mess up your system. To see the list of all the installed repositories on your Ubuntu system, open the Terminal and type the command :
ls -l etc/apt/source.list.d/
Step 2: Run this command to remove the PPA you want. Replace REPOSITORY_NAME with the name of PPA.
sudo rm /etc/apt/sources.list.d/REPOSITORY_NAME.list
4. Run Update
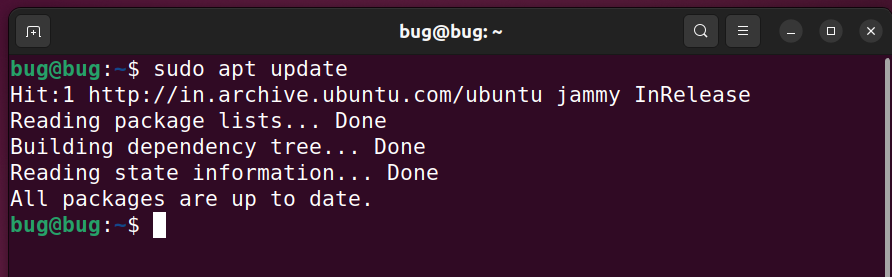
Step 1: Now we have done all the steps successfully. And now you are ready to run an update. Run the below command.
sudo apt update
Type your password when asked and press Enter.
Step 2: We have successfully restored the default state of the apt package manager in your Ubuntu machine. We can now upgrade your system
sudo apt upgrade
Last Updated :
11 Jul, 2022
Like Article
Save Article