На чтение 12 мин. Просмотров 19.3k.

Функция VBA InStr является одной из наиболее часто используемых функций в VBA. Он используется для нахождения текста внутри строки и действительно отлично справляется с работой.
Тем не менее, она часто используется, чтобы помочь извлечь часть строки, и эту задачу она выполняет плохо.
Если вы обнаружили, что извлечение текста в VBA является болезненным процессом, тогда читайте дальше. Эта статья покажет вам более простой и лучший способ, используя три реальных примера!
Содержание
- Краткое руководство к статье
- Краткая справка
- Введение
- Когда VBA InStr, Left, Right и Mid полезны
- Работа со строками различной длины
- Использование функции VBA InStr с Mid
- Функция Split
- Пример 1: Получение части имени файла
- Пример 2: диапазон IP-адресов
- Пример 3. Проверьте правильность имени файла
- Заключение
Краткое руководство к статье
В следующей таблице приведено краткое руководство к тому, что рассматривается в этой статье.
| Строка | Тип | Задача | Как |
| 1234ABC334 | Фиксированный размер | Оставить слева 4 символа | Left(s,4) |
| 1234ABC334 | Фиксированный размер | Оставить справа 3 символа |
Right(s,3) |
| 1234ABC334 | Фиксированный размер | Оставить 5, 6, 7 символы | Mid(s,5,3) |
| «Иван Петрович Сидоров» |
Переменный размер |
Оставить имя | Split(s,» «)(0) |
| «Иван Петрович Сидоров» |
Переменный размер |
Оставить отчество |
Split(s,» «)(1) |
| «Иван Петрович Сидоров» |
Переменный размер |
Оставить фамилию |
Split(s,» «)(2) |
| «Иван Петрович Сидоров» |
Переменный размер |
Оставить фамилию |
Dim v As Variant v = Split(s, » «) lastname= v(UBound(v)) |
Краткая справка
Чтобы узнать больше об элементах, упомянутых в статье, перейдите по следующим ссылкам:
- Если вы хотите узнать больше о функциях InStr или InStrRev, пожалуйста, прочитайте Поиск в строке.
- Если вы хотите узнать больше о функциях Mid, Left или Right, посмотрите раздел Извлечение части строки.
- Для получения дополнительной информации о функции Split проверьте Строка в массив, используя Split.
- Оператор Like включен в Сравнение строк с шаблоном
Я использую Debug.Print в моих примерах. Он печатает значения в Immediate Window, которое вы можете просмотреть, нажав Ctrl + G (или выберите View-> Immediate Window)
Введение
В этой статье я собираюсь показать вам лучший способ извлечения символов из строки, чем использование функции VBA InStr с Left, Right или Mid.
Эта статья разбита следующим образом:
- Раздел 1: Как извлечь из строк фиксированного размера.
- Раздел 2: Как извлечь из строк переменного размера.
- Раздел 3: Как извлечь из строки переменного размера, используя функцию Split.
- Разделы с 4 по 6: некоторые примеры из реальной жизни.
Когда VBA InStr, Left, Right и Mid полезны
Если вы хотите проверить, содержит ли строка значение, InStr подходит для этой работы. Если вы хотите сделать простое извлечение, то отлично подойдут Left, Right и Mid.
Использование InStr для проверки, содержит ли строка текст
В следующем примере мы проверяем, содержит ли ФИО «Петрович». Если возвращаемое значение InStr больше нуля, то строка содержит значение, которое мы проверяем.
' Проверьте, содержит ли строка Петрович
If InStr("Иван Петрович Сидоров", "Петрович") > 0 Then
Debug.Print "Найдено"
End If
Извлечение с Left, Right и Mid
Функция Left используется для получения символов слева от строки.
Функция Right используется для получения символов справа от строки.
Функция Mid используется для середины строки. Она такая же, как
Left, за исключением того, что вы даете ему стартовую позицию.
Sub IzvlechTekst()
Dim s As String: s = "ABCD-7789.WXYZ"
Debug.Print Left(s, 2) ' Печатает AB
Debug.Print Left(s, 4) ' Печатает ABCD
Debug.Print Right(s, 2) ' Печатает YZ
Debug.Print Right(s, 4) ' Печатает WXYZ
Debug.Print Mid(s, 1, 2) ' Печатает AB
Debug.Print Mid(s, 6, 4) ' Печатает 7789
End Sub
Эти три функции работают нормально, если требуемый текст всегда одинакового размера и в одном и том же месте. Для других сценариев они требуют использования InStr, чтобы найти определенную позицию в строке. Это усложняет их использование.
Используйте Left, Right или Mid, когда символы всегда будут в одной и той же позиции.
Работа со строками различной длины
Многие из строк, с которыми вы имеет дело, разной длины. Простой пример — когда у вас есть дело со списком имен. Длина строки и требуемая часть (например, имя) могут каждый раз отличаться. Например:
Brooke Hilt
Pamela Jurado
Zack Kinzel
Eddy Wormley
Kaitlyn Rainer
Jacque Trickett
Kandra Stanbery
Margo Hoppes
Berenice Meier
Garrett Hyre
(Если вам нужен случайный список имен, попробуйте этот генератор случайных имен)
Использование функции VBA InStr с Left
В следующем примере мы собираемся получить имя из строки. В этой строке первое имя — это имя перед первым пробелом.
Мы используем функцию VBA InStr, чтобы получить позицию первого пробела. Мы хотим получить все символы до пробела. Мы вычитаем одну из позиции, так как это дает нам позицию последней буквы имени.
Sub PoluchitImya()
Dim s As String, lPosition As Long
s = "John Henry Smith"
' Печатает John
lPosition = InStr(s, " ") - 1
Debug.Print Left(s, lPosition)
s = "Lorraine Huggard"
' Печатает Lorraine
lPosition = InStr(s, " ") - 1
Debug.Print Left(s, lPosition)
End Sub
Давайте посмотрим на первый пример в приведенном выше коде. Первый пробел находится в позиции 5. Мы вычтем 1, что дает нам позицию 4. Это позиция последней буквы John, т.е.
Затем мы даем 4 функции Left, и она возвращает первые четыре символа, например, «John»
Мы можем выполнить ту же задачу в одной строке, передав возвращаемое значение из InStr в функцию Left.
Dim s As String
s = "John Henry Smith"
' Печатает John
Debug.Print Left(s, InStr(s, " ") - 1)
Использование функции VBA InStr с Right
В этом примере мы получим последнее слово в строке, то есть Smith. Мы можем использовать функцию InStrRev. Это то же самое, что InStr, за исключением того, что поиск выполняется с конца строки.
Важно отметить, что InStrRev дает нам позицию с начала строки. Поэтому нам нужно использовать его немного иначе, чем мы использовали InStr и Left.
Sub PoluchitFamiliyu()
Dim s As String: s = "John,Henry,Smith"
Dim Position As Long, Length As Long
Position = InStrRev(s, ",")
Length = Len(s)
' Печатает Smith
Debug.Print Right(s, Length - Position)
' Альтернативный метод. Печатает Smith - делает в одну строку
Debug.Print Right(s, Len(s) - InStrRev(s, ","))
End Sub
Как работает приведенный выше пример:
- Мы получаем позицию последнего пробела, используя InStrRev: 11
- Мы получаем длину строки: 16.
- Вычитаем позицию из длины: 16-11 = 5
- Мы даем 5 функции Right и возвращаем Smith
Использование функции VBA InStr с Mid
В следующем примере мы получим «Henry» из строки. Слово, которое мы ищем, находится между первым и вторым пробелом.
Мы будем использовать функцию Mid здесь.
Sub PoluchitVtoroeImya()
Dim s As String: s = "John Henry Smith"
Dim firstChar As Long, secondChar As Long
Dim count As Long
' Найти пробел плюс 1. Результат 6
firstChar = InStr(s, " ") + 1
' Найти 2-й пробел. Результат 11
secondChar = InStr(firstChar, s, " ")
' Получить число символов. Результат 5
count = secondChar - firstChar
' Печатает Henry
Debug.Print Mid(s, firstChar, count)
End Sub
Как видите, это сложно сделать и требует немного усилий, чтобы выяснить. Нам нужно найти первое место. Тогда нам нужно найти второе место. Затем мы должны вычесть одно из другого, чтобы дать нам количество символов, которые нужно взять.
Если у вас есть строка с большим количеством слов, то это может быть очень сложно. К счастью для нас, гораздо проще было извлечь символы из строки. Это называется функцией Split.
Функция Split
Мы можем использовать функцию Split для выполнения приведенных выше примеров. Функция Split разбивает строку на массив. Тогда мы можем легко получить доступ к каждому элементу.
Давайте попробуем те же три примера еще раз, и на этот раз мы будем использовать Split.
Dim s As String: s = "John Henry Smith"
Debug.Print Split(s, " ")(0) ' John
Debug.Print Split(s, " ")(1) ' Henry
Debug.Print Split(s, " ")(2) ' Smith
Ого! Какая разница с использованием Split. Как это работает:
- Функция Split разбивает строку везде, где есть пробел.
- Каждый элемент помещается в массив, начиная с нуля.
- Используя номер местоположения, мы можем получить доступ к элементу массива.
В следующей таблице показано, как может выглядеть массив после использования Split.
Примечание: первая позиция в массиве равна нулю. Наличие нулевых массивов является стандартным в языках программирования.
| 0 | 1 | 2 |
| John | Henry | Smith |
В приведенном выше коде мы разделяем строку каждый раз, когда ее используем. Мы также можем разделить строку один раз и сохранить ее в переменной массива. Тогда мы можем получить к нему доступ, когда захотим.
Sub SplitName()
Dim s As String: s = "John Henry Smith"
Dim arr() As String
arr = Split(s, " ")
Debug.Print arr(0) ' John
Debug.Print arr(1) ' Henry
Debug.Print arr(2) ' Smith
End Sub
Если вы хотите узнать больше о массивах, я написал о них целую статью под названием «Полное руководство по использованию массивов в Excel VBA».
В следующих разделах мы рассмотрим примеры из реальной жизни. Вы увидите преимущество использования Split вместо функции InStr.
Пожалуйста, не стесняйтесь попробовать это сами. Это отличный способ учиться, и вы можете повеселиться, пытаясь понять их (или, может быть, только у меня так!)
Пример 1: Получение части имени файла
Представьте, что мы хотим извлечь числа из следующих имен файлов
«VB_23476_Val.xls»
«VV_987_Val.txt»
«VZZA_12223_Val.doc»
Это похоже на пример, где мы получаем второй элемент. Чтобы получить значения здесь, мы используем подчеркивание (то есть «_»), чтобы разбить строку. Смотрите пример кода ниже:
Sub PoluchitNomer()
' Печатает 23476
Debug.Print Split("VB_23476_Val.xls", "_")(1)
' Печатает 987
Debug.Print Split("VV_987_Val.txt", "_")(1)
' Печатает 12223
Debug.Print Split("ABBZA_12223_Val.doc", "_")(1)
End Sub
В реальном мире вы обычно читаете такие строки из разных ячеек. Допустим, эти имена файлов хранятся в ячейках от А1 до А3. Мы немного изменим приведенный выше код:
Sub ChitatNomera()
Dim c As Range
For Each c In Range("A1:A3")
' Разделите каждый элемент по мере его прочтения
Debug.Print Split(c, "_")(1)
Next c
End Sub
Пример 2: диапазон IP-адресов
Пример здесь взят из вопроса на веб-сайте StackOverflow.
У пользователя есть строка с IP-адресом в формате «BE-ABCDDD-DDS 172.16.23.3».
Он хочет, чтобы IP в диапазоне от 172,16 до 172,31 был действительным. Так например:
- «BE-ABCDDD-DDS 172.16.23.3» действителен
- «BE-ABCDDD-DDS 172.25.23.3» действителен
- «BE-ABCDDED-DDS 172.14.23.3» не действителен
- «BE-ABCDDDZZ-DDS 172.32.23.3» не действителен
Вот как бы я это сделал. Сначала я разбил строку по периодам. Число, которое мы ищем, находится между первым и вторым периодом. Поэтому это второй пункт. Когда мы разделяем строку, она помещается на первую позицию в массиве (помните, что массив начинается с нулевой позиции).
Полученный массив будет выглядеть так:
| 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 |
| BE-ABCDDD-DDS 172 | 31 | 23 | 3 |
Код ниже показывает, как это сделать.
Sub IPAdd()
' Проверьте номер, чтобы проверить разные IP-адреса
Dim s1 As String: s1 = "BE-ABCDDD-DDS 172.31.23.3"
' Разбить строку, используя символ точки
Dim num As Long
num = Split(s1, ".")(1)
' Проверьте правильность номера
Debug.Print num >= 16 And num <= 31
End Sub
Пример 3. Проверьте правильность имени файла
В этом последнем примере мы хотим проверить правильность имени файла. Есть три правила.
- Должно заканчиваться на .pdf
- Он должен содержать АА
- Он должен содержать 1234 после А
В следующих таблицах показаны некоторые допустимые и недействительные элементы:
| Имя файла | Статус |
| AA1234.pdf | Действителен |
| AA_ljgslf_1234.pdf | Действителен |
| AA1234.pdf1 | Недействительно — не заканчивается на .pdf |
| 1234 AA.pdf | Недействительно — АА не до 1234 |
| 12_AA_1234_NM.pdf | Действителен |
Сначала мы сделаем это, используя функции InStr и Right.
Sub IspInstr()
Dim f As String: f = "AA_1234_(5).pdf"
' Сначала найдите АА, так как 1234 должен идти после
Dim lPos As Long: lPos = InStr(f, "AA")
' Ищите 1234 и убедитесь, что последние четыре символа - .pdf
Debug.Print InStr(lPos, f, "1234") > 0 And Right(f, 4) = ".pdf"
End Sub
Этот код очень грязный. К счастью для нас, у VBA есть Сравнение с шаблоном. Мы можем проверить шаблон строки без необходимости искать элементы и позиции и т.д. Мы используем оператор Like в VBA для сопоставления с шаблоном. Пример ниже показывает, как это сделать.
Sub IspSravnenie()
Dim f As String: f = "AA_1234_(5).pdf"
' Определить шаблон
Dim pattern As String: pattern = "*AA*1234*.pdf"
' Проверьте каждый элемент по шаблону
Debug.Print f Like pattern ' ИСТИНА
End Sub
В приведенном выше примере звездочка в шаблоне относится к любому количеству символов.
Давайте разберем этот паттерн * AA * 1234 * .pdf
*- любая группа символов
AA — точные символы AА
*- любая группа символов
1234 — точные символы 1234
*- любая группа символов
.pdf — точные символы .pdf
Чтобы показать, что это работает правильно, давайте попробуем это на всех именах примеров в таблице.
Sub IspSravnenieTest()
' Создать коллекцию имен файлов
Dim coll As New Collection
coll.Add "AA1234.pdf"
coll.Add "AA_ljgslf_1234.pdf"
coll.Add "AA1234.pdf1"
coll.Add "1234 AA.pdf"
coll.Add "12_AA_1234_NM.pdf"
' Определить шаблон
Dim pattern As String: pattern = "*AA*1234*.pdf"
' Проверьте каждый элемент по шаблону
Dim f As Variant
For Each f In coll
Debug.Print f Like pattern
Next f
End Sub
На выходе:
ИСТИНА
ИСТИНА
ЛОЖЬ
ЛОЖЬ
ИСТИНА
Чтобы узнать больше о сопоставлении с шаблоном и ключевом слове Like, ознакомьтесь с этой публикацией.
Заключение
InStr и InStrRev действительно полезны только для простых задач, таких как проверка наличия текста в строке.
Left, Right и Mid полезны, когда положение текста всегда одинаково.
Функция Split — лучший способ извлечь переменную строку.
При попытке проверить формат строки, которая не является фиксированной по размеру, ключевое слово Like (т.е. Сопоставление с образцом) обычно обеспечивает более простое решение.
Excel VBA SubString
Excel VBA SubString is a very useful type of function in VBA which is used to slice and dice a data in a form of string. But in worksheet functions, we have three substring functions which are Left-right and mid function while in VBA we have Left-right mid and split functions as substring functions. As the name suggests itself substring function in VBA divides a string into multiple SubStrings. Also as explained above in VBA there are multiple VBA Substring functions. In this article, we will learn how to use these substring functions separately with examples. Before moving on with the examples first let us learn the syntax of these functions and what argument these functions take as input.
Syntax of Excel VBA SubString
Following are the different syntax:
Syntax of Left SubString Function:
Text string is the string we provide as input while the length is the number of characters we want from the input string.
Example: If we have a string as ANAND and want AN as substring the code will be
Left (“ANAND”,2)
Syntax of Right SubString Function:
Text string is the string we provide as input while the length is the number of characters we want from the input string.
Example: If we have a string as ANAND and use the same code as above the result will be
Right (“ANAND”,2)
This gives ND as a result.
Syntax of Mid SubString Function in VBA:
Text string is the string we provide as input and Start position is the position where we want the character to start for extraction while the length is the number of characters we want from the input string.
Example: We have a string as COMPUTER and we want to PUT as the substring then the code will be as follows:
MID (“COMPUTER”,4,3)
Syntax of Split SubString Function:
- Expression As String: This is a mandatory argument in the SPLIT function. It is basically the input string we provide.
- Delimiter: This is an optional argument. It is the specific delimiter that divides the string but by default, space is considered as default delimiter.
- Limit: This is also an optional argument. Limit means the maximum number of parts we want to do of a string. But again if we do not provide a limit to the function VBA treats it as default -1. This concludes that the string will be broken apart each time there is a delimiter in the string.
- Compare: This final argument is also an optional argument. Compare is a compare method which is one of the two below:
- Either it is 0 which means SPLIT will perform a binary comparison which means every character should match itself.
- Or it can be 1 which means the SPLIT function will do a textual comparison.
Split Function is the trickiest and most useful among them all the substring functions above. All the other three substring functions use one string as input while Split function uses an array of string.
For example if I write Split(“I AM A GOOD BOY”) will divide the string as separately (each word as separate). Now let us use these substrings functions in examples.
Note: To use VBA we need to have the developer’s tab enabled from the file tab under the Options section.
How to Use SubString Functions in VBA?
We will learn how to use the SubString function in Excel by using the VBA Code.
You can download this VBA SubString Excel Template here – VBA SubString Excel Template
Example #1
Left Substring Function in VBA. Let us use the first substring function in VBA. For this, follow the below steps:
Step 1: Go to the developer’s Tab and click on Visual Basic to open VB Editor.
Step 2: Insert a new module inside Visual Basic Editor (VBE). Click on Insert tab > select Module.
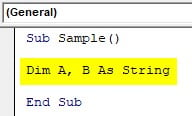
Step 3: Declare a sub-function to start writing the code.
Code:
Sub Sample() End Sub
Step 4: Declare two strings one to take input from the user and another to store the value of the result.
Code:
Sub Sample() Dim A, B As String End Sub
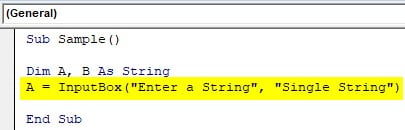
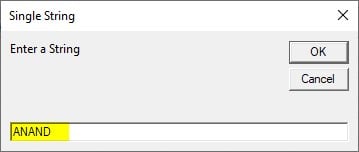
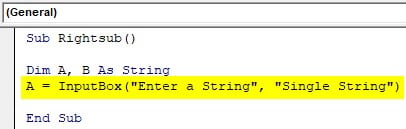
Step 5: Take the input from the user for the input string using the input box function.
Code:
Sub Sample() Dim A, B As String A = InputBox("Enter a String", "Single String") End Sub
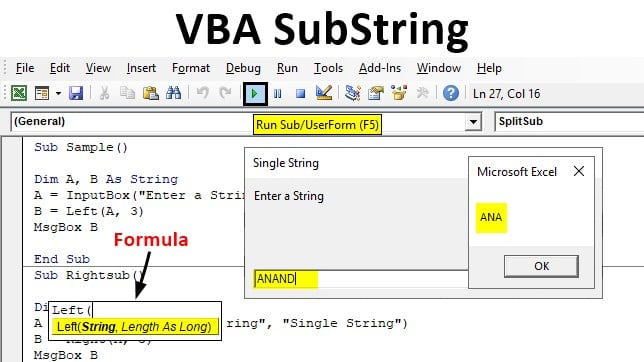
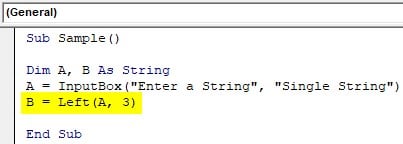
Step 6: In B variable store the value from the left function up to the third place.
Code:
Sub Sample() Dim A, B As String A = InputBox("Enter a String", "Single String") B = Left(A, 3) End Sub
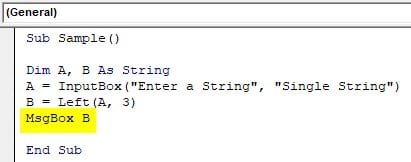
Step 7: Use Msgbox function to display the final result.
Code:
Sub Sample() Dim A, B As String A = InputBox("Enter a String", "Single String") B = Left(A, 3) MsgBox B End Sub
Step 8: Now run the above code by pressing the F5 key. and Write input String as ANAND.
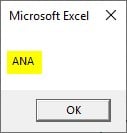
Step 9: When we press OK we see the result of the left substring function.
ANA is the three characters from the left of the string.
Example #2
RIGHT Substring function in VBA. For this, follow the below steps:
Step 1: In the same module declare another sub-function to start writing the code for the right substring function.
Code:
Sub Rightsub() End Sub
Step 2: Declare two variables A and B as string.
Code:
Sub Rightsub() Dim A, B As String End Sub
Step 3: Take the input from user and store the value in A variable.
Code:
Sub Rightsub() Dim A, B As String A = InputBox("Enter a String", "Single String") End Sub
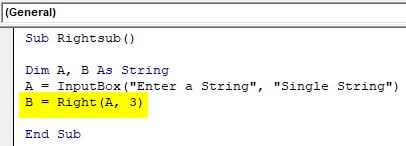
Step 4: Use the Right function on the string to the third place and store the value in B variable.
Code:
Sub Rightsub() Dim A, B As String A = InputBox("Enter a String", "Single String") B = Right(A, 3) End Sub
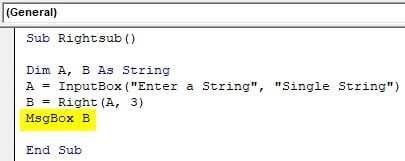
Step 5: Use Msgbox function to display the value of B.
Code:
Sub Rightsub() Dim A, B As String A = InputBox("Enter a String", "Single String") B = Right(A, 3) MsgBox B End Sub
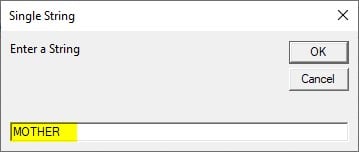
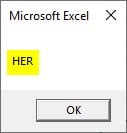
Step 6: Run the code and enter the input string as “MOTHER”.
Step 7: Press OK to see the result.
HER is the three characters from the right of the string.
Example #3
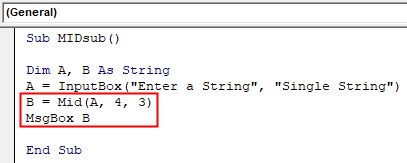
MID Substring Function in VBA. For this, follow the below steps:
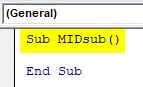
Step 1: In the same module declare another sub-function to start writing the code for Mid function.
Code:
Sub MIDsub() End Sub
Step 2: Declare two variables A and B as String.
Code:
Sub MIDsub() Dim A, B As String End Sub
Step 3: Take input from the user and store the value in Variable A.
Code:
Sub MIDsub() Dim A, B As String A = InputBox("Enter a String", "Single String") End Sub
Step 4: Use Mid function with starting position as 4 and length as 3 stores the value in B and display it using Msgbox function.
Code:
Sub MIDsub() Dim A, B As String A = InputBox("Enter a String", "Single String") B = Mid(A, 4, 3) MsgBox B End Sub
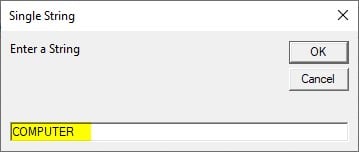
Step 5: Run the above code and give COMPUTER as input.
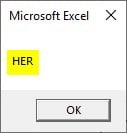
Step 6: Press OK to see the final result.
The substring PUT starts from 4th position and we have successfully extracted three characters.
Example #4
VBA Split SubString Function. For this, follow the below steps:
Step 1: In the same module declare a sub-function to start writing the code for sub-function.
Code:
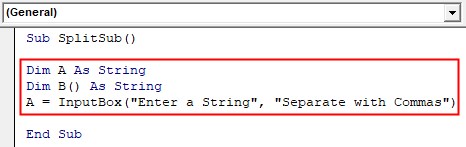
Sub SplitSub() End Sub
Step 2: Declare two Variables A as string and B as String array and take input string from the user and store it in Variable A.
Code:
Sub SplitSub() Dim A As String Dim B() As String A = InputBox("Enter a String", "Separate with Commas") End Sub
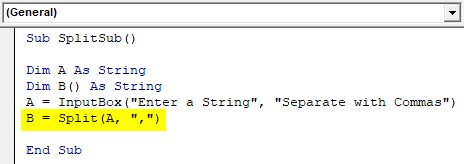
Step 3: Use the Split SubString function and store its value in Variable B.
Code:
Sub SplitSub() Dim A As String Dim B() As String A = InputBox("Enter a String", "Separate with Commas") B = Split(A, ",") End Sub
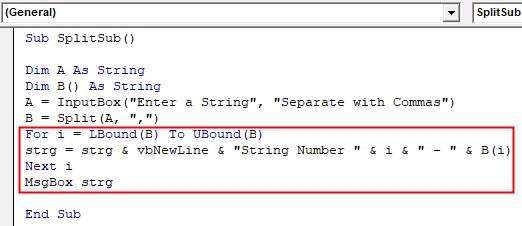
Step 4: Use For loop to display every SubString in a single line.
Code:
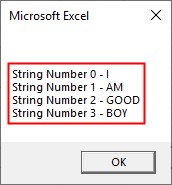
Sub SplitSub() Dim A As String Dim B() As String A = InputBox("Enter a String", "Separate with Commas") B = Split(A, ",") For i = LBound(B) To UBound(B) strg = strg & vbNewLine & "String Number " & i & " - " & B(i) Next i MsgBox strg End Sub
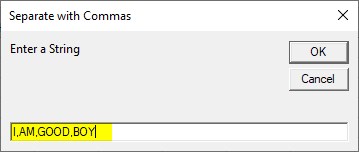
Step 5 Run the above code and give I,AM,GOOD,BOY as input.
Step 6: Press OK to see the result.
We used “,” as a delimiter in the above example.
Conclusion
Like worksheet substring functions VBA also has substring functions. They are Left Right Mid and Split Functions. Basically Substring functions divide a string or an array of string into multiple substrings. If we want a substring from the left of the string we use Left function or right in the opposite case. If we want a middle character of any given string we use MID functions. Also if we have an array of strings we use split functions.
Things to Remember
There are few things which we need to remember about Substring functions in VBA:
- It is similar to worksheet substring functions.
- Substring functions divide a given string into substrings.
- If we have an array of strings we use split functions.
- Only the input string in split function is mandatory while the others are optional.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to the VBA SubString. Here we discuss how to use the SubString function in Excel VBA along with practical examples and downloadable excel template. You can also go through our other suggested articles –
- VBA SendKeys
- VBA On Error Goto
- VBA Input
- VBA LBound
In this Article
- Extracting a Substring
- The VBA Left String Function
- The VBA Right String Function
- The VBA Mid String Function
- Finding the Position of a Substring
- The VBA Instr String Function
- The VBA InstrRev String Function
- Removing Spaces from a String
- The VBA LTrim String Function
- The VBA RTrim String Function
- The VBA Trim String Function
- VBA Case Functions
- The VBA LCase String Function
- The VBA UCase String Function
- The VBA StrConv Function
- Comparing Strings
- The VBA StrComp Function
- The VBA Like Operator
- Other Useful VBA String Functions
- The VBA Replace String Function
- The VBA StrReverse Function
- The VBA Len String Function
VBA has many string functions that will allow you to manipulate and work with text and strings in your code. In this tutorial, we are going to cover functions that will allow you to extract substrings from strings, remove spaces from strings, convert the case of a text or string, compare strings and other useful string functions.
The VBA Left String Function
The VBA Left Function allows you to extract a substring from a text or string starting from the left side. The syntax of the VBA Left String Function is:
Left(String, Num_of_characters) where:
- String – The original text.
- Num_of_characters – An integer that specifies the number of characters to extract from the original text starting from the beginning.
The following code shows you how to use the Left String Function to extract the first four characters of the given string:
Sub UsingTheLeftStringFunction()
Dim valueOne As String
Dim valueTwo As String
valueOne = "AutomateExcel"
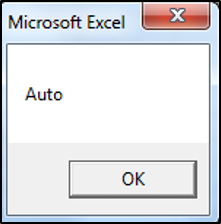
valueTwo = Left(valueOne, 4)
MsgBox valueTwo
End SubThe result is:
The Left Function has extracted the first four letters of AutomateExcel, which are Auto.
The VBA Right String Function
The VBA Right Function allows you to extract a substring from a text or string starting from the right side. The syntax of the VBA Right String Function is:
Right(String, Num_of_characters) where:
- String – The original text.
- Num_of_characters – An integer that specifies the number of characters to extract from the original text starting from the ending.
The following code shows you how to use the Right String Function to extract the last four characters of the string:
Sub UsingTheRightStringFunction()
Dim valueOne As String
Dim valueTwo As String
valueOne = "AutomateExcel"
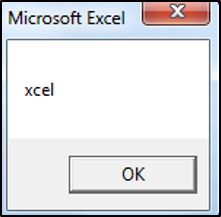
valueTwo = Right(valueOne, 4)
MsgBox valueTwo
End SubThe result is:
The Right Function has extracted the last four letters of AutomateExcel, which are xcel.
The VBA Mid String Function
The VBA Mid Function allows you to extract a substring from a text or string, starting from any position within the string that you specify. The syntax of the VBA Mid String Function is:
Mid(String, Starting_position, [Num_of_characters]) where:
- String – The original text.
- Starting_position – The position in the original text, where the function will begin to extract from.
- Num_of_characters (Optional) – An integer that specifies the number of characters to extract from the original text beginning from the Starting_position. If blank, the MID Function will return all the characters from the Starting_position.
The following code shows you how to use the Mid String Function to extract four characters, starting from the second position or character in the string:
Sub UsingTheMidStringFunction()
Dim valueOne As String
Dim valueTwo As String
valueOne = "AutomateExcel"
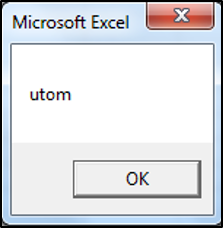
valueTwo = Mid(valueOne, 2, 4)
MsgBox valueTwo
End SubThe result is outputted to a msgbox:
The Mid Function has extracted the four letters of AutomateExcel starting from the second character/position/letter which are utom.
Finding the Position of a Substring
The VBA Instr String Function
The VBA Instr Function returns the starting position of a substring within another string. This function is case-sensitive. The syntax of the VBA Instr String Function is:
Instr([Start], String, Substring, [Compare]) where:
- Start (Optional) – This specifies the starting position for the function to search from. If blank, the default value of 1 is used.
- String – The original text.
- Substring– The substring within the original text that you want to find the position of.
- Compare (Optional) – This specifies the type of comparison to make. If blank, binary comparison is used.
-vbBinaryCompare – Binary comparison (Upper and lower case are regarded as different)
-vbTextCompare – Text comparison (Upper and lower case are regarded as the same)
-vbDatabaseCompare – Database comparison (This option is used in Microsoft Access only, and is a comparison based on the database)
The following code shows you how to use the Instr String Function to determine the first occurrence of the substring “Th” within the main string:
Sub UsingTheInstrStringFunction()
Dim valueOne As String
Dim positionofSubstring As Integer
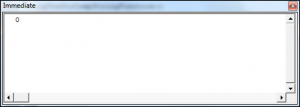
valueOne = "This is The Text "
positionofSubstring = InStr(1, valueOne, "Th")
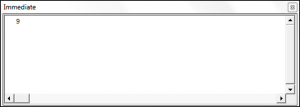
Debug.Print positionofSubstring
End SubThe result (outputted to the Immediate Window) is:
The Instr Function has returned the position of the first occurrence of the substring “Th” which is 1. Note this function includes the spaces in the count.
VBA Coding Made Easy
Stop searching for VBA code online. Learn more about AutoMacro — A VBA Code Builder that allows beginners to code procedures from scratch with minimal coding knowledge and with many time-saving features for all users!
Learn More
The VBA InstrRev String Function
The VBA InstrRev Function returns the starting position of a substring within another string but it starts counting the position, from the end of the string. This function is case-sensitive. The syntax of the VBA InstrRev String Function is:
InstrRev(String, Substring, [Start], [Compare]) where:
- String – The original text.
- Substring – The substring within the original text that you want to find the position of.
- Start (Optional) – This specifies the position to start searching from. If blank, the function starts searching from the last character.
- Compare (Optional) – This specifies the type of comparison to make. If blank, binary comparison is used.
-vbBinaryCompare – Binary comparison (Upper and lower case are regarded as different)
-vbTextCompare – Text comparison (Upper and lower case are regarded as the same)
-vbDatabaseCompare – Database comparison (This option is used in Microsoft Access only, and is a comparison based on the database)
The following code shows you how to use the InstrRev String Function to determine the first occurrence of the substring “Th” within the main string, starting from the end of the string:
Sub UsingTheInstrRevStringFunction()
Dim valueOne As String
Dim positionofSubstring As Integer
valueOne = "This is The Text "
positionofSubstring = InStrRev(valueOne, "Th")
Debug.Print positionofSubstring
End Sub
The result is outputted to the Immediate Window:
The InstrRev Function has returned the position of the first occurrence of the substring “Th”, but starting the counting from the end which is 9. Note this function includes the spaces in the count.
Removing Spaces from a String
The VBA LTrim String Function
The VBA LTrim Function removes all the leading spaces from a text or string. The syntax of the VBA LTrim String Function is:
LTrim(String) where:
- String – The original text.
The following code shows you how to use the VBA LTrim Function to remove the leading spaces in the given string:
Sub UsingTheLTrimStringFunction()
Dim valueOne As String
Dim valueTwo As String
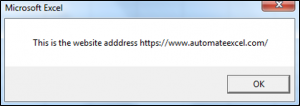
valueOne = " This is the website adddress https://www.automateexcel.com/excel/"
valueTwo = LTrim(valueOne)
MsgBox valueOne
MsgBox valueTwo
End SubThe results are:
The LTrim Function has removed the leading spaces for valuetwo, which is shown in the second Message Box.
VBA Programming | Code Generator does work for you!
The VBA RTrim String Function
The VBA RTrim Function removes all the trailing spaces from a text or string. The syntax of the VBA RTrim String Function is:
RTrim(String) where:
- String – The original text.
The following code shows you how to use the VBA RTrim Function to remove the trailing spaces in the given string:
Sub UsingTheRTrimStringFunction()
Dim valueOne As String
Dim valueTwo As String
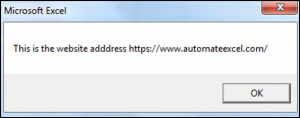
valueOne = "This is the website adddress https://www.automateexcel.com/excel/ "
valueTwo = RTrim(valueOne)
MsgBox valueOne
MsgBox valueTwo
End SubThe results delivered are:
The RTrim Function has removed the trailing spaces for valuetwo, which is shown in the second Message Box.
The VBA Trim String Function
The VBA Trim Function removes all leading and trailing spaces from a text or string. The syntax of the VBA Trim String Function is:
Trim(String) where:
- String – The original text.
The following code shows you how to use the VBA Trim Function to remove the leading and trailing spaces in the given string:
Sub UsingTheTrimStringFunction()
Dim valueOne As String
Dim valueTwo As String
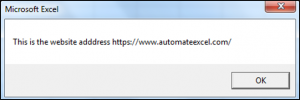
valueOne = " This is the website adddress https://www.automateexcel.com/excel/ "
valueTwo = Trim(valueOne)
MsgBox valueOne
MsgBox valueTwo
End SubThe results are:
The Trim Function has removed the leading and trailing spaces for valuetwo, which is shown in the second Message Box.
VBA Case Functions
The VBA LCase String Function
The VBA LCase Function converts letters in a text or string to lower case. The syntax of the VBA LCase String Function is:
LCase(String) where:
- String – The original text.
The following code shows you how to use the LCase String Function to convert all the letters in the given string to lower case:
Sub UsingTheLCaseStringFunction()
Dim valueOne As String
Dim valueTwo As String
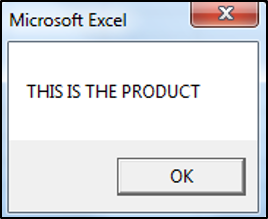
valueOne = "THIS IS THE PRODUCT"
valueTwo = LCase(valueOne)
MsgBox valueTwo
End SubThe result is:
The LCase Function has converted all the letters in the string to lower case.
The VBA UCase String Function
The VBA UCase Function converts letters in a text or string to upper case. The syntax of the VBA UCase String Function is:
UCase(String) where:
- String – The original text.
The following code shows you how to use the UCase String Function to convert all the letters in the given string to upper case:
Sub UsingTheUCaseStringFunction()
Dim valueOne As String
Dim valueTwo As String
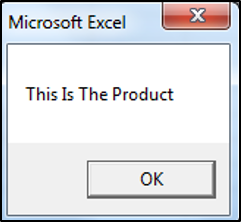
valueOne = "this is the product"
valueTwo = UCase(valueOne)
MsgBox valueTwo
End SubThe result is:
The UCase Function has converted all the letters in the string to upper case.
AutoMacro | Ultimate VBA Add-in | Click for Free Trial!
The VBA StrConv Function
The VBA StrConv Function can convert letters in a text or string to upper case, lower case, proper case or unicode depending on type of conversion you specify. The syntax of the VBA StrConv String Function is:
StrConv(String, Conversion, [LCID]) where:
- String – The original text.
- Conversion – The type of conversion that you want.
- [LCID] (Optional) – An optional parameter that specifies the LocaleID. If blank, the system LocaleID is used.
The following code shows you how to use the StrConv String Function to convert the string to proper case:
Sub UsingTheStrConvStringFunction()
Dim valueOne As String
Dim valueTwo As String
valueOne = "this is THE product"
valueTwo = StrConv(valueOne, vbProperCase)
MsgBox valueTwo
End SubThe result is:
You specify the type of conversion you want to perform using the conversion parameter:
- vbLowerCase converts all the letters in the text to lower case.
- vbUpperCase converts all the letters in the text to upper case.
- vbProperCase converts the first letter of each word in the text to upper case, while all the other letters are kept as lower case.
- vbUnicode converts a string to unicode.
- vbFromUnicode converts a string from unicode to the default code page of the system.
Comparing Strings
The VBA StrComp Function
The VBA StrComp String Function allows you to compare two strings. The function returns:
- 0 if the two strings match
- -1 if string1 is less than string2
- 1 if string1 is greater than string2
- A null value if either of the strings was Null
The following code shows you how to use the StrComp Function to compare two strings:
Sub UsingTheStrCompStringFunction()
Dim valueOne As String
Dim valueTwo As String
Dim resultofComparison As Integer
valueOne = "AutomateExcel"
valueTwo = "AutomateExcel"
resultofComparison = StrComp(valueOne, valueTwo)
Debug.Print resultofComparison
End SubThe result is:
The StrComp Function has found an exact match between the two strings and returned 0.
The VBA Like Operator
The VBA Like Operator allows you to compare a text or string to a pattern and see if there is a match. You would usually use the Like Operator in conjunction with wildcards. The following code shows you how to use the Like Operator:
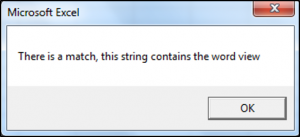
Sub UsingTheLikeOperatorInVBA()
Dim valueOne As String
valueOne = "Let's view the output"
If valueOne Like "*view*" Then
MsgBox "There is a match, this string contains the word view"
Else
MsgBox "No match was found"
End If
End SubThe result is:
The wildcards you can use with the Like Operator to find pattern matches include:
- ? which matches a single character
- # which matches a single digit
- * which matches zero or more characters
The following code shows you how you would use the Like Operator and the ? wildcard to match a pattern in your code:
Sub UsingTheLikeOperatorWithAWildcardInVBA()
Dim valueOne As String
valueOne = "The"
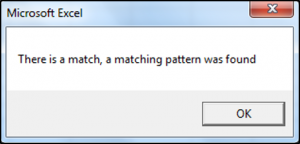
If valueOne Like "??e" Then
MsgBox "There is a match, a matching pattern was found"
Else
MsgBox "No match was found"
End If
End SubThe result delivered is:
AutoMacro | Ultimate VBA Add-in | Click for Free Trial!
Other Useful VBA String Functions
The VBA Replace String Function
The VBA Replace Function replaces a set of characters in a string with another set of characters. The syntax of the VBA Replace String Function is:
Replace(String, Find, Replace, [Start], [Count], [Compare]) where:
- String – The original text.
- Find – The substring to search for within the original text.
- Replace – The substring to replace the Find substring with.
- Start (Optional) – The position to begin searching from within the original text. If blank, the value of 1 is used and the function starts at the first character position.
- Count (Optional) – The number of occurrences of the Find substring in the original text to replace. If blank, all the occurrences of the Find substring are replaced.
- Compare (Optional) – This specifies the type of comparison to make. If blank, binary comparison is used.
-vbBinaryCompare – Binary comparison
-vbTextCompare – Text comparison
-vbDatabaseCompare – Database comparison (This option is used in Microsoft Access only, and is a comparison based on the database.)
The following code shows you how to use the Replace String Function:
Sub UsingTheReplaceStringFunction()
Dim valueOne As String
Dim valueTwo As String
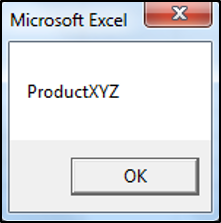
valueOne = "ProductABC"
valueTwo = Replace(valueOne, "ABC", "XYZ")
MsgBox valueTwo
End SubThe result is:
The Replace Function found the substring ABC within ProductABC and replaced it with the substring XYZ.
The VBA StrReverse Function
The VBA StrReverse Function reverses the characters in a given text or string. The syntax of the VBA StrReverse String Function is:
StrReverse(String) where:
- String – The original text.
The following code shows you how to use the VBA StrReverse Function to reverse the characters in the string Product:
Sub UsingTheStrReverseStringFunction()
Dim valueOne As String
Dim valueTwo As String
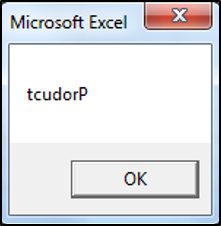
valueOne = "Product"
valueTwo = StrReverse(valueOne)
MsgBox valueTwo
End SubThe result is:
The VBA Len String Function
The VBA Len Function returns the number of characters in a text string. The syntax of the VBA Len String Function is:
Len(String) where:
- String – The original text.
The following code shows you how to use the Len String Function to determine the length of the string AutomateExcel:
Sub UsingTheLenFunction()
Dim valueOne As String
Dim stringLength As Integer
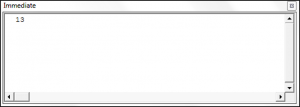
valueOne = "AutomateExcel"
stringLength = Len(valueOne)
Debug.Print stringLength
End SubThe result is:
The Len Function has counted all the characters in the text AutomateExcel, which is 13 letters.
Substring is one of the most popular functions in any programming language. It eases your tasks while dealing with strings. As the name suggests a substring function divides a string into different parts based on particular criteria.
There are multiple VBA Substring functions. In practical situations, these substring functions can be quite useful in extracting a portion of a string.
Today in this post I am going to explain all the VBA substring functions that you can use in Excel macros:
LEFT Substring function:
The LEFT function in Excel VBA is used for fetching a specified number of characters from the start of the string. The syntax of the LEFT function is as follows:
Left (text_string, length)
- Here ‘text_string’ refers to an input string that is to be separated.
- And ‘length’ refers to the number of characters to be extracted.
Examples:
Left ("Exceltrick", 5) 'gives an output "Excel"
Left ("SomeText", 4) 'gives the result "Some"
Note: Instead of using a hardcoded string in the first argument you can also fetch ‘text_string’ from your excel sheet like ActiveSheet.Range(«A1»).
Right Substring function:
The RIGHT Function in Excel VBA is just opposite to the LEFT function. It returns a specified number of characters from the end of the text string. The syntax of the RIGHT function is as follows:
Right (text_string, length)
- Here ‘text_string’ refers to an input string that is to be separated.
- And ‘length’ refers to the number of characters to be extracted but extraction begins from the right side.
Example:
Right ("Exceltrick", 5) 'gives an output "trick"
Right ("SomeText", 4) 'gives the result "Text"
Note: Instead of using a hardcoded string in the first argument you can also fetch ‘text_string’ from your excel sheet as ActiveSheet.Range(«A1»).
MID Substring function:
MID is a much better function than the first two, it gives you the ability to specify the start and end positions of the extracted string. The syntax of the MID VBA Substring function is as under:
Mid(text_string, start_position, Length)
- Here ‘text_string’ refers to an input string that is to be separated.
- ‘start_position’ refers to the numeric position from where extraction is to be started.
- And ‘length’ refers to the number of characters to be extracted.
Example:
MID ("Exceltrick", 2,4) 'gives an output "celt"
MID ("SomeText", 4,4) 'gives the result "Text"
Note: Instead of using a hardcoded string in the first argument you can also fetch ‘text_string’ from your excel sheet as ActiveSheet.Range(«A1»).
SPLIT Substring function:
The SPLIT function is another VBA function that can be used for sub-stringing or splitting a string. The SPLIT function can come very handy when you are dividing a text string into more than one parts based on a delimiter. The syntax of a split function is as under:
Split (text_string, Delimiter, limit, Compare)
- Here, ‘text_string’ refers to an input string that is to be separated.
- ‘Delimiter’ refers to the delimiter character which separates the string into parts. This is an optional argument, if it is left blank then, the space character » » is assumed to be the default delimiter.
- ‘limit’ refers to the maximum number of substring parts into which the string should be divided. It is also an optional argument, the default value is (-1) which means that substring should happen at every position where the delimiter is encountered.
- ‘compare’ is an optional numerical value that specifies the comparison to use when evaluating substrings.
Example:
For instance, you have a text string as «This is a text string» and now you have to break this string into individual words, so in this case, you will use space » » as a delimiter. The split function will be used as:
Split ("This is a text string", " ")
The result of this split function is an array of words: «This» «is» «a» «text» «string».
Recommended Reading: VBA Split Function
VBA Substring Macro Example:
Below I have created a macro that illustrates all the substring techniques available in VBA programming. This is a simple and self-explanatory macro, in this, I have simply divided a text string with the 4 methods that I have described above.
Below is the code that I have used for this macro:
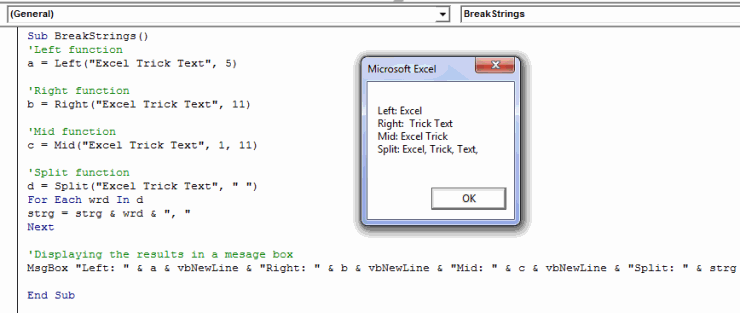
Sub BreakStrings()
'Left function
a = Left("Excel Trick Text", 5)
'Right function
b = Right("Excel Trick Text", 11)
'Mid function
c = Mid("Excel Trick Text", 1, 11)
'Split function
d = Split("Excel Trick Text", " ")
For Each wrd In d
strg = strg & wrd & ", "
Next
'Displaying the results in a mesage box
MsgBox "Left: " & a & vbNewLine & "Right: " & b & vbNewLine & "Mid: " & c & vbNewLine & "Split: " & strg
End Sub
So, this was all about VBA substring functions. Do share your view related to the topic.
Извлечение (вырезание) части строки с помощью кода VBA Excel из значения ячейки или переменной. Функции Left, Mid и Right, их синтаксис и аргументы. Пример.
Эта функция извлекает левую часть строки с заданным количеством символов.
Синтаксис функции Left:
Left(строка, длина)
- строка — обязательный аргумент: строковое выражение, из значения которого вырезается левая часть;
- длина — обязательный аргумент: числовое выражение, указывающее количество извлекаемых символов.
Если аргумент «длина» равен нулю, возвращается пустая строка. Если аргумент «длина» равен или больше длины строки, возвращается строка полностью.
Функция Mid
Эта функция извлекает часть строки с заданным количеством символов, начиная с указанного символа (по номеру).
Синтаксис функции Mid:
Mid(строка, начало, [длина])
- строка — обязательный аргумент: строковое выражение, из значения которого вырезается часть строки;
- начало — обязательный аргумент: числовое выражение, указывающее положение символа в строке, с которого начинается извлекаемая часть;
- длина — необязательный аргумент: числовое выражение, указывающее количество вырезаемых символов.
Если аргумент «начало» больше, чем количество символов в строке, функция Mid возвращает пустую строку. Если аргумент «длина» опущен или его значение превышает количество символов в строке, начиная с начального, возвращаются все символы от начальной позиции до конца строки.
Функция Right
Эта функция извлекает правую часть строки с заданным количеством символов.
Синтаксис функции Right:
Right(строка, длина)
- строка — обязательный аргумент: строковое выражение, из значения которого вырезается правая часть;
- длина — обязательный аргумент: числовое выражение, указывающее количество извлекаемых символов.
Если аргумент «длина» равен нулю, возвращается пустая строка. Если аргумент «длина» равен или больше длины строки, возвращается строка полностью.
Пример
В этом примере будем использовать все три представленные выше функции для извлечения из ФИО его составных частей. Для этого запишем в ячейку «A1» строку «Иванов Сидор Петрович», из которой вырежем отдельные компоненты и запишем их в ячейки «A2:A4».
|
Sub Primer() Dim n1 As Long, n2 As Long Range(«A1») = «Иванов Сидор Петрович» ‘Определяем позицию первого пробела n1 = InStr(1, Range(«A1»), » «) ‘Определяем позицию второго пробела n2 = InStr(n1 + 1, Range(«A1»), » «) ‘Извлекаем фамилию Range(«A2») = Left(Range(«A1»), n1 — 1) ‘Извлекаем имя Range(«A3») = Mid(Range(«A1»), n1 + 1, n2 — n1 — 1) ‘Извлекаем отчество Range(«A4») = Right(Range(«A1»), Len(Range(«A1»)) — n2) End Sub |
На практике часто встречаются строки с лишними пробелами, которые необходимо удалить перед извлечением отдельных слов.