4. Дисперсность. Удельная поверхность дисперсных систем, методы ее измерения
Основная характеристика дисперсных систем — размеры частиц, или дисперсность. Дисперсные системы делят на грубодисперсные (низкодисперсные) и тонкодисперсные (высокодисперсные), или коллоидные системы (коллоиды). В грубодисперсных системах частицы имеют размер от 10–4 см и выше, в коллоидных — от 10–4 до 10–5 — 10–7 см. Дисперсность определяется по трем измерениям тела, либо характеризуется величиной, обратной минимальному размеру и названной дисперсностью, либо через удельную площадь поверхности Sуд (отношение межфазной поверхности к объему тела). Количественной характеристикой дисперсности (раздробленности) вещества является степень дисперсности (степень раздробленности D) — величина, обратная размеру дисперсных частиц а: D = 1/a, где а равно диаметру сферических или волокнистых частиц, или длине ребра кубических частиц, или толщине пленок. Все частицы дисперсной фазы имеют одинаковые размеры — монодисперсная система. Частицы дисперсной фазы неодинакового размера — полидисперсная система. Соотношение между поверхностью и объемом характеризует удельная поверхность:
Sуд = S / V.
Для частиц сферической формы она равна:
Sуд = 4 πr2 / (4 / 3 πr) = 3 / r = 6 / d.
Для частиц кубической формы —
Sуд = 6l2 / l3 = 6 / l,
где r — радиус шара; d — его диаметр; l — длина ребра куба.
Дисперсность D связана с удельной поверхностью Sуд:
Sуд = S / V = k / d = kD,
где V — объем дисперсной фазы, мл.
Для сферических частиц уравнение принимает вид:
k — коэффициент формы частиц; d — диаметр частицы, м2.
Формула для расчета удельной поверхности (Sуд) системы с шарообразными частицами:
где n — число частиц, м3; S0 — поверхность каждой частицы.
где n1 — число частиц, кг; r — плотность вещества, г/см3.
Корреляционная спектроскопия рассеянного света: в определенном оптическом объеме V0, подсчитывают число частиц n. Зная концентрацию частиц С и n, находят объем частицы 

где d — плотность дисперсной фазы.
Зная объем, можно вычислить радиус частиц:
Зная радиус частиц, можно вычислить удельную поверхность Sуд.
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
A uniform (monodisperse) collection
A non-uniform (polydisperse) collection
In chemistry, the dispersity is a measure of the heterogeneity of sizes of molecules or particles in a mixture. A collection of objects is called uniform if the objects have the same size, shape, or mass. A sample of objects that have an inconsistent size, shape and mass distribution is called non-uniform. The objects can be in any form of chemical dispersion, such as particles in a colloid, droplets in a cloud,[1] crystals in a rock,[2]
or polymer macromolecules in a solution or a solid polymer mass.[3] Polymers can be described by molecular mass distribution; a population of particles can be described by size, surface area, and/or mass distribution; and thin films can be described by film thickness distribution.[citation needed]
IUPAC has deprecated the use of the term polydispersity index, having replaced it with the term dispersity, represented by the symbol Đ (pronounced D-stroke[4]) which can refer to either molecular mass or degree of polymerization. It can be calculated using the equation ĐM = Mw/Mn, where Mw is the weight-average molar mass and Mn is the number-average molar mass. It can also be calculated according to degree of polymerization, where ĐX = Xw/Xn, where Xw is the weight-average degree of polymerization and Xn is the number-average degree of polymerization. In certain limiting cases where ĐM = ĐX, it is simply referred to as Đ. IUPAC has also deprecated the terms monodisperse, which is considered to be self-contradictory, and polydisperse, which is considered redundant, preferring the terms uniform and non-uniform instead.
Overview[edit]
A uniform polymer (often referred to as a monodisperse polymer) is composed of molecules of the same mass.[5] Nearly all natural polymers are uniform.[6] Synthetic near-uniform polymer chains can be made by processes such as anionic polymerization, a method using an anionic catalyst to produce chains that are similar in length. This technique is also known as living polymerization. It is used commercially for the production of block copolymers. Uniform collections can be easily created through the use of template-based synthesis, a common method of synthesis in nanotechnology.[citation needed]
A polymer material is denoted by the term disperse, or non-uniform, if its chain lengths vary over a wide range of molecular masses. This is characteristic of man-made polymers.[7] Natural organic matter produced by the decomposition of plants and wood debris in soils (humic substances) also has a pronounced polydispersed character. It is the case of humic acids and fulvic acids, natural polyelectrolyte substances having respectively higher and lower molecular weights. Another interpretation of dispersity is explained in the article Dynamic light scattering (cumulant method subheading). In this sense, the dispersity values are in the range from 0 to 1.
The dispersity (Đ), also known as the polydispersity index (PDI) or heterogeneity index, is a measure of the distribution of molecular mass in a given polymer sample. Đ (PDI) of a polymer is calculated:
,
where 



Effect of polymerization mechanism[edit]
Typical dispersities vary based on the mechanism of polymerization and can be affected by a variety of reaction conditions. In synthetic polymers, it can vary greatly due to reactant ratio, how close the polymerization went to completion, etc. For typical addition polymerization, Đ can range around 5 to 20. For typical step polymerization, most probable values of Đ are around 2 —Carothers’ equation limits Đ to values of 2 and below.
Living polymerization, a special case of addition polymerization, leads to values very close to 1. Such is the case also in biological polymers, where the dispersity can be very close or equal to 1, indicating only one length of polymer is present.
Effect of reactor type[edit]
The reactor polymerization reactions take place in can also affect the dispersity of the resulting polymer. For bulk radical polymerization with low (<10%) conversion, anionic polymerization, and step growth polymerization to high conversion (>99%), typical dispersities are in the table below.[9]
| Polymerization Method | Batch Reactor | Plug Flow Reactor (PFR) | Homogeneous CSTR | Segregated CSTR |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Radical Polymerization (RP) | 1.5-2.0 | 1.5-2.0 | 1.5-2.0 | 1.5-2.0 |
| Anionic Polymerization | 1.0 + ε | 1.0 + ε | 2.0 | 1.0-2.0 |
| Step-Growth | 2.0 | 2.0 | Unbounded (~50) | Unbounded (~20-25) |
With respect to batch and plug flow reactors (PFRs), the dispersities for the different polymerization methods are the same. This is largely because while batch reactors depend entirely on time of reaction, plug flow reactors depend on distance traveled in the reactor and its length. Since time and distance are related by velocity, plug flow reactors can be designed to mirror batch reactors by controlling the velocity and length of the reactor. Continuously stirred-tank reactors (CSTRs) however have a residence time distribution and cannot mirror batch or plug flow reactors, which can cause a difference in the dispersity of final polymer.
The effects of reactor type on dispersity depend largely on the relative timescales associated with the reactor, and with the polymerization type. In conventional bulk free radical polymerization, the dispersity is often controlled by the proportion of chains that terminate via combination or disproportionation.[10] The rate of reaction for free radical polymerization is exceedingly quick, due to the reactivity of the radical intermediates. When these radicals react in any reactor, their lifetimes, and as a result, the time needed for reaction are much shorter than any reactor residence time. For FRPs that have a constant monomer and initiator concentration, such that the DPn is constant, the dispersity of the resulting monomer is between 1.5 and 2.0. As a result, reactor type does not affect dispersity for free radical polymerization reactions in any noticeable amount as long as conversion is low.
For anionic polymerization, a form of living polymerization, the reactive anion intermediates have the ability to remain reactive for a very long time. In batch reactors or PFRs, well-controlled anionic polymerization can result in almost uniform polymer. When introduced into a CSTR however, the residence time distribution for reactants in the CSTR affects the dispersity of the anionic polymer due to the anion lifetime. For a homogeneous CSTR, the residence time distribution is the most probable distribution.[11] Since the anionic polymerization dispersity for a batch reactor or PFR is basically uniform, the molecular weight distribution takes on the distribution of the CSTR residence times, resulting in a dispersity of 2. Heterogeneous CSTRs are similar to homogeneous CSTRs, but the mixing within the reactor is not as good as in a homogeneous CSTR. As a result, there are small sections within the reactor that act as smaller batch reactors within the CSTR and end up with different concentrations of reactants. As a result, the dispersity of the reactor lies between that of a batch and that of a homogeneous CSTR.[9]
Step growth polymerization is most affected by reactor type. To achieve any high molecular weight polymer, the fractional conversion must exceed 0.99, and the dispersity of this reaction mechanism in a batch or PFR is 2.0. Running a step-growth polymerization in a CSTR will allow some polymer chains out of the reactor before achieving high molecular weight, while others stay in the reactor for a long time and continue to react. The result is a much more broad molecular weight distribution, which leads to much larger dispersities. For a homogeneous CSTR, the dispersity is proportional to the square root of the Damköhler number, but for a heterogeneous CSTR, dispersity is proportional to the natural log of the Damköhler number.[9] Thus, for the similar reasons as anionic polymerization, the dispersity for heterogeneous CSTRs lies between that of a batch and a homogeneous CSTR.
Determination methods[edit]
- Gel permeation chromatography (also known as size-exclusion chromatography)
- Light scattering measurements such as dynamic light scattering
- Direct measurement via mass spectrometry, using matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization (MALDI) or electrospray ionization with tandem mass spectrometry (ESI-MS/MS)
See also[edit]
- Polyelectrolyte – Polymers whose repeating units bear an electrolyte group
References[edit]
- ^ Martins, J. A.; Silva Dias, M. A. F. (2009). «The impact of smoke from forest fires on the spectral dispersion of cloud droplet size distributions in the Amazonian region» (PDF). Environmental Research Letters. 4 (1): 015002. Bibcode:2009ERL…..4a5002M. doi:10.1088/1748-9326/4/1/015002.
- ^ Higgins, Michael D. (2000). «Measurement of crystal size distributions» (PDF). American Mineralogist. 85 (9): 1105–1116. Bibcode:2000AmMin..85.1105H. doi:10.2138/am-2000-8-901. S2CID 101422067. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2017-08-08.
- ^ Okita, K.; Teramoto, A.; Kawahara, K.; Fujita, H. (1968). «Light scattering and refractometry of a monodisperse polymer in binary mixed solvents». The Journal of Physical Chemistry. 72: 278–285. doi:10.1021/j100847a053.
- ^ Stepto, R. F. T.; Gilbert, R. G.; Hess, M.; Jenkins, A. D.; Jones, R. G.; Kratochvíl P. (2009). «Dispersity in Polymer Science» Pure Appl. Chem. 81 (2): 351–353. DOI:10.1351/PAC-REC-08-05-02.
- ^ «monodisperse polymer (See: uniform polymer)». IUPAC Gold Book. International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry. doi:10.1351/goldbook.M04012. Retrieved 25 January 2012.
- ^ Brown, William H.; Foote, Christopher S.; Iverson, Brent L.; Anslyn, Eric V. (2012). Organic chemistry (6 ed.). Cengage Learning. p. 1161. ISBN 978-0-8400-5498-2.
- ^ «Definition of polydisperse — Chemistry Dictionary».
- ^ Peter Atkins and Julio De Paula, Atkins’ Physical Chemistry, 9th edition (Oxford University Press, 2010, ISBN 978-0-19-954337-3)
- ^ a b c Dotson, Neil A.; Galván, Rafael; Laurence, Robert L.; Tirrell, Matthew (1996). Polymerization Process Modeling. VCH Publishers, Inc. pp. 260–279. ISBN 1-56081-693-7.
- ^ Chanda, Manas (2013). Introduction to Polymer Science and Chemistry: A Problem-Solving Approach, Second Edition. CRC Press. ISBN 978-1-4665-5384-2.
- ^ Levenspiel, Octave (1999). Chemical Reaction Engineering, Third Edition. John Wiley & Sons. ISBN 0-471-25424-X.
External links[edit]
- Introduction to Polymers
Дисперсность
Предположим,
что полученные дисперсные системы с
одинаковым составом дисперсных фаз и
дисперсионных сред. Различие заключается
лишь в том, что одна система содержит
дисперсную фазу в виде частиц одного и
того же размера, а другая
частицы разного размера. Это простейший
пример, когда различие между системами
устанавливается указанием размера
частиц. Однако наиболее часто встречаются
системы, в которых частицы дисперсной
фазы неодинаковы по размерам.
Мерой
раздробленности всякой дисперсной
системы может служить либо поперечный
размер частиц а
(для сферических частиц – диаметр d,
а частиц, имеющих форму куба, – ребро
l),
либо обратная ему величина
,
называемая обычно просто дисперсностью,
либо,
удельная поверхность Sуд,
т. е. межфазная поверхность, приходящаяся
на единицу объема дисперсной фазы. Все
эти величины взаимосвязаны. Чем меньше
размеры частиц, тем больше дисперсность
или удельная поверхность наоборот.
В
качестве характеристики, используемой
для сравнения дисперсных систем, В.
Оствальд предложил применять степень
дисперсности,
мерой которой
служит удельная поверхность.
Удельной
поверхностью
называют площадь раздела фаз, на единицу
массы или объема дисперсной фазы. Если
частицы дисперсной фазы имеют форму
куба или сферы и одинаковы по размерам,
то удельная поверхность системы
вычисляется по формуле
Sуд
=
(1)
где
Sч
поверхность частицы;
Vч
ее объем;
а
длина ребра кубической частицы (диаметр
сферической частицы).
В общем случае для
систем, содержащих одинаковые частицы
произвольной формы,
Sуд
= kа1,
(2)
где
k
коэффициент, зависящий от формы частиц
(для пленки k
= 2, для бруска k
= 4, для куба и сферы k
= 6);
а
выбранный линейный размер частиц.
Удельная поверхность
системы с частицами одной формы, но
разных размеров определяется по формуле
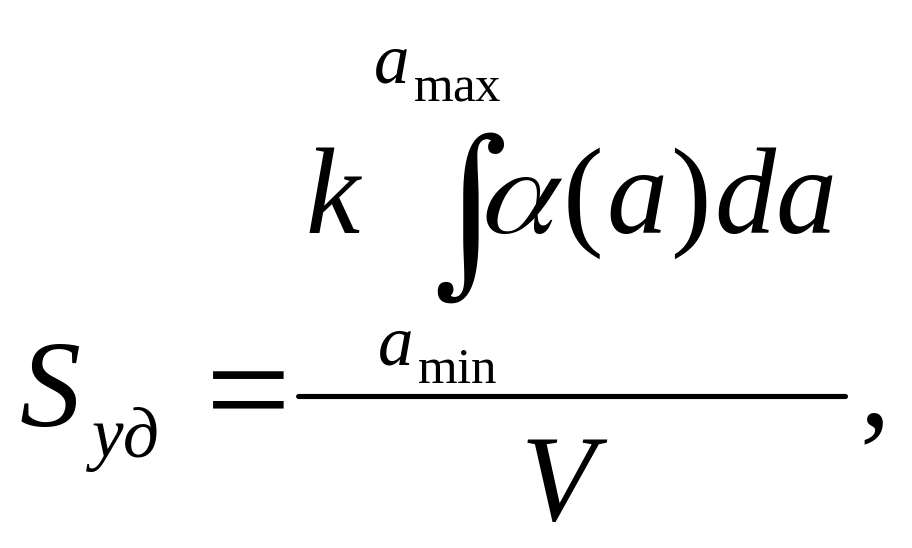
где
(а)
относительное содержание в системе
частиц дисперсной фазы, имеющих выбранный
линейный размер а;
amin
и amax
минимальный и максимальный размеры
частиц дисперсной фазы;
V
объем дисперсной фазы.
Число сферических
частиц в 1 кг дисперсной фазы
n
= (4r3/3)1,
(3)
где
плотность вещества дисперсной фазы,
кг/м3;
r
– радиус частиц, м.
удельная
поверхность раздела фаз определяется
по формуле:
Sуд
= Sуд
.
n (4)
C
учетом плотности вещества дисперсной
фазы формула (2) принимает вид:
Sуд
= k(а)1
(5)
Используя
удельную поверхность как усредненную
характеристику, можно сравнивать микро-
и ультрамикрогетерогенные системы с
пористыми телами, также включаемыми в
класс дисперсных
систем.
Например, средний размер частиц в
ультрамикрогетерогенных системах можно
принять равным 108
м, чему
соответствует удельная поверхность
109
м2/м3.
Имеющие развитую внутреннюю поверхность
активированный уголь и силикагель по
этому показателю близки к
ультрамикрогетерогенным систем; их
удельная поверхность соответственно
8 .105
м2/кг
и 4.105
м2/кг.
Соседние файлы в предмете [НЕСОРТИРОВАННОЕ]
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #







