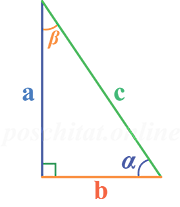
Калькулятор прямоугольного треугольника вычисляет все свойства прямоугольного треугольника, такие как площадь, периметр, стороны и углы, при условии достаточного подмножества этих свойств. Прямоугольный треугольник — это многоугольник с тремя вершинами (углами) и тремя ребрами (сторонами), две из которых пересекаются под прямым углом. Прямоугольный треугольник статья в Википедии
Related calculators:
Калькулятор произвольного треугольника
Калькулятор равностороннего треугольника
Калькулятор равнобедренного треугольника
Показать правила синтаксиса
В прямоугольном треугольнике, зная катеты, можно найти гипотенузу через теорему Пифагора. Для этого нужно извлечь квадратный корень из суммы квадратов катетов.
с=√(a^2+b^2 )
Площадь прямоугольного треугольника равна половине произведения катетов, а периметр – сумме катетов и гипотенузы.
S=ab/2
P=a+b+c=a+b+√(a^2+b^2 )
Углы в прямоугольном треугольнике найти, зная катеты, тоже невероятно просто. Отношение одного катета к другому будет тангенсом противоположного угла и котангенсом близлежащего. (рис. 79.1)
tanα=a/b
cotα=a/b
С другой стороны, зная один из углов, можно найти второй, отняв его из 90 градусов.
α=90°-β
Высота у прямоугольного треугольника всего одна, и она относится к любому из катетов как косинус прилежащего к нему угла. (рис. 79.2)
cosα=h/b
h=b cosα
cosβ=h/a
h=a cosβ
Формула медианы в прямоугольном треугольнике преобразуется в отношение гипотенузы к двум или радикала из суммы квадратов катетов к двум, если даны только катеты. (рис. 79.3)
m_c=√(2a^2+2b^2-c^2 )/2=√(2c^2-c^2 )/2=√(c^2 )/2=c/2=√(a^2+b^2 )/2
m_b=√(2a^2+2c^2-b^2 )/2=√(2a^2+2a^2+2b^2-b^2 )/2=√(4a^2+b^2 )/2
m_a=√(2c^2+2b^2-a^2 )/2=√(2a^2+2b^2+2b^2-a^2 )/2=√(4b^2+a^2 )/2
Биссектриса, опущенная на гипотенузу, вычисляется аналогично произвольному треугольнику, с подстановкой радикала вместо гипотенузы. (рис.79.4)
l_c=√(ab(a+b+c)(a+b-c))/(a+b)=√(ab((a+b)^2-с^2))/(a+b)=√(ab(a^2+2ab+b^2-a^2-b^2))/(a+b)=√(ab*2ab)/(a+b)=(ab√2)/(a+b)
l_a=√(bc(a+b+c)(b+c-a) )/(b+c)=√(bc((b-c)^2-a^2 ) )/(b+c)=√(bc(b^2+2bc+c^2-a^2 ) )/(b+c)=√(bc(b^2+2bc+b^2 ) )/(b+c)=√(bc(2b^2+2bc) )/(b+c)=(b√(2c(b+c) ))/(b+c)
l_b=√(ac(a+b+c)(a+c-b) )/(a+c)=(a√(2c(a+c) ))/(a+c)
Средние линии прямоугольного треугольника образуют внутри него еще один прямоугольный треугольник. Внутренний треугольник будет подобен внешнему, так как средние линии параллельны катетам и гипотенузе, и равны соответственно их половинам. Поскольку гипотенуза неизвестна, для нахождения средней линии M_c нужно подставить радикал из теоремы Пифагора. (рис.79.7)
M_a=a/2
M_b=b/2
M_c=c/2=√(a^2+b^2 )/2
Радиус вписанной окружности в прямоугольном треугольнике вычисляется по упрощенной формуле для произвольного треугольника, а радиус описанной окружности является половиной гипотенузы и совпадает с медианой. (рис. 79.5, 79.6)
r=(a+b-c)/2=(a+b-√(a^2+b^2 ))/2
R=m=c/2=√(a^2+b^2 )/2
Как найти стороны прямоугольного треугольника
- Главная
- /
- Математика
- /
- Геометрия
- /
- Как найти стороны прямоугольного треугольника
Чтобы посчитать стороны прямоугольного треугольника воспользуйтесь нашим очень удобным онлайн калькулятором:
Онлайн калькулятор
Чтобы вычислить длины сторон прямоугольного треугольника вам нужно знать следующие параметры (либо-либо):
- для гипотенузы (с):
- длины катетов a и b
- длину катета (a или b) и прилежащий к нему острый угол (β или α, соответственно)
- длину катета (a или b) и противолежащий к нему острый угол (α или β, соответственно)
- для катета:
- длину гипотенузы (с) и длину одного из катетов
- длину гипотенузы (с) и прилежащий к искомому катету (a или b) острый угол (β или α, соответственно)
- длину гипотенузы (с) и противолежащий к искомому катету (a или b) острый угол (α или β, соответственно)
- длину одного из катетов (a или b) и прилежащий к нему острый угол (β или α, соответственно)
- длину одного из катетов (a или b) и противолежащий к нему острый угол (α или β, соответственно)
Введите их в соответствующие поля и получите результат.
Найти гипотенузу (c)
Найти гипотенузу по двум катетам
Катет a =
Катет b =
Гипотенуза c =
0
Чему равна гипотенуза (сторона с) если известны оба катета (стороны a и b)?
Формула
Теорема Пифагора: квадрат гипотенузы равен сумме квадратов катетов:
c² = a² + b²
следовательно: c = √a² + b²
Пример
Для примера посчитаем чему равна гипотенуза прямоугольного треугольника если катет a = 3 см, а катет b = 4 см:
c = √3² + 4² = √9 + 16 = √25 = 5 см
Найти гипотенузу по катету и прилежащему к нему острому углу
Катет (a или b) =
Прилежащий угол (β или α) =
Гипотенуза c =
0
Чему равна гипотенуза (сторона с) если известны один из катетов (a или b) и прилежащий к нему угол?
Формула
c = a/cos(β) = b/cos(α)
Пример
Для примера посчитаем чему равна гипотенуза прямоугольного треугольника если катет a = 2 см, а прилежащий к нему ∠β = 60°:
c = 2 / cos(60) = 2 / 0.5 = 4 см
Найти гипотенузу по катету и противолежащему к нему острому углу
Катет (a или b) =
Противолежащий угол (α или β) =
Гипотенуза c =
0
Чему равна гипотенуза (сторона с) если известны один из катетов (a или b) и противолежащий к нему угол?
Формула
c = a/sin(α) = b/sin(β)
Пример
Для примера посчитаем чему равна гипотенуза прямоугольного треугольника если катет a = 2 см, а противолежащий к нему ∠α = 30°:
c = 2 / sin(30) = 2 / 0.5 = 4 см
Найти гипотенузу по двум углам
Найти гипотенузу прямоугольного треугольника только по двум острым углам невозможно.
Найти катет
Найти катет по гипотенузе и катету
Гипотенуза c =
Катет (известный) =
Катет (искомый) =
0
Чему равен один из катетов прямоугольного треугольника если известны гипотенуза и второй катет?
Формула
a = √c² — b²
b = √c² — a²
Пример
Для примера посчитаем чему равен катет a прямоугольного треугольника если гипотенуза c = 5 см, а катет b = 4 см:
a = √5² — 4² = √25 — 16 = √9 = 3 см
Найти катет по гипотенузе и прилежащему к нему острому углу
Гипотенуза c =
Угол (прилежащий катету) = °
Катет =
0
Чему равен один из катетов прямоугольного треугольника если известны гипотенуза и прилежащий к искомому катету острый угол?
Формула
a = c ⋅ cos(β)
b = c ⋅ cos(α)
Пример
Для примера посчитаем чему равен катет b прямоугольного треугольника если гипотенуза c = 5 см, а ∠α = 60°:
b = 5 ⋅ cos(60) = 5 ⋅ 0.5 = 2.5 см
Найти катет по гипотенузе и противолежащему к нему острому углу
Гипотенуза c =
Угол (противолежащий катету) = °
Катет =
0
Чему равен один из катетов прямоугольного треугольника если известны гипотенуза и противолежащий к искомому катету острый угол?
Формула
a = c ⋅ sin(α)
b = c ⋅ sin(β)
Пример
Для примера посчитаем чему равен катет a прямоугольного треугольника если гипотенуза c = 4 см, а ∠α = 30°:
a = 4 ⋅ sin(30) = 4 ⋅ 0.5 = 2 см
Найти катет по второму катету и прилежащему к нему острому углу
Катет (известный) =
Угол (прилежащий известному катету) = °
Катет (искомый) =
0
Чему равен один из катетов прямоугольного треугольника если известен другой катет и прилежащий к нему острый угол?
Формула
a = b ⋅ tg(α)
b = a ⋅ tg(β)
Пример
Для примера посчитаем чему равен катет b прямоугольного треугольника если катет a = 2 см, а ∠β = 45°:
b = 2 ⋅ tg(45) = 2 ⋅ 1 = 2 см
Найти катет по второму катету и противолежащему к нему острому углу
Катет (известный) =
Угол (противолежащий известному катету) = °
Катет (искомый) =
0
Чему равен один из катетов прямоугольного треугольника если известен другой катет и противолежащий к нему острый угол?
Формула
a = b / tg(β)
b = a / tg(α)
Пример
Для примера посчитаем чему равен катет a прямоугольного треугольника если катет b = 3 см, а ∠β = 35°:
a = 3 / tg(35) ≈ 3 / 0.7 ≈ 4.28 см
См. также
Какую сторону треугольника нужно посчитать?
Гипотенузу
Катет
Укажите размеры:
Результат:
Решение:
Ссылка на страницу с результатом:
# Теория
Треугольник — это геометрическая фигура, образованная тремя отрезками соединяющихся тремя точками, у которой все углы внутренние.
Катет — это прилежащая прямому углу сторона треугольника.
Гипотенуза — это сторона треугольника противолежащая прямому углу. Гипотенуза является самой длинной стороной треугольника.
Теорема Пифагора
Квадрат гипотенузы равен сумме квадратов катетов
a
b
c
c^2 = a^2 + b^2
- c — гипотенуза
- a — катет
- b — катет
Как посчитать сторону прямоугольного треугольника
Гипотенуза:
c = sqrt{a^2 + b^2}
Катеты:
a = sqrt{c^2 — b^2}
b = sqrt{c^2 — a^2}
Проверочные числа
Часто используют удобный приём магии чисел 3, 4, 5. Это ряд чисел попадает под теорему Пифагора.
Так, если взять треугольник с соотношением сторон 3 : 4 : 5
3
4
5
то этот треугольник будет прямоугольным. Доказывается это просто.
Если теорема Пифагора верна:
a^2 + b^2 = c^2
, то размеры такого треугольника подходят к теореме Пифагора:
3^2 + 4^2 = 5^2
9 + 16 = 25
Значит треугольник со сторонами 3, 4, 5 является прямоугольным.
Похожие калькуляторы:
Войдите чтобы писать комментарии
Enter any two known values for a right triangle below to calculate the edge lengths, altitude, angles, area, perimeter, inradius, and circumradius.
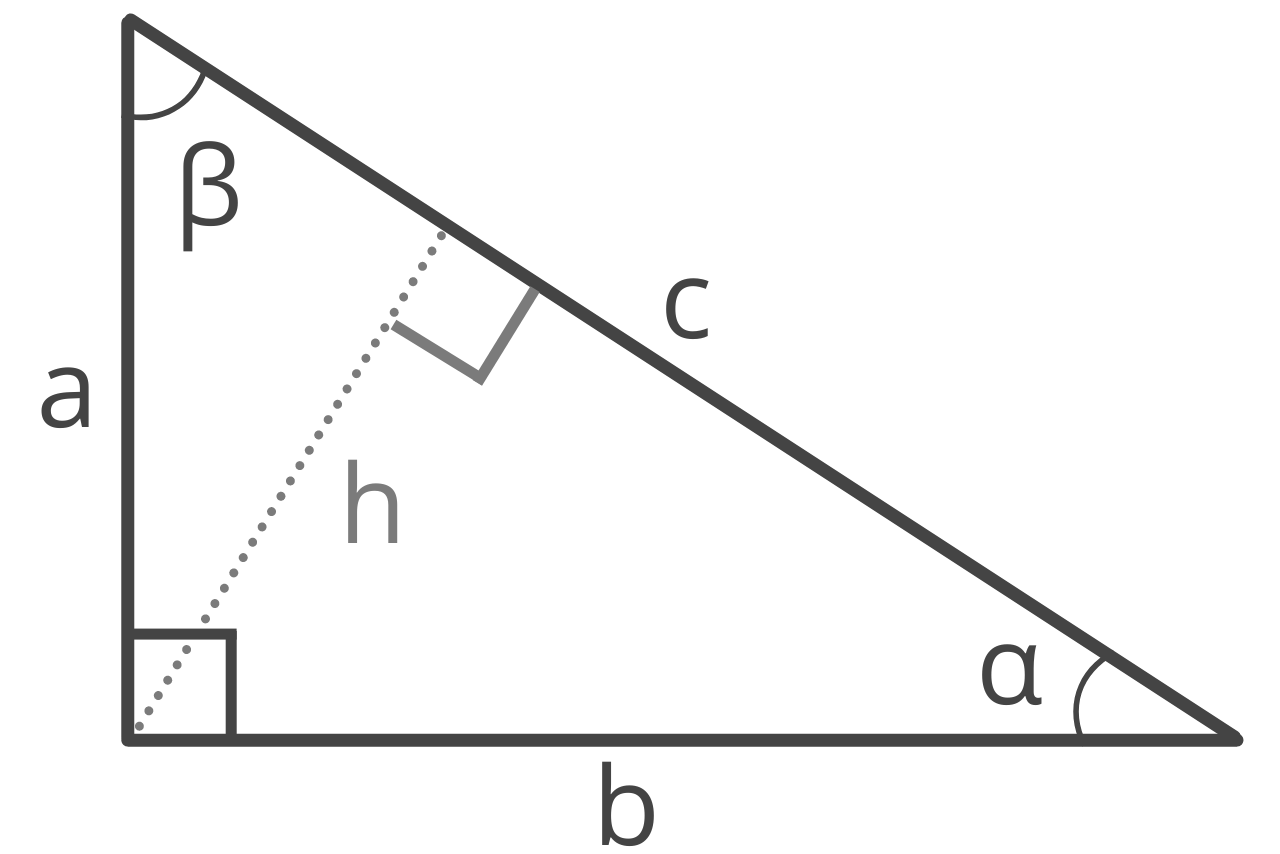
Right Triangle Properties:
| leg a: |
3 |
| leg b: |
4 |
| hypotenuse c: |
5 |
| angle α: |
36.87° | 0.6435 rad |
| angle β: |
53.13° | 0.9273 rad |
| height h: |
2.4 |
| area: |
6 |
| perimeter: |
12 |
| inradius: |
1 |
| circumradius: |
2.5 |
Type of Right Triangle:
scalene triangle
(3:4:5 Pythagorean triple)
Learn how we calculated this below
scroll down
On this page:
-
Calculator
-
What is a Right Triangle?
-
Types of Right Triangles
-
How to Find the Hypotenuse of a Right Triangle
-
How to Find a Missing Side
-
How to Find the Angle of a Right Triangle
-
How to Find the Area of a Right Triangle
-
Method One: Using Two Legs
-
Method Two: Using Hypotenuse and One Leg
-
Method Three: Using One Leg and One Angle
-
How to Find the Perimeter
-
Special Right Triangles
-
Formulas for 30 60 90 Right Triangles
-
Formulas for 45 45 90 Right Triangles
What is a Right Triangle?
A right triangle, sometimes called a right-angled triangle, is a triangle that has one interior angle equal to exactly 90 degrees, forming what is called a right angle.
The sides adjacent to the right angle are referred to as legs a and b, and are also often referred to as the base and height. The calculator uses the term height to represent the altitude of a triangle.
The side opposite the right angle is called the hypotenuse c.

Types of Right Triangles
Right triangles can be broken into two categories: isosceles and scalene.
An isosceles right triangle is a special isosceles triangle that has two angles that are 45 degrees and legs a and b of equal length.
A scalene right triangle is one where all the angles are unequal, and all the sides are unequal in length.
How to Find the Hypotenuse of a Right Triangle
To calculate the length of the hypotenuse in a right triangle when you know the length of the two legs, you can use the Pythagorean theorem.
The Pythagorean theorem states that side a squared plus side b squared is equal to side c squared. Note, keep in mind that sides a and b specifically refer to the legs, and side c refers to the hypotenuse.
a² + b² = c²
To find the hypotenuse, take the square root of the sum of a squared and b squared.
c = a² + b²
So, the value of the hypotenuse is equal to the square root of leg a squared plus leg b squared.
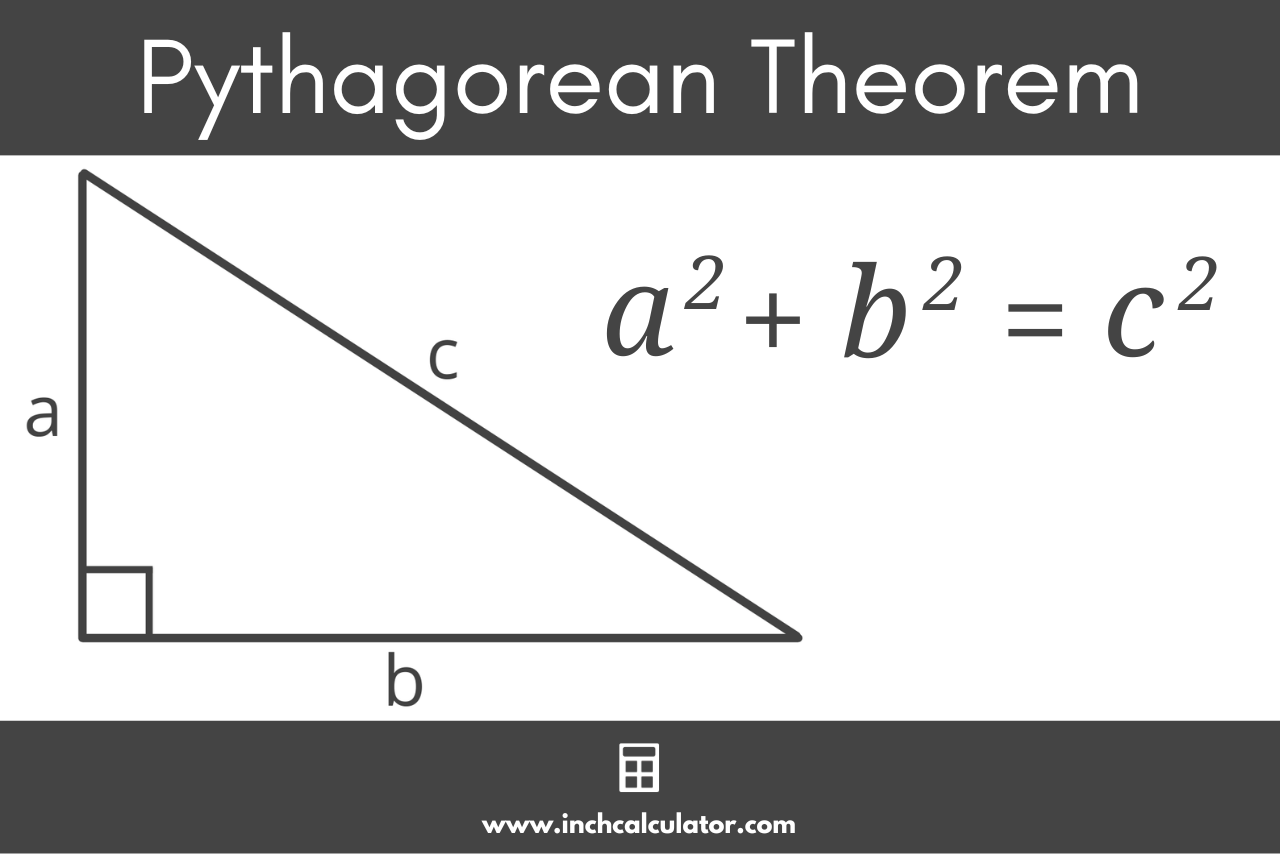
For example, let’s find the hypotenuse c for a triangle with leg a = 3 and leg b = 4.
3² + 4² = c²
9 + 16 = c²
25 = c²
25 = c
5 = c
So, the hypotenuse c is equal to 5 for a right triangle with legs a = 3 and b = 4.
How to Find a Missing Side
To calculate the length of a missing side, you can use a known side and the hypotenuse and rearrange the Pythagorean theorem to solve the missing variable.
For instance, to find leg b, rearrange the Pythagorean theorem to solve for b by subtracting a² from both sides.
a² + b² = c²
a² + b² – a² = c² – a²
b² = c² – a²
Then take the square root of the right side of the equation to isolate the missing leg, which is b in this example.
b = c² – a²
So, the value of the missing leg b is equal to the square root of the hypotenuse c squared minus the length of the known leg a squared.
How to Find the Angle of a Right Triangle
If you know the lengths of two sides of a right triangle, then you can determine the interior angles using the trigonometric functions sine, cosine, and tangent. These are usually shortened to sin, cos, and tan.
To find the angle given two side lengths, you can use the following formulas:
sin(θ) = opposite ÷ hypotenuse
cos(θ) = adjacent ÷ hypotenuse
tan(θ) = opposite ÷ adjacent
In a right triangle, the adjacent side to θ is the side of the triangle that forms part of the angle θ but is not the hypotenuse. The opposite side to θ is the side that does not form part of the angle θ.
To find one of the angles, choose the formula that can be used given the two known side lengths, then substitute the known values in the formula and solve.
For example, let’s find the angle of a triangle if the adjacent side length is 7 and the hypotenuse is 15.
Start by choosing the equation using adjacent and hypotenuse:
cos(θ) = adjacent ÷ hypotenuse
cos(θ) = 7 ÷ 15
cos(θ) = 0.4667
θ = cos-1(0.4667)
θ = 62.18°
So, for a right triangle with angle θ, with an adjacent side length of 7 and hypotenuse of 15, the angle θ is 62.18°. Note, in the above example, the inverse of cosine was used in the second to last question to isolate θ.
You can find the remaining angle in a few ways. The first way is to repeat using the same method as before, but with a different formula to find the remaining angle.
You can also use the special rule of triangles where the sum of all angles must equal 180°. Subtract 90° (because this is a right triangle, we know one of the angles is 90°) and the angle you just found from 180 to find the missing angle.
You can use the mnemonic SOHCAHTOA to help remember the equations above.
If you split SOHCAHTOA into three parts, each part represents one of the formulas, where each letter is the first letter in the part of the equation.
SOH · CAH · TOA
SOH: sin(θ) = opposite ÷ hypotenuse
CAH: cos(θ) = adjacent ÷ hypotenuse
TOA: tan(θ) = opposite ÷ adjacent
How to Find the Area of a Right Triangle
There are a few methods to find the area of a right triangle.
Method One: Using Two Legs
If you know the length of the two legs in a right triangle, then you can find the area using the formula:
A = 1 / 2a × b
The area A of a right triangle is equal to one-half times leg a times leg b.
Method Two: Using Hypotenuse and One Leg
If you know the hypotenuse and one of the legs, then you can use a variation of the Pythagorean theorem to find the area:
A = a × 1 / 2c² – a²
The area A of a right triangle is equal to leg a times 1/2 times the square root of the hypotenuse c squared times minus leg a squared. Notice the √(c² – a²) portion of this formula is simply the Pythagorean theorem isolated for b.
Method Three: Using One Leg and One Angle
If you know the length of one leg and the value of an adjacent angle, then you can use the tangent function to find the area.
Given the value of leg a and angle β, find the area using the following formula:
A = a² × tan(β) / 2
Given the value of leg b and angle α, find the area using the following formula:
A = b² × tan(α) / 2
The area A of a right triangle is equal to leg a squared times one-half the tangent of angle β, or leg b squared times one-half the tangent of angle α.
Keep in mind that in the above formulas, angle β must be adjacent to leg a, and angle α must be adjacent to leg b.
How to Find the Perimeter
The formula to find the perimeter of a right triangle is:
perimeter = a + b + c
The perimeter is equal to leg a plus leg b plus hypotenuse c.
You can use the formulas above to find the lengths of the missing leg or hypotenuse if any are missing.
Special Right Triangles
There are a few types of special right triangles, which are triangles that have specific proportions. These special right triangles also have formulas to simplify solving them.
Formulas for 30 60 90 Right Triangles
A 30 60 90 triangle is a special right triangle with 30° and 60° interior angles adjacent to the right 90° angle.
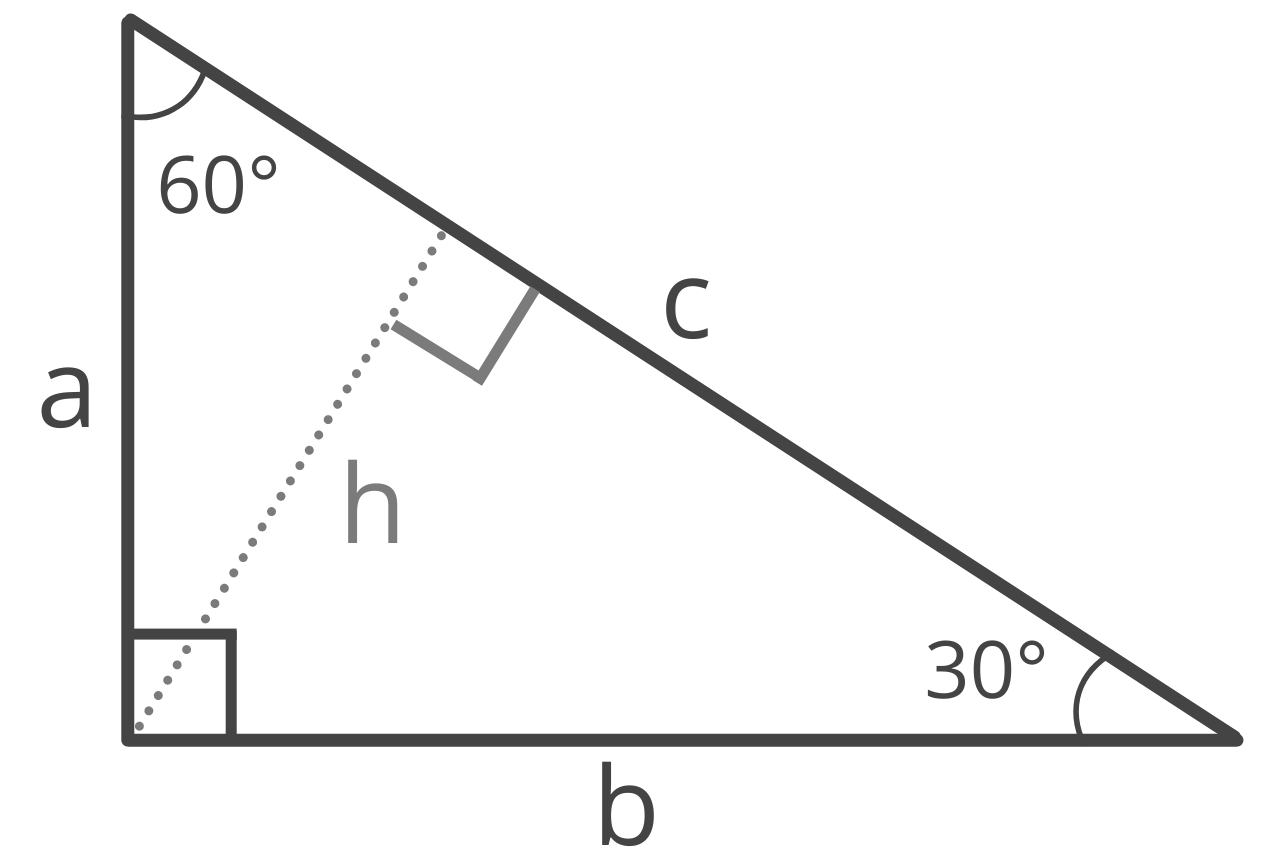
Leg a
Given the length of leg b (the side opposite the 60° angle), the formula to find the length of a is:
a = b × √3 / 3
The length of leg a is equal to b times the square root of 3, divided by 3.
Leg b
Given the length of leg a (the side opposite the 30° angle), the formula to find the length of b is:
b = a√3
The length of leg b is equal to a times the square root of 3.
Hypotenuse c
In the case of a 30 60 90 right triangle, the length of the hypotenuse is always equal to two times the length of the shortest leg. So, given the length of the short leg a, the formula to find the hypotenuse is:
c = 2a
The length of c is equal to 2 times a.
Formulas for 45 45 90 Right Triangles
A 45 45 90 triangle is a special right isosceles triangle with 45° interior angles adjacent to the 90° right angle.
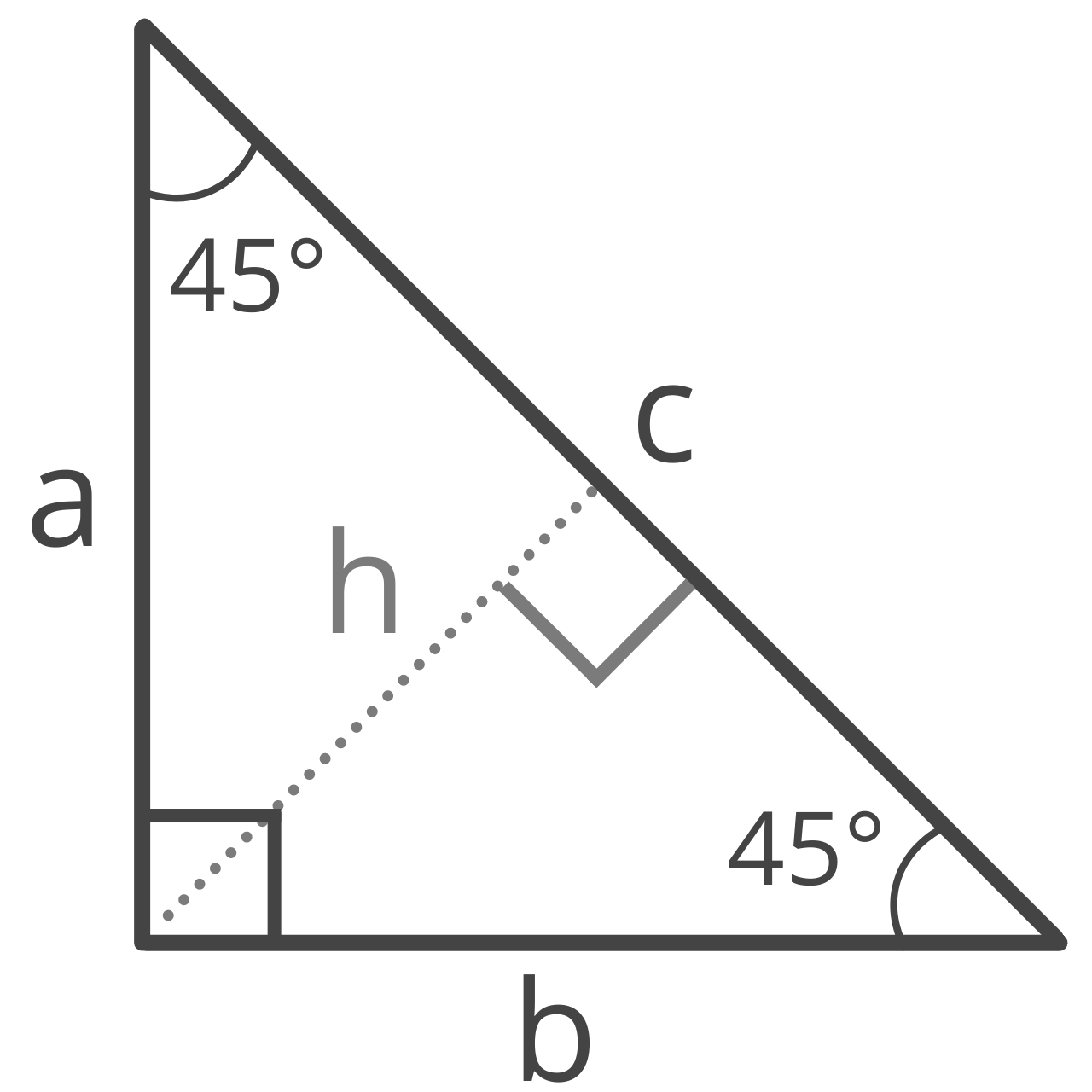
Legs a & b
Given the hypotenuse, you can find the length of the legs a and b in a 45 45 90 triangle using the formula:
a = b = c√2 / 2
The length of legs a and b are equal to hypotenuse c times the square root of 2, divided by 2.
Hypotenuse c
Since it is an isosceles triangle, both legs are the same length, so there is a special formula to find the length of the hypotenuse.
c = a√2
The length of side c is equal to the length of side a times the square root of 2.
Area
There is also a special formula to find the area of a 45 45 90 right triangle:
A = a² / 2
The area A of the right triangle is equal to the length of leg a squared, divided by 2.