How to get string length in C#?
To get the string length in C#, use the .Length property.
For example:
Examples
What is String Length in C#?
String Length in C# is a property on the String object that returns the number of characters in a string. The returned length value is of type Int32.
The Length property of a string is the number of Char objects it contains, not the number of Unicode characters.
The length property returns the number of Char objects instead of the number of Unicode characters because a Unicode character might be represented by more than one character.
What is the max string length in C#?
The maximum string length in C# is 2^31 characters. That’s because String.Length is a 32-bit integer.
How to change string length in C#?
You can’t change the string length in C#. The String.Length property is read-only.
To change the string length, you need to create a new string.
If you try to change the Length property, you will get an error:
error CS0200: Property or indexer 'string.Length' cannot be assigned to -- it is read only
How to access each Unicode character?
To access each Unicode character in a C# string, you use the System.Globalization.StringInfo class to work with each Unicode character instead of each character.
Exception
One of the most frequent null-reference exceptions is with String.Length property.
If you try to access the Length property on a null string, you will get a NullReferenceException.
Many developers forget to check for null before accessing the Length property.
Index vs Length
In C#, string length returns the number of characters in a string.
The index property returns the zero-based position of the character that is located at a specified location within an instance of String.
The length property doesn’t start at 0. It starts at the first character in the string. But the index property starts at 0.
Under the hood
Internally, C# stores strings as a read-only collection of Char objects. There’s also a null-terminating character at the end of a C# string.
C# doesn’t count the null-terminating character in the length of a string. The null-character is just a way C# marks the end of a string under the hood.
Termination
Programming languages have different approaches to determine the string end:
- Null-terminated — Strings in C are null-terminated sequences of characters, with a special character following the last character—written «» — to show the end of the string.
- Length-prefixed -Pascal stores the length in the first bytes of the string.
- Length-and-Character Array — String as a structure with an array of characters, and stores the length in a separate allocation.
Changes in length
Programming languages have different approaches to handle changes in string length:
- Static string length is fixed and cannot be changed at runtime.
- Limited Dynamic string length can be increased or decreased, but the number of characters that can be stored in it is limited.
- Dynamic string length can grow or shrink as needed, up to the maximum size allowed by the underlying system.
In C#, strings have dynamic string length. It means that the string can grow or shrink as needed.
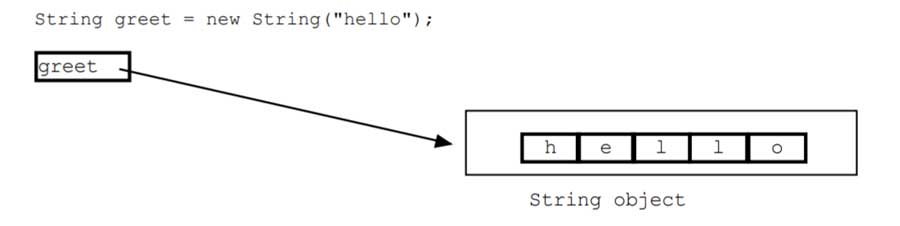
String class
The String class holds the implementation details and the string manipulation functionality. Looking at the source code, we can see that the string length is crucial for the string class.
Functionality such as String.Substring, String.IndexOf, and String.Remove require the length of a string in order to work correctly.
System.String class.
Published on: Feb 1, 2022
Работа со строками
Строки и класс String
Последнее обновление: 05.01.2022
Довольно большое количество задач, которые могут встретиться при разработке приложений, так или
иначе связано с обработкой строк — парсинг веб-страниц, поиск в тексте, какие-то аналитические задачи, связанные с извлечением нужной информации
из текста и т.д. Поэтому в этом плане работе со строками уделяется особое внимание.
В языке C# строковые значения представляет тип string, а вся функциональность работы с данным типом сосредоточена в классе
System.String. Собственно string является псевдонимом для класса String. Объекты этого класса представляют текст как последовательность символов Unicode. Максимальный размер объекта String может составлять в памяти 2 ГБ, или около 1 миллиарда символов.
Создание строк
Создавать строки можно, как используя переменную типа string и присваивая ей значение, так и применяя один из конструкторов класса String:
string s1 = "hello";
string s2 = new String('a', 6); // результатом будет строка "aaaaaa"
string s3 = new String(new char[] { 'w', 'o', 'r', 'l', 'd' });
string s4 = new String(new char[] { 'w', 'o', 'r', 'l', 'd' }, 1, 3); // orl
Console.WriteLine(s1); // hello
Console.WriteLine(s2); // aaaaaaa
Console.WriteLine(s3); // world
Console.WriteLine(s4); // orl
Конструктор String имеет различное число версий. Так, вызов конструктора
new String('a', 6)
6 раз повторит объект из первого параметра, то есть фактически создаст строку «aaaaaa».
Еще один конструктор принимает массив символов, из которых создается строка
string s3 = new String(new char[] { 'w', 'o', 'r', 'l', 'd' });
Третий использованный выше в примере конструктор позволяет создать строку из части массива символов. Второй параметр передает начальный индекс, с которого извлкаются символы, а третий параметр
указывает на количество символов:
string s4 = new String(new char[] { 'w', 'o', 'r', 'l', 'd' }, 1, 3); // orl
Строка как набор символов
Так как строка хранит коллекцию символов, в ней определен индексатор для доступа к этим символам:
public char this[int index] {get;}
Применяя индексатор, мы можем обратиться к строке как к массиву символов и получить по индексу любой из ее символов:
string message = "hello"; // получаем символ char firstChar = message[1]; // символ 'e' Console.WriteLine(firstChar); //e Console.WriteLine(message.Length); // длина строки
Используя свойство Length, как и в обычном массиве, можно получить длину строки.
Перебор строк
Класс String реализует интерфейс IEnumerable, благодаря чему строку можно перебрать в цикле foreach как набор объектов char. Также можно с помощью
других типов циклов перебрать строку, применяя обращение к символам по индексу:
string message = "hello";
for(var i =0; i < message.Length; i++)
{
Console.WriteLine(message[i]);
}
foreach(var ch in message)
{
Console.WriteLine(ch);
}
Сравнение строк
В отличие от других классов строки сравниваются по значению их символов, а не по ссылкам:
string message1 = "hello"; string message2 = "hello"; Console.WriteLine(message1 == message2); // true
Многострочные строки
Начиная с C# 11 с помощью трех пар двойных кавычек можно оформить многострочный текст, в том числе с применением интерполяции:
Print();
PrintValue("hello");
void Print()
{
string text = """
<element attr="content">
<body>
</body>
</element>
""";
Console.WriteLine(text);
}
void PrintValue(string val)
{
string text = $"""
<element attr="content">
<body>
{val}
</body>
</element>
""";
//// или так
//string text = $$"""
//
//
// {{val}}
//
//
// """;
Console.WriteLine(text);
}
Основные методы строк
Основная функциональность класса String раскрывается через его методы, среди которых можно выделить следующие:
-
Compare: сравнивает две строки с учетом текущей культуры (локали) пользователя
-
CompareOrdinal: сравнивает две строки без учета локали
-
Contains: определяет, содержится ли подстрока в строке
-
Concat: соединяет строки
-
CopyTo: копирует часть строки, начиная с определенного индекса в массив
-
EndsWith: определяет, совпадает ли конец строки с подстрокой
-
Format: форматирует строку
-
IndexOf: находит индекс первого вхождения символа или подстроки в строке
-
Insert: вставляет в строку подстроку
-
Join: соединяет элементы массива строк
-
LastIndexOf: находит индекс последнего вхождения символа или подстроки в строке
-
Replace: замещает в строке символ или подстроку другим символом или подстрокой
-
Split: разделяет одну строку на массив строк
-
Substring: извлекает из строки подстроку, начиная с указанной позиции
-
ToLower: переводит все символы строки в нижний регистр
-
ToUpper: переводит все символы строки в верхний регистр
-
Trim: удаляет начальные и конечные пробелы из строки
Разберем работу этих методов.
Тема работы со строками является одной из значимых при изучении любого языка программирования. В приведенном материале будут рассмотрены как базовые концепции работы со строками, так и расширенные возможности, предоставляемые C#.
- Знакомство со строками в C#
- Создание и инициализация объекта класса String
- Базовый API для работы со строками
- Объединение строк. Оператор +, методы Concat и Join
- Поиск и извлечение элементов из строки. Оператор [], методы IndexOf, IndexOfAny, LastIndexOf, LastIndexOfAny, Substring
- Сравнение срок
- Модификация срок
- Методы и свойства общего назначения
- Форматирование строк
- Представление чисел
- Представление даты и времени
- $ — интерполяция строк
- Управляющие символы (литералы)
- @ – буквальный идентификатор
- Класс StringBuilder
Исходный код примеров из этой статьи можете скачать из нашего github-репозитория.
За представление строк в C# отвечает класс System.String. В коде, для объявления переменной соответствующего типа, предпочтительно использовать следующий вариант написания: string – с маленькой буквы. Это ключевое слово языка, используя которое можно объявлять строковые переменные, также как int является псевдонимом для System.Int32, а bool – для System.Boolean.
string s1 = "Hello, World!"; Console.WriteLine(s1);
Допустимо объявление строковых переменных через ключевое слово var:
var s2 = "Create by var"; Console.WriteLine(s2);
Для объединения строк используется оператор +:
string s3 = "Hello, "; string s4 = s3 + "John!"; Console.WriteLine(s4);
При работе со String следует помнить, что при переопределении значения переменной создается новый экземпляр строковой переменной в памяти. Поэтому, если вам нужно собрать строку из большого количества составляющих, то использование оператора + не самый лучший вариант. В этом случае будет происходить перерасход памяти: при выполнении операции объединения с присваиванием для очень большого количества подстрок, приложение может аварийно завершиться из-за того, что сборщик мусора не будет успевать удалять неиспользуемые объекты, а новые будут продолжать появляться с большой скоростью. Для решения этой задачи используйте StringBuilder, о нем будет рассказано в конце этого урока.
Создание и инициализация объекта класса String
Существует несколько способов создать объект класса String и проинициализировать его. Рассмотрим варианты, которые доступны в C#. Наиболее распространенный способ сделать эту операцию – это присвоить строковое значение переменной без явного вызова конструктора, так, как мы это делали в предыдущем разделе:
string s5 = "test1"; var s6 = "test2";
Для дословного представления строки, для того чтобы проигнорировать управляющие последовательности, используйте префикс @ перед значением. Сравните вывод следующей конструкции:
Console.WriteLine("first linenSecond line");
С вариантом:
Console.WriteLine(@"first linenSecond line");
Если требуется подготовить строковое значение с использованием набора переменных, то можно воспользоваться статическим методом Format класса String, либо префиксом $:
int age = 27;
Console.WriteLine(String.Format("Age: {0}", age));
Console.WriteLine("");
Console.WriteLine($"Age: {age}");
Console.WriteLine("");
Можно явно вызвать конструктор типа c передачей в него параметров. Самый простой вариант – это передать строку:
string s7 = new string("test3");
В качестве параметра может выступать массив Char элементов:
char[] charArray = {'H', 'e', 'l', 'l', 'o'};
string s8 = new string(charArray);
Ещё вариант – это указать элемент типа char и количество раз, которое его нужно повторить:
string s9 = new string('O', 10); // "OOOOOOOOOO"
Для создания строки также можно использовать указатели на Char* и SByte*, но в данном уроке эта тема рассматриваться не будет.
Базовый API для работы со строками
В рамках данного раздела рассмотрим наиболее интересные и полезные методы и свойства класса String.
Объединение строк. Оператор +, методы Concat и Join
Сцеплять строки между собой можно с помощью оператора +, при этом, в результате объединения, будет создан новый объект:
string s10 = "Area";
string s11 = " 51";
Console.WriteLine("Concat by +: " + s10 + s11);
В составе API, который предоставляет System.String, есть метод Concat, который может выполнять ту же работу:
Console.WriteLine("Concat by Concat(): " + string.Concat(s10, s11));
Метод Concat позволяет объединить до четырех строк через прямое перечисление. Если нужно таким образом объединить больше строковых переменных и значений, то используйте оператор +. Полезным свойством Concat является то, что он может принять на вход массив элементов типа String и объединить их:
string[] sArr1 = {"First ", "Second ", "Third "};
Console.WriteLine(string.Concat(sArr1));
Для объединения элементов с указанием разделителя используется метод Join. В предыдущем примере, элементы в массиве sArr1 уже содержали пробел, это не всегда удобно, решим задачу объединения элементов, которые не содержат разделителей, с помощью Join:
string[] sArr2 = {"First", "Second", "Third"};
Console.WriteLine("Join elements in array by Join() with space: " + string.Join(" ", sArr2));
В качестве разделителя можно использовать любую строку:
Console.WriteLine("Join elements in array by Join() with <->: " + string.Join("<->", sArr2));
Поиск и извлечение элементов из строки. Оператор [], методы IndexOf, IndexOfAny, LastIndexOf, LastIndexOfAny, Substring
Для получения символа из строки с конкретной позиции можно использовать синтаксис подобный тому, что применяется при работе с массивами – через квадратные скобки []:
string s12 = "Hello";
Console.WriteLine("Get element by index s12[3]: " + s12[3]);
Для решения обратной задачи: поиск индекса первого (последнего) вхождения элемента или сроки в данной строке используются методы IndexOf, IndexOfAny и LastIndexOf, LastIndexOfAny.
В таблице ниже перечислены некоторые из предоставляемых System.String вариантов этих методов.
|
Метод |
Описание |
|
IndexOf(Char) |
Возвращает индекс первого вхождения символа. |
|
IndexOf(Char, Int32) |
Возвращает индекс первого вхождения символа начиная с заданной позиции. |
|
IndexOf(Char, Int32, Int32) |
Возвращает индекс первого вхождения символа начиная с заданной позиции, проверяется указанное количество элементов. |
|
IndexOf(String) |
Назначение методов совпадает с перечисленными выше, но поиск выполняется для строки. |
|
IndexOfAny(Char[]) |
Назначение методов совпадает с перечисленными выше, но выполняется поиск индекса первого вхождения любого из переданных в массиве элементов. |
|
LastIndexOf([Char | String]) |
Возвращает индекс последнего вхождения символа или строки. Можно задавать индекс, с которого начинать поиск и количество проверяемых позиций. [Char | String] – означает Char или String |
|
LastIndexOfAny(Char[]) |
Возвращает индекс последнего вхождения любого из переданных в массиве элементов.Можно задавать индекс с которого начинать поиск и количество проверяемых позиций |
// s1 = "Hello, World!"
// Поиск первого вхождения символа 'r'
Console.WriteLine("Index of 'r': " + s1.IndexOf('r'));
// Поиск первого вхождения символа 'l' начиная с позиции 4
Console.WriteLine("Index of 'l', start at 4: " + s1.IndexOf('l', 4));
// Поиск первого вхождения строки "World"
Console.WriteLine("Index of "World": " + s1.IndexOf("World"));
// Поиск первого вхождения символа из набора ['o', 'd', ',']
Console.WriteLine("Index of pos of any symbol in array: " + s1.IndexOfAny(new char[] {'o', 'd', ','}));
// Поиск последнего вхождения символа 'l'
Console.WriteLine("Last index of 'l': " + s1.LastIndexOf('l'));
// Поиск последнего вхождения строки "or"
Console.WriteLine("Last index of "or": " + s1.LastIndexOf("or"));
// Поиск последнего вхождения символа из набора ['o', 'd', ',']
Console.WriteLine("Last index of pos of any symbol in array: " + s1.LastIndexOfAny(new char[] {'o', 'd', ','}));
Для определения того, содержит ли данная строка указанную подстроку, а также для проверки равенства начала или конца строки заданному значению используйте методы: Contains, StartsWith и EndsWith.
|
Метод |
Описание |
|
Contains(Char) |
Возвращает True если строка содержит указанный символ или подстроки. |
|
StartsWith(Char) |
Возвращает True если строка начинается с заданного символа или подстроки. |
|
EndsWith(Char) |
Возвращает True если строка заканчивается на заданный символ или подстроку. |
Console.WriteLine("Contains "World"? " + s1.Contains("World")); // True
Console.WriteLine("Starts with "He"? " + s1.StartsWith("He")); // True
Console.WriteLine("Ends with "ld"? " + s1.EndsWith("ld")); // False
Задачу извлечения подстроки из данной строки решает метод SubString:
|
Метод |
Описание |
|
Substring(Int32) |
Возвращает подстроку начиная с указанной позиции и до конца исходной строки. |
|
Substring(Int32, Int32) |
Возвращает подстроку начиная с указанной позиции с заданной длины. |
Console.WriteLine("Substring start at pos 7: " + s1.Substring(7)); // World!
Console.WriteLine("Substring start at pos 7 (4 chars): " + s1.Substring(7, 4)); // Worl
Сравнение срок
Для сравнения строк можно использовать оператор сравнения ==, при этом будут сравниваться значения строковых переменных, а не их ссылки, как это делается для других ссылочных типов.
string t1 = "John";
string t2 = "John";
string t3 = "Mary";
Console.WriteLine("t1 == t2: " + (t1 == t2)); // True
Console.WriteLine("t1 != t2: " + (t1 != t2)); // False
Console.WriteLine("t1 == t3: " + (t1 == t3)); // False
Для сравнения также можно использовать метод Equals, но это менее удобный вариант:
Console.WriteLine("Equals method: t1.Equals(t2)" + t1.Equals(t2)); // True
Console.WriteLine("Equals method: t1.Equals(t3)" + t1.Equals(t3)); // False
Модификация срок
Класс String предоставляет довольно большое количество инструментов для изменения строк.
Вставка строки в исходную в заданную позицию осуществляется с помощью метода Insert:
Console.WriteLine("Insert: " + "26".Insert(1, "[4]")); // 2[4]6
Для приведения строки к заданной длине с выравниванием по левому (правому) краю с заполнением недостающих символов пробелами используются методы PadLeft и PadRight:
Console.WriteLine("PadLeft: ");
Console.WriteLine("some string".PadLeft(15)); // " some string"
Console.WriteLine("some string".PadLeft(15, '*')); // "****some string"
Console.WriteLine("PadRight: ");
Console.WriteLine("some string".PadRight(15)); // "some string "
Console.WriteLine("some string".PadRight(15, '*')); // "some string****"
Метод Remove удаляет подстроку из исходной строки. Возможны два варианта использования:
|
Метод |
Описание |
|
Remove(Int32) |
Удаляет все символы начиная с заданного и до конца строки. |
|
Remove(Int32, Int32) |
Удаляет с указанной позиции заданное число символов. |
Console.WriteLine("Remove demo1: " + "Hello".Remove(2));
Console.WriteLine("Remove demo2: " + "Hello".Remove(2, 2));
Замена элементов строки производится с помощью метода Replace. Наиболее часто используемые варианты – это замена символа на символ и строки на подстроку:
Console.WriteLine("Hello, World!".Replace('!', '.')); // Hello, World.
Console.WriteLine("Hello, World!".Replace("World", "John")); // Hello, John!
Для преобразования строки к верхнему регистру используйте метод ToUpper(), к нижнему – ToLower():
Console.WriteLine("Hello, World!".ToUpper()); // HELLO, WORLD!
Console.WriteLine("Hello, World!".ToLower()); // hello, world!
За удаление начальных и конечных символов отвечают методы, начинающиеся на Trim (см. таблицу ниже).
|
Метод |
Описание |
|
Trim() |
Удаляет символы пробелы из начала и конца строки. |
|
Trim(Char) |
Удаляет экземпляры символа из начала и конца строки. |
|
Trim(Char[]) |
Удаляет экземпляры символов из начала и конца строки. |
|
TrimStart() |
Удаляет экземпляры символов из начала строки. |
|
TrimEnd() |
Удаляет экземпляры символов из конца строки. |
Console.WriteLine(" hello ".Trim()); // "hello"
Console.WriteLine("***hello---".Trim('*')); // "hello---"
Console.WriteLine("***hello---".Trim(new char[] {'*', '-'})); // "hello"
Console.WriteLine(" hello ".TrimStart()); // "hello "
Console.WriteLine(" hello ".TrimEnd()); // " hello"
Методы и свойства общего назначения
Рассмотрим некоторые из полезных методов и свойств, которые не вошли в приведенные выше группы.
System.Length – возвращает длину строки:
Console.WriteLine("Hello".Length); // 5
System.Split() – разделяет заданную строку на подстроки, в качестве разделителя используется указанный через параметр символ (или группа символов):
foreach(var s in "1 2 3".Split(' '))
Console.WriteLine(s);
foreach(var s in "1 2 3-4-5-6".Split(new char[]{' ', '-'}))
Console.WriteLine(s);
System.Empty – возвращает пустую строку.
Форматирование строк
Под форматированием строк, в рамках данного раздела, понимается встраивание в строку различных элементом (число, дата и т.п.), представленных в заданном формате. Форматирование можно осуществлять с помощью метода ToString с передачей в него нужных описателей, метода Format, который, в качестве аргументов, получает строку со специальными вставками, определяющими представление элементов и непосредственно сами элементы.
Для начала рассмотрим на нескольких примерах работу с этими методоми:
// ToString
Console.WriteLine(12345.ToString("X"));
// String.Format
Console.WriteLine(string.Format("value: {0}", 1.23456));
Console.WriteLine(string.Format("value: {0:F}", 1.23456));
Console.WriteLine(string.Format("value: {0:d}", 1.23456));
// WriteLine без использования String.Format
Console.WriteLine("value: {0}", 1.23456); // 1,23456
Console.WriteLine("value: {0:F}", 1.23456); // 1.235
Console.WriteLine("date: {0:d}", DateTime.Now); // 07.09.2020
Эта функциональность также доступна для методов StringBuilder.AppendFormat, TextWriter.WriteLine, Debug.WriteLine, методов из Trace, которые выводят текстовые сообщения, например: Trace.TraceError и метод TraceSource.TraceInformation.
Каждый элемент форматирования представляется следующим образом:
{index[,alignment][:formatString]}
где index – это индекс элемента, которым будет замещена данная конструкция;
alignment – выравнивание;
formatString – формат.
Ниже приведены примеры использования элементов форматирования:
Console.WriteLine("Only index: {0}", 123); // Only index: 123
Console.WriteLine("Index with alignment: {0,-5}{1,5}", 123, 456); // Index with alignment: 123 456
Console.WriteLine("Index with format: 0x{0:X}", 123); // Index with format: 0x7B
Представление чисел
Для представления чисел используются следующие описатели формата (список не полный, более детальную информацию можете найти в официальной документации):
|
Описатель формата |
Описание |
|
“C” или “c” |
Представление валюты. |
|
“D” или “d” |
Представление целого числа. |
|
“E” или “e” |
Представление числа в экспоненциальном виде. |
|
“F” или “f” |
Представление числа в формате с плавающей точкой. |
|
“P” или “p” |
Представление процентов, выводит число умноженное на 100 со знаком процента. |
|
“X” или “x” |
Шестнадцатеричное представление. |
|
“0” |
Заместитель нуля. |
|
“#” |
Заместитель цифры. |
|
“.” |
Разделитель целой и дробной части. |
Примеры использования описателей формата для чисел:
Console.WriteLine("C symbol: {0:C}", 123); // 123,00 ₽
Console.WriteLine("D symbol: {0:D5}", 123); // 00123
Console.WriteLine("E symbol: {0:E}", 123456789);// 1,234568E+008
Console.WriteLine("F symbol: {0:F2}", 123.4567);// 123,46
Console.WriteLine("P symbol: {0:P}", 0.123); // 123,46
Console.WriteLine("X symbol: 0x{0:X}", 567); // 0x237
Console.WriteLine("0 symbol: {0:000.00}", 12.6789);// 012,68
Console.WriteLine("# symbol: {0:##}", 14.6789); // 15
Представление даты и времени
Для представления даты и времени используются следующие описатели формата (список не полный, более детальную информацию можете найти в официальной документации):
|
Описатель формата |
Описание |
|
“d” |
Сокращенный формат даты |
|
“D” |
Полный формат даты |
|
“f”, “F” |
Полный формат даты и времени с коротким (полным) форматом времени |
|
“g”, “G” |
Общий формат даты и времени с коротким (полным) форматом времени |
|
“t” |
Короткий формат времени |
|
“T” |
Полный формат времени |
|
“M”, “m” |
Шаблон дней месяца. |
|
“Y”, “y” |
Шаблон месяца года. |
Примеры использования описателей формата для даты и времени:
Console.WriteLine("d symbol: {0:d}", DateTime.Now);
Console.WriteLine("D symbol: {0:D}", DateTime.Now);
Console.WriteLine("f symbol: {0:f}", DateTime.Now);
Console.WriteLine("F symbol: {0:F}", DateTime.Now);
Console.WriteLine("g symbol: {0:g}", DateTime.Now);
Console.WriteLine("G symbol: {0:G}", DateTime.Now);
Console.WriteLine("t symbol: {0:t}", DateTime.Now);
Console.WriteLine("T symbol: {0:T}", DateTime.Now);
Console.WriteLine("{0:yyyy-MM-dd}", DateTime.Now);
Console.WriteLine("{0:dd/MM/yy}", DateTime.Now);
Console.WriteLine("{0:dd/MM/yy HH:mm:ss}", DateTime.Now);
$ — интерполяция строк
Начиная с C# 6 появилась возможность строить интерполированную строку, формат которой позволяет более просто, по сравнению с составным форматированием, рассмотренным нами выше, создавать строки. Интерполированная строка содержит специальные выражения интерполяции, они похожи на элементы форматирования. Выражения интерполяции имеют следующий вид:
{<interpolationExpression>[,<alignment>][:<formatString>]}
где interpolationExpression – элемент, значение, которого будет интегрироваться в строку;
alignment – выравнивание;
formatString – формат (см. форматирование строк).
Примеры работы с интерполированной строкой:
int n1 = 45678;
double d1 = 123.34567;
bool b1 = true;
string sv = "test";
Console.WriteLine($"int val: {n1}, double val: {d1:#.###}");
Console.WriteLine($"bool val: {b1}, string val: {sv}");
Управляющие символы (литералы)
Управляющие символы позволяют вводить в текст команды управления кареткой и символы, которые имеют специальное назначение (одинарные и двойные кавычки). Ниже представлена таблица с управляющими символами.
|
Управляющий символ |
Описание |
|
a |
Звуковой сигнал |
|
b |
Возврат на одну позицию |
|
f |
Перевод страницы |
|
n |
Новая строка |
|
r |
Возврат каретки |
|
t |
Горизонтальная табуляция |
|
v |
Вертикальная табуляция |
|
|
Пустой символ |
|
’ |
Одинарная кавычка |
|
” |
Двойная кавычка |
|
\ |
Обратная косая черта |
Пример использования управляющих символов:
Console.WriteLine("aName:t"John"nAge:t"27"");
@ – буквальный идентификатор
Еще один элемент, который можно использовать при создании срок – это буквальный идентификатор @. Если его поставить перед строкой, то она будет интерпретироваться буквально, в ней, escape-последовательности представляются без преобразования.
Пример работы с буквальным идентификатором:
Console.WriteLine(@"escape is not work: atnx1234");
Класс StringBuilder
Класс StringBuilder следует использовать, если вам нужно собрать строку из большого набора элементов через конкатенацию, которая, например, может осуществляется в цикле. В этом случае использование String может оказаться не эффективным решением.
Если для построения итоговой строки использовать оператор +, как это сделано в примере ниже, то при выполнении операции += каждый раз будет создавать новый объект класса String в памяти. Если количество таких присваиваний будет достаточно большим, то программа может аварийно завершиться из-за нехватки памяти, либо занять ее в очень большом объеме. Это происходит из-за того, что сборщик мусора не будет успевать уничтожать неиспользуемые объекты, которые создаются с большой скоростью. Пример реализации с использованием оператора +:
string outString = "";
for(int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
outString += i.ToString() + " - ";
}
Console.WriteLine(outString);
Более эффективным решением будет использование StringBuilder:
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
for(int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
sb.Append(i.ToString());
sb.Append(" - ");
}
outString = sb.ToString();
Console.WriteLine(outString);
Исходный код примеров из этой статьи можете скачать из нашего github-репозитория.
<< Back to C-SHARP
Use the Length property on the string type. Length gets the character count.
Length. Every string object has a Length property. Every character (no matter its value) is counted in this property. Length is cached on strings.
Length, notes. Length gets the character count in the string instance. The string cannot be null. It is possible to avoid exceptions with help from Length.Null
An example. The string class has a Length property, which returns the number of characters in its internal buffer. You do not need to iterate through every character of a string.
Here: The 4 strings we use are all of different Lengths. There are variable strings, constant strings, and literal strings.
Final part: This treats a string literal, contained in quotation marks, as an object in the C# language.
String Literal
C# program that uses Length
using System;
class Program
{
static void Main()
{
// An example string.
string a = «One example»;
Console.WriteLine(«LENGTH: « + a.
Length
);
// An empty example string.
string b = «»;
Console.WriteLine(«LENGTH: « + b.
Length
);
// A constant string.
const string c = «Three»;
Console.WriteLine(«LENGTH: « + c.
Length
);
// A literal string.
Console.WriteLine(«LENGTH: « + «Four».
Length
);
}
}
Output
LENGTH: 11
LENGTH: 0
LENGTH: 5
LENGTH: 4
Null. We must first test for null strings before calling the Length property. This is because you cannot access members on null reference types. The IsNullOrEmpty method is ideal for this.IsNullOrEmpty, IsNullOrWhiteSpace
Also: There are some interesting behaviors with null strings at the class level.
Null Strings
C# program that deals with null Length
using System;
class Program
{
static void Main()
{
F(
null
);
F(«cat»);
F(«book»);
F(«»);
}
static void F(string a)
{
if (string.IsNullOrEmpty(a))
{
// String is null or empty.
Console.WriteLine(true);
}
else
{
// Print length of string.
Console.WriteLine(a.Length);
}
}
}
Output
True
3
4
True
Error, cannot be assigned. We cannot assign to Length. We can only read the value of Length and change the string reference in other ways. This is an important aspect of the C# string type.
C# program that causes assigned error
class Program
{
static void Main()
{
string value = «test»;
value.Length = 10;
}
}
Output
error CS0200: Property or indexer ‘string.Length’ cannot be assigned to — it is read only
Research. Microsoft’s article on this subject has some interesting details. It tells you that the Length is not derived from the number of chars, but not symbolic Unicode chars.
Tip: It is possible for null characters to be in the middle of C# strings. But this is not a common occurrence in purely managed code.
Quote: The Length property returns the number of Char objects in this instance, not the number of Unicode characters. The reason is that a Unicode character might be represented by more than one Char.
String.Length Property: Microsoft Docs
Callvirt. When accessing string Length, the callvirt MSIL instruction will be generated. This will be slower than using a constant integer.IL: callvirt
Performance, hoisting length. In earlier versions of the .NET Framework, hoisting the Length and using a local helped speedup programs.
But: In 2019, this optimization seems to have lost its effectiveness. The JIT compiler inlines Length accesses well.
Opinion: It is probably worth storing the Length of a string in a local if you use it many times, but do not expect a huge performance win.
A summary. The Length property finds the number of chars in a string. It is precomputed, so is fast to access repeatedly. It returns its result in constant time.Property
Related Links:
- C# Array Examples, String Arrays
- C# ArrayList Examples
- C# ArraySegment: Get Array Range, Offset and Count
- C# break Statement
- C# Buffer BlockCopy Example
- C# BufferedStream: Optimize Read and Write
- 404 Not Found
- C# 24 Hour Time Formats
- C# 2D Array Examples
- 7 Zip Command Line Examples
- C# 7 Zip Executable (Process.Start)
- C# All Method: All Elements Match a Condition
- C# Alphabetize String
- C# Alphanumeric Sorting
- C# Arithmetic Expression Optimization
- C# Array.AsReadOnly Method (ObjectModel)
- C# Array.BinarySearch Method
- C# Array.Clear Examples
- C# Array.IndexOf, LastIndexOf: Search Arrays
- C# async, await Examples
- C# Attribute Examples
- C# Average Method
- C# BackgroundWorker
- C# base Keyword
- C# String Between, Before, After
- C# Binary Representation int (Convert, toBase 2)
- C# BinarySearch List
- C# bool Array (Memory Usage, One Byte Per Element)
- C# bool.Parse, TryParse: Convert String to Bool
- C# bool Type
- C# Array Length Property, Get Size of Array
- C# Button Example
- C# Byte Array: Memory Usage, Read All Bytes
- C# Byte and sbyte Types
- C# Capacity for List, Dictionary
- C# Case Insensitive Dictionary
- C# case Example (Switch Case)
- C# Char Array
- C# Checked and Unchecked Keywords
- C# CheckedListBox: Windows Forms
- C# Color Table
- C# Color Examples: FromKnownColor, FromName
- C# ColorDialog Example
- C# Comment: Single Line and Multiline
- C# Concat Extension: Combine Lists and Arrays
- C# Conditional Attribute
- C# Console Color, Text and BackgroundColor
- C# String Clone() method
- C# Constructor Examples
- C# Contains Extension Method
- C# String GetTypeCode() method
- C# String ToLowerInvariant() method
- C# Customized Dialog Box
- C# DataColumn Example: Columns.Add
- C# DataGridView Add Rows
- DataGridView Columns, Edit Columns Dialog
- C# DataGridView Row Colors (Alternating)
- C# DataGridView Tutorial
- C# DataGridView
- C# DataRow Examples
- C# DataSet Examples
- C# DataSource Example
- C# DataTable Compare Rows
- C# DataTable foreach Loop
- C# DataTable RowChanged Example: AcceptChanges
- C# DataTable Select Example
- C# DataTable Examples
- C# DataView Examples
- C# String ToString() method
- C# String ToUpper() method
- C# Digit Separator
- C# DateTime.MinValue (Null DateTime)
- C# DateTime.Month Property
- C# DateTime.Parse: Convert String to DateTime
- C# DateTime Subtract Method
- C# Decompress GZIP
- C# Remove Duplicates From List
- C# dynamic Keyword
- C# ElementAt, ElementAtOrDefault Use
- C# Encapsulate Field
- C# Enum Array Example, Use Enum as Array Index
- C# enum Flags Attribute Examples
- C# Enum ToString: Convert Enum to String
- C# enum Examples
- C# Enumerable.Range, Repeat and Empty
- C# Environment Type
- C# EventLog Example
- C# Exception Handling
- C# explicit and implicit Keywords
- C# Factory Design Pattern
- C# File.Copy Examples
- C# typeof and nameof Operators
- C# String TrimEnd() method
- C# var Examples
- C# virtual Keyword
- C# void Method, Return No Value
- C# volatile Example
- C# WebBrowser Control (Navigate Method)
- C# WebClient: DownloadData, Headers
- C# Where Method and Keyword
- C# String TrimStart() method
- C# delegate Keyword
- C# descending, ascending Keywords
- C# while Loop Examples
- C# Whitespace Methods: Convert UNIX, Windows Newlines
- C# XmlReader, Parse XML File
- C# XmlTextReader
- C# XmlTextWriter
- C# XmlWriter, Create XML File
- C# XOR Operator (Bitwise)
- C# yield Example
- C# float Numbers
- FlowLayoutPanel Control
- C# Focused Property
- C# FolderBrowserDialog Control
- C# Font Type: FontFamily and FontStyle
- C# FontDialog Example
- C# for Loop Examples
- C# foreach Loop Examples
- ForeColor, BackColor: Windows Forms
- C# Form: Event Handlers
- C# Contains String Method
- C# ContainsValue Method (Value Exists in Dictionary)
- C# ContextMenuStrip Example
- C# continue Keyword
- C# Control: Windows Forms
- C# Windows Forms Controls
- C# Convert Char Array to String
- C# Convert Char to String
- C# Convert Days to Months
- C# Convert String to Byte Array
- C# String Format
- C# Func Object (Lambda That Returns a Value)
- C# GC.Collect Examples: CollectionCount, GetTotalMemory
- C# Path.GetDirectoryName (Remove File From Path)
- C# goto Examples
- C# HttpClient Example: System.Net.Http
- ASP.NET HttpContext Request Property
- IL Disassembler Tutorial
- C# Intermediate Language (IL)
- C# IndexOf Examples
- C# IndexOfAny Examples
- C# Initialize Array
- C# Initialize List
- C# InitializeComponent Method: Windows Forms
- C# Inline Optimization
- C# Dictionary Equals: If Contents Are the Same
- C# Dictionary Versus List Loop
- C# Dictionary Order, Use Keys Added Last
- C# Dictionary Size and Performance
- C# Dictionary Versus List Lookup Time
- C# Dictionary Examples
- C# Get Directory Size (Total Bytes in All Files)
- C# Directory Type
- C# Distinct Method, Get Unique Elements Only
- C# Divide by Powers of Two (Bitwise Shift)
- C# Divide Numbers (Cast Ints)
- C# DomainUpDown Control Example
- C# Double Type: double.MaxValue, double.Parse
- C# Remove Duplicate Chars
- C# IEqualityComparer
- C# If Preprocessing Directive: Elif and Endif
- C# If Versus Switch Performance
- C# if Statement
- C# int.MaxValue, MinValue (Get Lowest Number)
- C# Program to reverse number
- C# Int and uint Types
- C# Integer Append Optimization
- C# Keywords
- C# Label Example: Windows Forms
- C# Lambda Expressions
- C# LastIndexOf Examples
- C# Last, LastOrDefault Methods
- C# Mutex Example (OpenExisting)
- C# Named Parameters
- C# Let Keyword (Use Variable in Query Expression)
- C# Levenshtein Distance
- C# LinkLabel Example: Windows Forms
- C# LINQ
- C# List Add Method, Append Element to List
- C# List AddRange, InsertRange (Append Array to List)
- C# List Clear Example
- C# List Contains Method
- C# List Remove Examples
- C# List Examples
- C# ListBox Tutorial (DataSource, SelectedIndex)
- C# ListView Tutorial: Windows Forms
- C# Maze Pathfinding Algorithm
- C# Memoization
- C# Memory Usage for Arrays of Objects
- C# MessageBox.Show Examples
- C# Method Call Depth Performance
- C# Method Parameter Performance
- C# Method Size Optimization
- C# Multidimensional Array
- C# MultiMap Class (Dictionary of Lists)
- C# Optimization
- C# new Keyword
- C# NotifyIcon: Windows Forms
- C# NotImplementedException
- C# Null Array
- C# String GetType() method
- C# Null Coalescing and Null Conditional Operators
- C# Null List (NullReferenceException)
- C# Numeric Casts
- C# NumericUpDown Control: Windows Forms
- C# object.ReferenceEquals Method
- C# Object Examples
- C# Optional Parameters
- C# Prime Number
- C# OrderBy, OrderByDescending Examples
- C# Process Examples (Process.Start)
- Panel, Windows Forms (Create Group of Controls)
- C# Path Examples
- C# Get Percentage From Number With Format String
- ASP.NET PhysicalApplicationPath
- C# PictureBox: Windows Forms
- C# PNG Optimization
- C# Position Windows: Use WorkingArea and Location
- Visual Studio Post Build, Pre Build Macros
- C# ProfileOptimization
- C# ProgressBar Example
- C# Property Examples
- C# PropertyGrid: Windows Forms
- C# Protected and internal Keywords
- C# Public and private Methods
- C# Remove Punctuation From String
- C# Query Windows Forms (Controls.OfType)
- C# Queryable: IQueryable Interface and AsQueryable
- ASP.NET QueryString Examples
- C# Queue Collection: Enqueue
- C# RadioButton Use: Windows Forms
- C# ReadOnlyCollection Use (ObjectModel)
- C# Recursion Optimization
- C# Recursive File List: GetFiles With AllDirectories
- C# ref Keyword
- C# Reflection Examples
- C# Regex.Escape and Unescape Methods
- C# StringBuilder Examples
- C# StringComparison and StringComparer
- C# StringReader Class (Get Parts of Strings)
- C# String GetEnumerator() method
- C# String GetHashCode() method
- C# Regex Versus Loop: Use For Loop Instead of Regex
- C# Regex.Match Examples: Regular Expressions
- C# RemoveAll: Use Lambda to Delete From List
- C# Replace String Examples
- ASP.NET Response.BinaryWrite
- ASP.NET Response.Write
- C# Return Optimization: out Performance
- C# SaveFileDialog: Use ShowDialog and FileName
- C# Scraping HTML Links
- C# sealed Keyword
- C# Seek File Examples: ReadBytes
- C# select new Example: LINQ
- C# Select Method (Use Lambda to Modify Elements)
- C# Serialize List (Write to File With BinaryFormatter)
- C# Settings.settings in Visual Studio
- C# Shuffle Array: KeyValuePair and List
- C# Single and Double Types
- C# Single Instance Windows Form
- C# Snippet Examples
- C# Sort DateTime List
- C# Sort List With Lambda, Comparison Method
- C# Sort Number Strings
- C# Sort Examples: Arrays and Lists
- C# SortedDictionary
- C# SortedList
- C# SortedSet Examples
- C# Split String Examples
- C# String Copy() method
- C# SplitContainer: Windows Forms
- C# SqlClient Tutorial: SqlConnection, SqlCommand
- C# SqlCommand Example: SELECT TOP, ORDER BY
- C# SqlCommandBuilder Example: GetInsertCommand
- C# SqlConnection Example: Using, SqlCommand
- C# SqlDataAdapter Example
- C# SqlDataReader: GetInt32, GetString
- C# SqlParameter Example: Constructor, Add
- C# Stack Collection: Push, Pop
- C# Static List: Global List Variable
- C# Static Regex
- C# Static String
- C# static Keyword
- C# StatusStrip Example: Windows Forms
- C# String Chars (Get Char at Index)
- C# string.Concat Examples
- C# String Interpolation Examples
- C# string.Join Examples
- C# String Performance, Memory Usage Info
- C# String Property
- C# String Slice, Get Substring Between Indexes
- C# String Switch Examples
- C# String
- C# StringBuilder Append Performance
- C# StringBuilder Cache
- C# ToBase64String (Data URI Image)
- C# Struct Versus Class
- C# struct Examples
- C# Substring Examples
- C# Numeric Suffix Examples
- C# switch Examples
- C# String IsNormalized() method
- C# TabControl: Windows Forms
- TableLayoutPanel: Windows Forms
- C# Take and TakeWhile Examples
- C# Task Examples (Task.Run, ContinueWith and Wait)
- C# Ternary Operator
- C# Text Property: Windows Forms
- C# TextBox.AppendText Method
- C# TextBox Example
- C# TextChanged Event
- C# TextFieldParser Examples: Read CSV
- C# ThreadStart and ParameterizedThreadStart
- C# throw Keyword Examples
- C# Timer Examples
- C# TimeSpan Examples
- C# TrimEnd and TrimStart
- C# True and False
- C# Truncate String
- C# String ToLower() method
- C# String ToCharArray() method
- C# String ToUpperInvariant() method
- C# String Trim() method
- C# Assign Variables Optimization
- C# Array.Resize Examples
- C# Array.Sort: Keys, Values and Ranges
- C# Array.Reverse Example
- C# Array Slice, Get Elements Between Indexes
- C# Array.TrueForAll: Use Lambda to Test All Elements
- C# ArrayTypeMismatchException
- C# as: Cast Examples
- C# ASCII Table
- C# ASCII Transformation, Convert Char to Index
- C# AsEnumerable Method
- C# AsParallel Example
- ASP.NET AspLiteral
- C# BaseStream Property
- C# Console.Beep Example
- C# Benchmark
- C# BinaryReader Example (Use ReadInt32)
- C# BinaryWriter Type
- C# BitArray Examples
- C# BitConverter Examples
- C# Bitcount Examples
- C# Bool Methods, Return True and False
- C# bool Sort Examples (True to False)
- C# Caesar Cipher
- C# Cast Extension: System.Linq
- C# Cast to Int (Convert Double to Int)
- C# Cast Examples
- C# catch Examples
- C# Change Characters in String (ToCharArray, For Loop)
- C# Char Combine: Get String From Chars
- C# char.IsDigit (If Char Is Between 0 and 9)
- C# char.IsLower and IsUpper
- C# Character Literal (const char)
- C# Char Lowercase Optimization
- C# Char Test (If Char in String Equals a Value)
- C# char.ToLower and ToUpper
- C# char Examples
- C# abstract Keyword
- C# Action Object (Lambda That Returns Void)
- C# Aggregate: Use Lambda to Accumulate Value
- C# AggressiveInlining: MethodImpl Attribute
- C# Anagram Method
- C# And Bitwise Operator
- C# Anonymous Function (Delegate With No Name)
- C# Any Method, Returns True If Match Exists
- C# StringBuilder Append and AppendLine
- C# StringBuilder AppendFormat
- ASP.NET appSettings Example
- C# ArgumentException: Invalid Arguments
- C# Array.ConvertAll, Change Type of Elements
- C# Array.Copy Examples
- C# Array.CreateInstance Method
- C# Array and Dictionary Test, Integer Lookups
- C# Array.Exists Method, Search Arrays
- C# Array.Find Examples, Search Array With Lambda
- C# Array.ForEach: Use Lambda on Every Element
- C# Array Versus List Memory Usage
- C# Array Property, Return Empty Array
- C# CharEnumerator
- C# Chart, Windows Forms (Series and Points)
- C# CheckBox: Windows Forms
- C# class Examples
- C# Clear Dictionary: Remove All Keys
- C# Clone Examples: ICloneable Interface
- C# Closest Date (Find Dates Nearest in Time)
- C# Combine Arrays: List, Array.Copy and Buffer.BlockCopy
- C# Combine Dictionary Keys
- C# ComboBox: Windows Forms
- C# CompareTo Int Method
- C# Comparison Object, Used With Array.Sort
- C# Compress Data: GZIP
- C# Console.Read Method
- C# Console.ReadKey Example
- C# Console.ReadLine Example (While Loop)
- C# Console.SetOut and Console.SetIn
- C# Console.WindowHeight
- C# Console.Write, Append With No Newline
- C# Console.WriteLine (Print)
- C# const Example
- C# Constraint Puzzle Solver
- C# Count Characters in String
- C# Count, Dictionary (Get Number of Keys)
- C# Count Letter Frequencies
- C# Count Extension Method: Use Lambda to Count
- C# CSV Methods (Parse and Segment)
- C# DataRow Field Method: Cast DataTable Cell
- C# Get Day Count Elapsed From DateTime
- C# DateTime Format
- C# DateTime.Now (Current Time)
- C# DateTime.Today (Current Day With Zero Time)
- C# DateTime.TryParse and TryParseExact
- C# DateTime Examples
- C# DateTimePicker Example
- C# Debug.Write Examples
- C# Visual Studio Debugging Tutorial
- C# decimal Examples
- C# DayOfWeek
- C# Enum.Format Method (typeof Enum)
- C# Enum.GetName, GetNames: Get String Array From Enum
- C# Enum.Parse, TryParse: Convert String to Enum
- C# Error and Warning Directives
- C# ErrorProvider Control: Windows Forms
- C# event Examples
- C# Get Every Nth Element From List (Modulo)
- C# Excel Interop Example
- C# Except (Remove Elements From Collection)
- C# Extension Method
- C# extern alias Example
- C# Convert Feet, Inches
- C# File.Delete
- C# File Equals: Compare Files
- C# File.Exists Method
- C# try Keyword
- C# TryGetValue (Get Value From Dictionary)
- C# Tuple Examples
- C# Type Class: Returned by typeof, GetType
- C# TypeInitializationException
- C# Union: Combine and Remove Duplicate Elements
- C# Unreachable Code Detected
- C# Unsafe Keyword: Fixed, Pointers
- C# Uppercase First Letter
- C# Uri and UriBuilder Classes
- C# Using Alias Example
- C# using Statement: Dispose and IDisposable
- C# value Keyword
- C# ValueTuple Examples (System.ValueTuple, ToTuple)
- C# ValueType Examples
- C# Variable Initializer for Class Field
- C# Word Count
- C# Word Interop: Microsoft.Office.Interop.Word
- C# XElement Example (XElement.Load, XName)
- C# Zip Method (Use Lambda on Two Collections)
- C# File.Move Method, Rename File
- C# File.Open Examples
- C# File.ReadAllBytes, Get Byte Array From File
- C# File.ReadAllLines, Get String Array From File
- C# File.ReadAllText, Get String From File
- C# File.ReadLines, Use foreach Over Strings
- C# File.Replace Method
- C# FileInfo Length, Get File Size
- C# FileInfo Examples
- C# File Handling
- C# Filename With Date Example (DateTime.Now)
- C# FileNotFoundException (catch Example)
- C# FileStream Length, Get Byte Count From File
- C# FileStream Example, File.Create
- C# FileSystemWatcher Tutorial (Changed, e.Name)
- C# finally Keyword
- C# First Sentence
- C# FirstOrDefault (Get First Element If It Exists)
- C# Fisher Yates Shuffle: Generic Method
- C# fixed Keyword (unsafe)
- C# Flatten Array (Convert 2D to 1D)
- C# First Words in String
- C# First (Get Matching Element With Lambda)
- C# ContainsKey Method (Key Exists in Dictionary)
- C# Convert ArrayList to Array (Use ToArray)
- C# Convert ArrayList to List
- C# Convert Bool to Int
- C# Convert Bytes to Megabytes
- C# Convert Degrees Celsius to Fahrenheit
- C# Convert Dictionary to List
- C# Convert Dictionary to String (Write to File)
- C# Convert List to Array
- C# Convert List to DataTable (DataGridView)
- C# Convert List to String
- C# Convert Miles to Kilometers
- C# Convert Milliseconds, Seconds, Minutes
- C# Convert Nanoseconds, Microseconds, Milliseconds
- C# Convert String Array to String
- C# Convert TimeSpan to Long
- C# Convert Types
- C# Copy Dictionary
- C# Count Elements in Array and List
- C# FromOADate and Excel Dates
- C# Generic Class, Generic Method Examples
- C# GetEnumerator: While MoveNext, Get Current
- C# GetHashCode (String Method)
- C# Thumbnail Image With GetThumbnailImage
- C# GetType Method
- C# Global Variable Examples (Public Static Property)
- ASP.NET Global Variables Example
- C# Group By Operator: LINQ
- GroupBox: Windows Forms
- C# GroupBy Method: LINQ
- C# GroupJoin Method
- C# GZipStream Example (DeflateStream)
- C# HashSet Examples
- C# Hashtable Examples
- HelpProvider Control Use
- C# HTML and XML Handling
- C# HtmlEncode and HtmlDecode
- C# HtmlTextWriter Example
- C# HttpUtility.HtmlEncode Methods
- C# HybridDictionary
- C# default Operator
- C# DefaultIfEmpty Method
- C# Define and Undef Directives
- C# Destructor
- C# DialogResult: Windows Forms
- C# Dictionary, Read and Write Binary File
- C# Dictionary Memory
- C# Dictionary Optimization, Increase Capacity
- C# Dictionary Optimization, Test With ContainsKey
- C# DictionaryEntry Example (Hashtable)
- C# Directives
- C# Directory.CreateDirectory, Create New Folder
- C# Directory.GetFiles Example (Get List of Files)
- C# DivideByZeroException
- C# DllImport Attribute
- C# Do While Loop Example
- C# DriveInfo Examples
- C# DropDownItems Control
- C# IComparable Example, CompareTo: Sort Objects
- C# IDictionary Generic Interface
- C# IEnumerable Examples
- C# IList Generic Interface: List and Array
- C# Image Type
- C# ImageList Use: Windows Forms
- C# Increment String That Contains a Number
- C# Increment, Preincrement and Decrement Ints
- Dot Net Perls
- C# Indexer Examples (This Keyword, get and set)
- C# IndexOutOfRangeException
- C# Inheritance
- C# Insert String Examples
- C# int Array
- C# Interface Examples
- C# Interlocked Examples: Add, CompareExchange
- C# Intersect: Get Common Elements
- C# InvalidCastException
- C# InvalidOperationException: Collection Was Modified
- C# IOException Type: File, Directory Not Found
- C# IOrderedEnumerable (Query Expression With orderby)
- C# is: Cast Examples
- C# IsFixedSize, IsReadOnly and IsSynchronized Arrays
- C# string.IsNullOrEmpty, IsNullOrWhiteSpace
- C# IsSorted Method: If Array Is Already Sorted
- C# Jagged Array Examples
- C# join Examples (LINQ)
- C# KeyCode Property and KeyDown
- C# KeyNotFoundException: Key Not Present in Dictionary
- C# KeyValuePair Examples
- C# Line Count for File
- C# Line Directive
- C# LinkedList
- C# List CopyTo (Copy List Elements to Array)
- C# List Equals (If Elements Are the Same)
- C# List Find and Exists Examples
- C# List Insert Performance
- ASP.NET LiteralControl Example
- C# Locality Optimizations (Memory Hierarchy)
- C# lock Keyword
- C# Long and ulong Types
- C# Loop Over String Chars: Foreach, For
- C# Loop Over String Array
- C# Main args Examples
- C# Map Example
- ASP.NET MapPath: Virtual and Physical Paths
- C# Mask Optimization
- C# MaskedTextBox Example
- C# Math.Abs: Absolute Value
- C# Math.Ceiling Usage
- C# Math.Floor Method
- C# Math.Max and Math.Min Examples
- C# Math.Pow Method, Exponents
- C# Math.Round Examples: MidpointRounding
- C# Math Type
- C# Max and Min: Get Highest or Lowest Element
- C# MemoryFailPoint and InsufficientMemoryException
- C# MemoryStream: Use Stream on Byte Array
- C# MenuStrip: Windows Forms
- C# Modulo Operator: Get Remainder From Division
- C# MonthCalendar Control: Windows Forms
- C# Multiple Return Values
- C# Multiply Numbers
- C# namespace Keyword
- C# NameValueCollection Usage
- C# Nested Lists: Create 2D List or Jagged List
- C# Nested Switch Statement
- C# Environment.NewLine
- C# Normalize, IsNormalized Methods
- C# Null String Example
- C# null Keyword
- C# Nullable Examples
- C# NullReferenceException and Null Parameter
- C# Object Array
- C# Obsolete Attribute
- C# OfType Examples
- C# OpenFileDialog Example
- C# operator Keyword
- C# Odd and Even Numbers
- C# Bitwise Or
- C# orderby Query Keyword
- C# out Parameter
- C# OutOfMemoryException
- C# OverflowException
- C# Overload Method
- C# Override Method
- C# PadRight and PadLeft: String Columns
- C# Get Paragraph From HTML With Regex
- C# Parallel.For Example (Benchmark)
- C# Parallel.Invoke: Run Methods on Separate Threads
- C# Parameter Optimization
- C# Parameter Passing, ref and out
- C# params Keyword
- C# int.Parse: Convert Strings to Integers
- C# partial Keyword
- C# Path.ChangeExtension
- C# Path Exists Example
- C# Path.GetExtension: File Extension
- C# Path.GetRandomFileName Method
- C# Pragma Directive
- C# Predicate (Lambda That Returns True or False)
- C# Pretty Date Format (Hours or Minutes Ago)
- C# PreviewKeyDown Event
- C# Random Lowercase Letter
- C# Random Paragraphs and Sentences
- C# Random String
- C# Random Number Examples
- C# StreamReader ReadLine, ReadLineAsync Examples
- C# readonly Keyword
- C# Recursion Example
- C# Regex, Read and Match File Lines
- C# Regex Groups, Named Group Example
- C# Regex.Matches Quote Example
- C# Regex.Matches Method: foreach Match, Capture
- C# Regex.Replace, Matching End of String
- C# Regex.Replace, Remove Numbers From String
- C# Regex.Replace, Merge Multiple Spaces
- C# Regex.Replace Examples: MatchEvaluator
- C# Regex.Split, Get Numbers From String
- C# Regex.Split Examples
- C# Regex Trim, Remove Start and End Spaces
- C# RegexOptions.Compiled
- C# RegexOptions.IgnoreCase Example
- C# RegexOptions.Multiline
- C# Region and endregion
- C# Remove Char From String at Index
- C# Remove Element
- C# Remove HTML Tags
- C# Remove String
- C# Reserved Filenames
- C# return Keyword
- C# Reverse String
- C# Reverse Words
- C# Reverse Extension Method
- C# RichTextBox Example
- C# Right String Part
- C# RNGCryptoServiceProvider Example
- C# ROT13 Method, Char Lookup Table
- C# SelectMany Example: LINQ
- C# Sentinel Optimization
- C# SequenceEqual Method (If Two Arrays Are Equal)
- C# Shift Operators (Bitwise)
- C# Short and ushort Types
- C# Single Method: Get Element If Only One Matches
- C# SingleOrDefault
- C# Singleton Pattern Versus Static Class
- C# Singleton Class
- C# sizeof Keyword
- C# Skip and SkipWhile Examples
- C# Sleep Method (Pause)
- C# Sort Dictionary: Keys and Values
- C# Sort by File Size
- C# Sort, Ignore Leading Chars
- C# Sort KeyValuePair List: CompareTo
- C# Sort Strings by Length
- C# Thread.SpinWait Example
- C# Math.Sqrt Method
- C# stackalloc Operator
- C# StackOverflowException
- C# StartsWith and EndsWith String Methods
- C# Static Array
- C# Static Dictionary
- C# Stopwatch Examples
- C# Stream
- C# StreamReader ReadToEnd Example (Read Entire File)
- C# StreamReader ReadToEndAsync Example (Performance)
- C# StreamReader Examples
- C# StreamWriter Examples
- C# String Append (Add Strings)
- C# String Compare and CompareTo Methods
- C# String Constructor (new string)
- C# string.Copy Method
- C# CopyTo String Method: Put Chars in Array
- C# Empty String Examples
- C# String Equals Examples
- C# String For Loop, Count Spaces in String
- C# string.Intern and IsInterned
- C# String IsUpper, IsLower
- C# String Length Property: Get Character Count
- C# String Literal: Newline and Quote Examples
- C# StringBuilder Capacity
- C# StringBuilder Clear (Set Length to Zero)
- C# StringBuilder Data Types
- C# StringBuilder Performance
- C# StringBuilder Equals (If Chars Are Equal)
- C# StringBuilder Memory
- C# StringBuilder ToString: Get String From StringBuilder
- C# StringWriter Class
- C# Sum Method: Add up All Numbers
- C# Switch Char, Test Chars With Cases
- C# Switch Enum
- C# System (using System namespace)
- C# Tag Property: Windows Forms
- C# TextInfo Examples
- C# TextReader, Returned by File.OpenText
- C# TextWriter, Returned by File.CreateText
- C# this Keyword
- C# ThreadPool
- C# Thread Join Method (Join Array of Threads)
- C# ThreadPool.SetMinThreads Method
- C# TimeZone Examples
- C# Get Title From HTML With Regex
- C# ToArray Extension Method
- C# ToCharArray: Convert String to Array
- C# ToDictionary Method
- C# Token
- C# ToList Extension Method
- C# ToLookup Method (Get ILookup)
- C# ToLower and ToUpper: Uppercase and Lowercase Strings
- ToolStripContainer Control: Dock, Properties
- C# ToolTip: Windows Forms
- C# ToString Integer Optimization
- C# ToString: Get String From Object
- C# ToTitleCase Method
- C# TrackBar: Windows Forms
- C# Tree and Nodes Example: Directed Acyclic Word Graph
- C# TreeView Tutorial
- C# Trim Strings
- C# Thread Methods
- C# History
- C# Features
- C# Variables
- C# Data Types
- C# Operators
- C# Keywords
- C# New Features | C# Version Features
- C# Programs
- C# Program to swap numbers without third variable
- C# Program to convert Decimal to Binary
- C# Program to Convert Number in Characters
- C# Program to Print Alphabet Triangle
- C# Program to print Number Triangle
- C# Program to generate Fibonacci Triangle
- C# String Compare() method
- C# String CompareOrdinal() method
- C# String CompareTo() method
- C# String Concat() method
- C# String Contains() method
- C# String CopyTo() method
- C# String EndsWith() method
- C# String Equals() method
- C# String Format() method
- C# String IndexOf() method
- C# String Insert() method
- C# String Intern(String str) method
- C# String IsInterned() method
- C# String Normalize() method
- C# String IsNullOrEmpty() method
- C# String IsNullOrWhiteSpace() method
- C# String Join() method
- C# String LastIndexOf() method
- C# String LastIndexOfAny() method
- C# String PadLeft() method
- C# String PadRight() method
- C# Nullable
- C# String Remove() method
- C# String Replace() method
- C# String Split() method
- C# String StartsWith() method
- C# String SubString() method
- C# Partial Types
- C# Iterators
- C# Delegate Covariance
- C# Delegate Inference
- C# Anonymous Types
- C# Extension Methods
- C# Query Expression
- C# Partial Method
- C# Implicitly Typed Local Variable
- C# Object and Collection Initializer
- C# Auto Implemented Properties
- C# Dynamic Binding
- C# Named and Optional Arguments
- C# Asynchronous Methods
- C# Caller Info Attributes
- C# Using Static Directive
- C# Exception Filters
- C# Await in Catch Finally Blocks
- C# Default Values for Getter Only Properties
- C# Expression Bodied Members
- C# Null Propagator
- C# String Interpolation
- C# nameof operator
- C# Dictionary Initializer
- C# Pattern Matching
- C# Tuples
- C# Deconstruction
- C# Local Functions
- C# Binary Literals
- C# Ref Returns and Locals
- C# Expression Bodied Constructors and Finalizers
- C# Expression Bodied Getters and Setters
- C# Async Main
- C# Default Expression
Related Links
Adjectives
Ado
Ai
Android
Angular
Antonyms
Apache
Articles
Asp
Autocad
Automata
Aws
Azure
Basic
Binary
Bitcoin
Blockchain
C
Cassandra
Change
Coa
Computer
Control
Cpp
Create
Creating
C-Sharp
Cyber
Daa
Data
Dbms
Deletion
Devops
Difference
Discrete
Es6
Ethical
Examples
Features
Firebase
Flutter
Fs
Git
Go
Hbase
History
Hive
Hiveql
How
Html
Idioms
Insertion
Installing
Ios
Java
Joomla
Js
Kafka
Kali
Laravel
Logical
Machine
Matlab
Matrix
Mongodb
Mysql
One
Opencv
Oracle
Ordering
Os
Pandas
Php
Pig
Pl
Postgresql
Powershell
Prepositions
Program
Python
React
Ruby
Scala
Selecting
Selenium
Sentence
Seo
Sharepoint
Software
Spellings
Spotting
Spring
Sql
Sqlite
Sqoop
Svn
Swift
Synonyms
Talend
Testng
Types
Uml
Unity
Vbnet
Verbal
Webdriver
What
Wpf



