Принципы горизонтальной системы небесных координат и примеры навигационных расчетов.
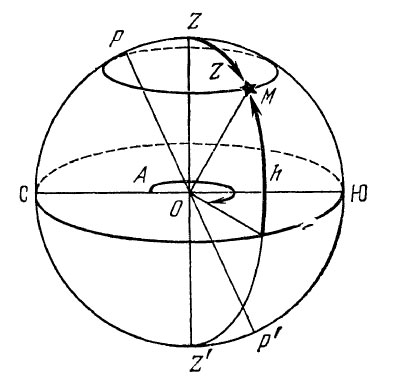
Горизонтальная система небесных координат – навигационная система для авиационного и морского транспорта, в которой положение светила на небесной сфере ориентируют относительно истинного горизонта. Если проще, то в горизонтальной системе небесных координат за основную плоскость принимается плоскость истинного горизонта, а полюсами, соответственно, являются зенит и надир (самая верхняя и с самая нижняя точки) небесной сферы.
Положение светила в горизонтальной системе координат определяется азимутом и высотой светила.
Общая схема принципа действия горизонтальной системы небесных координат
Принцип горизонтальной системы небесных координат
Азимутом светила А называется двугранный угол в плоскости истинного горизонта, заключенный между плоскостью небесного меридиана и плоскостью вертикала светила. Азимут отсчитывается от северного направления небесного меридиана по ходу часовой стрелки от 0 до 360°. Светила, находящиеся на одном вертикале, имеют одинаковые азимуты.
Положение светила на вертикале определяется другой координатой —высотой. Высотой светила h называется угол между плоскостью истинного горизонта и направлением на светило из центра небесной сферы. Высоту можно измерять также дугой вертикала от плоскости истинного горизонта до альмукантарата светила. Высота измеряется от 0 до ±90°.
Положительные высоты светила отсчитываются к зениту, а отрицательные к надиру, т. е. светила, находящиеся над горизонтом, имеют положительную высоту, а находящиеся под горизонтом — отрицательную. Вместо высоты светила иногда пользуются другой координатой — зенитным расстоянием.
Зенитным расстоянием Z называется угол в плоскости вертикала, заключенный между вертикалью наблюдателя и направлением на светило из центра небесной сферы. Зенитное расстояние отсчитывается от точки зенита до направления на светило от 0 до 180°.
Между высотой и зенитным расстоянием светила существует следующая зависимость:
h+Z = 90°, откуда Z = 90° — h; h = 90° — Z.
Светила, находящиеся на одном альмукантарате, имеют одинаковые высоты и одинаковые зенитные расстояния.
Особенности горизонтальной системы небесных координат
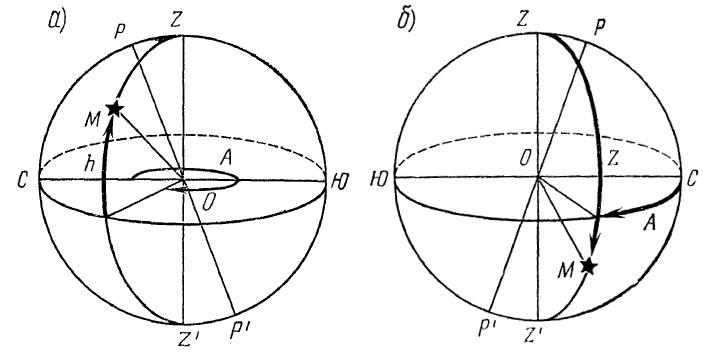
Горизонтальные координаты светил непрерывно и неравномерно изменяются вследствие суточного вращения Земли. Они изменяются также и с переменой места наблюдателя. Однако горизонтальные координаты удобны тем, что их можно непосредственно измерить с помощью специальных приборов и по ним легко можно представить положение светила на небесной сфере. Ниже приведены примеры графического изображения положения светил на небесной сфере по за-данным горизонтальным координатам.
- Пример 1. Азимут светила А =300°; высота светила h = + 50°.
- Пример 2. Азимут светила А = 50°; зенитное расстояние светила Z = 120°.
Иллюстрация принципа определения координат объекта с помощью горизонтальной системы небесных координат (к примерам 1 и 2 выше)
источник: по книге “Авиационная астрономия”
Как известно, люди с древних времён использовали звездные координаты в своей повседневной жизни. Например, по светилам мореплаватели ориентировались в пространстве, да и не только они, начинались или заканчивались сельскохозяйственные работы и многое другое. Более того, создавались настоящие календари работ, где положение звезд, можно сказать, советовало и диктовало людям когда и чем заниматься.
Какие существуют звездные координаты и системы
Разумеется, с течением времени человек более или менее упорядочил информацию о светилах. В результате в астрономии существует несколько видов систематизации звёзд.
Горизонтальная или топоцентрическая система
Проще говоря, она отражает положение светил относительно земного горизонта. Если точнее, то показывает две звездные координаты:
1) Высота над горизонтом, имеющая угловое значение и измеряемая в градусах. Здесь важно понимать, что обозначает расположение объекта.
Во-первых, наивысшая точка — зенит (+90). Во-вторых, если звёздное тело лежит на линии горизонта, то значит имеет нулевое значение. И, в-третьих, прямо противоположное зениту положение-надир (-90), когда светило находится как будто прямо под наблюдателем.
2) Азимут — угловое значение между линиями, лежащими на горизонте, которые имеют направление на объект и на север.
Горизонтальную систему часто называют топоцентрической, поскольку данные звездные координаты связаны с какой-либо определённой точкой на земной поверхности.
Стоит отметить, что оба значения постоянно меняются, поэтому определять координаты звезд на звездной карте довольно проблематично.
Первая экваториальная система
В отличие от предыдущей, экваториальные координаты звезд связаны не только с земной поверхностью, но и со сферой неба. Более того, основной плоскостью выступает небесный экватор. Также имеет две основные звездные координаты:
1) Склонение, которое, к слову, относительно постоянно. Для его определения измеряют угол между экваториальной плоскостью и прямой линией, направленной на звезду.
Как оказалось, дуга круга склонения отсчитывается к северному полюсу мира от 0 до +90 градусов, а также к южному полюсу мира от 0 до -90 градусов.
2) Часовой угол между небесным меридианом и линией, направленной на светило. Прежде всего, эта координата зависит от того, где и в какое время располагается наблюдатель.
А вот отсчёт часового угла ведётся в сторону суточного вращения неба от 0 до 360 градусов (в сторону запада).
Небесный меридиан — круг небесной сферы, проходящий сквозь зенит, полюс мира, южный полюс и надир.
Однако применение данной системы не совсем удобно для того, чтобы определять положение звезд.
Вторая экваториальная система
Вот её как раз применяют для определения звездных координат на небесной сфере. Хотя основной плоскостью также является экваториальная плоскость неба. Правда, одна из её координат точно такая же, как у первой системы. А именно склонение.
Собственно говоря, отличие заключается во втором значении положения светила. Она называется прямым восхождением и отражает угол между двумя линиями, расположенными на небесном экваторе, которые пересекаются там, где этот экватор пересекается с осью мира.
Таким образом получается, что первая линия тянется к точке весеннего равноденствия, а вторая к точке проекции звезды на экватор неба.
Прямое восхождение, точнее его угол, измеряется по экваториальной дуге. Причем обязательно по часовой стрелке. Что интересно, единицей измерения могут быть как градусы, так и минуты и часы. Один час равен 15 градусам.
Между прочим, во второй системе оси являются недвижимыми для удалённых объектов космоса.
Ось мира — это прямая, соответствующая географической земной оси, которая проходит сквозь небесный свод в Северном и Южном полюсах мира.
Эклиптическая система
Для того, чтобы определять координаты близких к Земле звезд на звездной карте неба, используют эклиптическую систему. Главным образом, она отличается от других способов тем, что за основную плоскость берут плоскость эклиптики. То есть область, где проходит земная орбита при вращении вокруг Солнца.
Звездные координаты эклиптической системы:
- Широта эклиптики-дуга круга широты, которая берёт начало от эклиптики и протянута до светила.
- Долгота эклиптики-дуга от точки весеннего равноденствия до круга широты звёзд.
Помимо того, что такой подход позволяет узнать положение ближайших космических тел, его использование показывает, где находится Земля относительно других астрономических объектов.
Галактическая система
На самом деле, галактическая система координирования необходима при более масштабных поисках и расчётах. Поскольку ни один из перечисленных выше способов не актуален при определении расположения удалённых от нас космических объектов, к примеру галактик и туманностей.
Здесь, собственно говоря, основой выступает плоскость галактики Млечный Путь. А координирующими значениями являются галактические широта и долгота.
Таблица экваториальные координаты звезд
Как вы понимаете, здесь важно отметить значения склонения и прямого восхождения светил. Например, возьмём несколько разных звёзд.
| Звезда | Склонение (градусы/минуты) | Прямое восхождение (ч/мин) |
| Альтаир | +8/44 | 19/48,3 |
| Арктур | +19/27 | 14/13,4 |
| Вега | +38/44 | 18/35,2 |
| Ригель | -8/15 | 5/12,1 |
Итак, для того, чтобы найти звезды, используют поиск по координатам. Ведь они как раз отражают местоположение тела на карте неба. Кроме того, для определения их положения также применяют координаты или определённую систему.
Как видно, звездные координаты указывают с помощью двух величин или дуг, которые характеризуют, где располагается звезда на небесной сфере. Помимо этого, можно выделить главные различия между каждой системой. В первую очередь, это выбор центральной плоскости. А во вторую очередь, отличие заключается в выборе начала отсчёта.
Стоит отметить, что карта неба не отражает расстояние до светил. А лишь указывает, где они находятся. Вероятно, по этой причине при ориентировании на местности удобно обращаться к светящимся космическим соседям. Что, собственно говоря, на протяжении многих лет и делали люди.
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia

A star’s galactic, ecliptic, and equatorial coordinates, as projected on the celestial sphere. Ecliptic and equatorial coordinates share the March equinox as the primary direction, and galactic coordinates are referred to the galactic center. The origin of coordinates (the «center of the sphere») is ambiguous; see celestial sphere for more information. |
Astronomical (or celestial) coordinate systems are organized arrangements for specifying positions of satellites, planets, stars, galaxies, and other celestial objects relative to physical reference points available to a situated observer (e.g. the true horizon and north to an observer on Earth’s surface).[1] Coordinate systems in astronomy can specify an object’s position in three-dimensional space or plot merely its direction on a celestial sphere, if the object’s distance is unknown or trivial.
Spherical coordinates, projected on the celestial sphere, are analogous to the geographic coordinate system used on the surface of Earth. These differ in their choice of fundamental plane, which divides the celestial sphere into two equal hemispheres along a great circle. Rectangular coordinates, in appropriate units, have the same fundamental (x, y) plane and primary (x-axis) direction, such as an axis of rotation. Each coordinate system is named after its choice of fundamental plane.
Coordinate systems[edit]
The following table lists the common coordinate systems in use by the astronomical community. The fundamental plane divides the celestial sphere into two equal hemispheres and defines the baseline for the latitudinal coordinates, similar to the equator in the geographic coordinate system. The poles are located at ±90° from the fundamental plane. The primary direction is the starting point of the longitudinal coordinates. The origin is the zero distance point, the «center of the celestial sphere», although the definition of celestial sphere is ambiguous about the definition of its center point.
| Coordinate system[2] | Center point (origin) |
Fundamental plane (0° latitude) |
Poles | Coordinates | Primary direction (0° longitude) |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Latitude | Longitude | |||||
| Horizontal (also called alt—az or el-az) | Observer | Horizon | Zenith, nadir | Altitude (a) or elevation | Azimuth (A) | North or south point of horizon |
| Equatorial | Center of the Earth (geocentric), or Sun (heliocentric) | Celestial equator | Celestial poles | Declination (δ) | Right ascension (α) or hour angle (h) |
March equinox |
| Ecliptic | Ecliptic | Ecliptic poles | Ecliptic latitude (β) | Ecliptic longitude (λ) | ||
| Galactic | Center of the Sun | Galactic plane | Galactic poles | Galactic latitude (b) | Galactic longitude (l) | Galactic Center |
| Supergalactic | Supergalactic plane | Supergalactic poles | Supergalactic latitude (SGB) | Supergalactic longitude (SGL) | Intersection of supergalactic plane and galactic plane |
Horizontal system[edit]
The horizontal, or altitude-azimuth, system is based on the position of the observer on Earth, which revolves around its own axis once per sidereal day (23 hours, 56 minutes and 4.091 seconds) in relation to the star background. The positioning of a celestial object by the horizontal system varies with time, but is a useful coordinate system for locating and tracking objects for observers on Earth. It is based on the position of stars relative to an observer’s ideal horizon.
Equatorial system[edit]
The equatorial coordinate system is centered at Earth’s center, but fixed relative to the celestial poles and the March equinox. The coordinates are based on the location of stars relative to Earth’s equator if it were projected out to an infinite distance. The equatorial describes the sky as seen from the Solar System, and modern star maps almost exclusively use equatorial coordinates.
The equatorial system is the normal coordinate system for most professional and many amateur astronomers having an equatorial mount that follows the movement of the sky during the night. Celestial objects are found by adjusting the telescope’s or other instrument’s scales so that they match the equatorial coordinates of the selected object to observe.
Popular choices of pole and equator are the older B1950 and the modern J2000 systems, but a pole and equator «of date» can also be used, meaning one appropriate to the date under consideration, such as when a measurement of the position of a planet or spacecraft is made. There are also subdivisions into «mean of date» coordinates, which average out or ignore nutation, and «true of date,» which include nutation.
Ecliptic system[edit]
The fundamental plane is the plane of the Earth’s orbit, called the ecliptic plane. There are two principal variants of the ecliptic coordinate system: geocentric ecliptic coordinates centered on the Earth and heliocentric ecliptic coordinates centered on the center of mass of the Solar System.
The geocentric ecliptic system was the principal coordinate system for ancient astronomy and is still useful for computing the apparent motions of the Sun, Moon, and planets.[3]
The heliocentric ecliptic system describes the planets’ orbital movement around the Sun, and centers on the barycenter of the Solar System (i.e. very close to the center of the Sun). The system is primarily used for computing the positions of planets and other Solar System bodies, as well as defining their orbital elements.
Galactic system[edit]
The galactic coordinate system uses the approximate plane of our galaxy as its fundamental plane. The Solar System is still the center of the coordinate system, and the zero point is defined as the direction towards the galactic center. Galactic latitude resembles the elevation above the galactic plane and galactic longitude determines direction relative to the center of the galaxy.
Supergalactic system[edit]
The supergalactic coordinate system corresponds to a fundamental plane that contains a higher than average number of local galaxies in the sky as seen from Earth.
Converting coordinates[edit]
Conversions between the various coordinate systems are given.[4] See the notes before using these equations.
Notation[edit]
- Horizontal coordinates
- A, azimuth
- a, altitude
- Equatorial coordinates
- α, right ascension
- δ, declination
- h, hour angle
- Ecliptic coordinates
- λ, ecliptic longitude
- β, ecliptic latitude
- Galactic coordinates
- l, galactic longitude
- b, galactic latitude
- Miscellaneous
- λo, observer’s longitude
- ϕo, observer’s latitude
- ε, obliquity of the ecliptic (about 23.4°)
- θL, local sidereal time
- θG, Greenwich sidereal time
Hour angle ↔ right ascension[edit]
Equatorial ↔ ecliptic[edit]
The classical equations, derived from spherical trigonometry, for the longitudinal coordinate are presented to the right of a bracket; dividing the first equation by the second gives the convenient tangent equation seen on the left.[5] The rotation matrix equivalent is given beneath each case.[6] This division is ambiguous because tan has a period of 180° (π) whereas cos and sin have periods of 360° (2π).
Equatorial ↔ horizontal[edit]
Azimuth (A) is measured from the south point, turning positive to the west.[7]
Zenith distance, the angular distance along the great circle from the zenith to a celestial object, is simply the complementary angle of the altitude: 90° − a.[8]
In solving the tan(A) equation for A, in order to avoid the ambiguity of the arctangent, use of the two-argument arctangent, denoted arctan(x,y), is recommended. The two-argument arctangent computes the arctangent of y/x, and accounts for the quadrant in which it is being computed. Thus, consistent with the convention of azimuth being measured from the south and opening positive to the west,
,
where
.
If the above formula produces a negative value for A, it can be rendered positive by simply adding 360°.
[a]
Again, in solving the tan(h) equation for h, use of the two-argument arctangent that accounts for the quadrant is recommended. Thus, again consistent with the convention of azimuth being measured from the south and opening positive to the west,
,
where
Equatorial ↔ galactic[edit]
These equations[14] are for converting equatorial coordinates to Galactic coordinates.


If the equatorial coordinates are referred to another equinox, they must be precessed to their place at J2000.0 before applying these formulae.
These equations convert to equatorial coordinates referred to B2000.0.
Notes on conversion[edit]
- Angles in the degrees ( ° ), minutes ( ′ ), and seconds ( ″ ) of sexagesimal measure must be converted to decimal before calculations are performed. Whether they are converted to decimal degrees or radians depends upon the particular calculating machine or program. Negative angles must be carefully handled; –10° 20′ 30″ must be converted as −10° −20′ −30″.
- Angles in the hours ( h ), minutes ( m ), and seconds ( s ) of time measure must be converted to decimal degrees or radians before calculations are performed. 1h = 15°; 1m = 15′; 1s = 15″
- Angles greater than 360° (2π) or less than 0° may need to be reduced to the range 0°−360° (0–2π) depending upon the particular calculating machine or program.
- The cosine of a latitude (declination, ecliptic and Galactic latitude, and altitude) are never negative by definition, since the latitude varies between −90° and +90°.
- Inverse trigonometric functions arcsine, arccosine and arctangent are quadrant-ambiguous, and results should be carefully evaluated. Use of the second arctangent function (denoted in computing as atn2(y,x) or atan2(y,x), which calculates the arctangent of y/x using the sign of both arguments to determine the right quadrant) is recommended when calculating longitude/right ascension/azimuth. An equation which finds the sine, followed by the arcsin function, is recommended when calculating latitude/declination/altitude.
- Azimuth (A) is referred here to the south point of the horizon, the common astronomical reckoning. An object on the meridian to the south of the observer has A = h = 0° with this usage. However, n Astropy’s AltAz, in the Large Binocular Telescope FITS file convention, in XEphem, in the IAU library Standards of Fundamental Astronomy and Section B of the Astronomical Almanac for example, the azimuth is East of North. In navigation and some other disciplines, azimuth is figured from the north.
- The equations for altitude (a) do not account for atmospheric refraction.
- The equations for horizontal coordinates do not account for diurnal parallax, that is, the small offset in the position of a celestial object caused by the position of the observer on the Earth’s surface. This effect is significant for the Moon, less so for the planets, minute for stars or more distant objects.
- Observer’s longitude (λo) here is measured positively westward from the prime meridian; this is contrary to current IAU standards.
See also[edit]
- Apparent longitude
- Azimuth – Horizontal angle from north or other reference cardinal direction
- Barycentric celestial reference system – Celestial coordinate system
- Celestial sphere – Imaginary sphere of arbitrarily large radius, concentric with the observer
- International Celestial Reference System and Frame – Current standard celestial reference system and frame
- Orbital elements – Parameters that uniquely identify a specific orbit
- Planetary coordinate system – Coordinate system for planets
- Terrestrial reference frame – The reference frame as one views from earth
Notes[edit]
- ^ Depending on the azimuth convention in use, the signs of cos A and sin A appear in all four different combinations. Karttunen et al.,[9] Taff,[10] and Roth[11] define A clockwise from the south. Lang[12] defines it north through east, Smart[13] north through west. Meeus (1991),[4] p. 89: sin δ = sin φ sin a − cos φ cos a cos A; Explanatory Supplement (1961),[5] p. 26: sin δ = sin a sin φ + cos a cos A cos φ.
References[edit]
- ^ Kanas, Nick (2021). «Star and Solar System Maps: A History of Celestial Cartography». Research Notes of the AAS. American Astronomical Society. 5 (4): 69. Bibcode:2021RNAAS…5…69K. doi:10.3847/2515-5172/abf35c. S2CID 233522547.
- ^ Majewski, Steve. «Coordinate Systems». UVa Department of Astronomy. Archived from the original on 12 March 2016. Retrieved 19 March 2011.
- ^ Aaboe, Asger. 2001 Episodes from the Early History of Astronomy. New York: Springer-Verlag., pp. 17–19.
- ^ a b
Meeus, Jean (1991). Astronomical Algorithms. Willmann-Bell, Inc., Richmond, VA. ISBN 0-943396-35-2., chap. 12 - ^ a b
U.S. Naval Observatory, Nautical Almanac Office; H.M. Nautical Almanac Office (1961). Explanatory Supplement to the Astronomical Ephemeris and the American Ephemeris and Nautical Almanac. H.M. Stationery Office, London., sec. 2A - ^
U.S. Naval Observatory, Nautical Almanac Office (1992). P. Kenneth Seidelmann (ed.). Explanatory Supplement to the Astronomical Almanac. University Science Books, Mill Valley, CA. ISBN 0-935702-68-7., section 11.43 - ^
Montenbruck, Oliver; Pfleger, Thomas (2000). Astronomy on the Personal Computer. Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg. ISBN 978-3-540-67221-0., pp 35-37 - ^
U.S. Naval Observatory, Nautical Almanac Office; U.K. Hydrographic Office, H.M. Nautical Almanac Office (2008). The Astronomical Almanac for the Year 2010. U.S. Govt. Printing Office. p. M18. ISBN 978-0160820083. - ^ Karttunen, H.; Kröger, P.; Oja, H.; Poutanen, M.; Donner, H. J. (2006). Fundamental Astronomy (5 ed.). Bibcode:2003fuas.book…..K. ISBN 978-3-540-34143-7.
- ^ Taff, L. G. (1981). Computational spherical astronomy. Wiley. Bibcode:1981csa..book…..T. ISBN 0-471-06257-X.
- ^ Roth, G. D. (23 October 1989). Handbuch für Sternenfreunde. Springer. ISBN 3-540-19436-3.
- ^ Lang, Kenneth R. (1978). Astrophysical Formulae. Springer. Bibcode:1978afcp.book…..L. ISBN 3-540-09064-9.
- ^ Smart, William Marshall (1949). Text-book on spherical astronomy. Cambridge University Press. Bibcode:1965tbsa.book…..S.
- ^ Poleski, Radosław (2013). «Transformation of the equatorial proper motion to the Galactic system». arXiv:1306.2945 [astro-ph.IM].
External links[edit]
- NOVAS, the United States Naval Observatory’s Vector Astrometry Software, an integrated package of subroutines and functions for computing various commonly needed quantities in positional astronomy.
- SOFA, the IAU’s Standards of Fundamental Astronomy, an accessible and authoritative set of algorithms and procedures that implement standard models used in fundamental astronomy.
- This article was originally based on Jason Harris’ Astroinfo, which comes along with KStars, a KDE Desktop Planetarium for Linux/KDE.








![{displaystyle {begin{aligned}tan left(lambda right)&={sin left(alpha right)cos left(varepsilon right)+tan left(delta right)sin left(varepsilon right) over cos left(alpha right)};qquad {begin{cases}cos left(beta right)sin left(lambda right)=cos left(delta right)sin left(alpha right)cos left(varepsilon right)+sin left(delta right)sin left(varepsilon right);\cos left(beta right)cos left(lambda right)=cos left(delta right)cos left(alpha right).end{cases}}\sin left(beta right)&=sin left(delta right)cos left(varepsilon right)-cos left(delta right)sin left(varepsilon right)sin left(alpha right)\[3pt]{begin{bmatrix}cos left(beta right)cos left(lambda right)\cos left(beta right)sin left(lambda right)\sin left(beta right)end{bmatrix}}&={begin{bmatrix}1&0&0\0&cos left(varepsilon right)&sin left(varepsilon right)\0&-sin left(varepsilon right)&cos left(varepsilon right)end{bmatrix}}{begin{bmatrix}cos left(delta right)cos left(alpha right)\cos left(delta right)sin left(alpha right)\sin left(delta right)end{bmatrix}}\[6pt]tan left(alpha right)&={sin left(lambda right)cos left(varepsilon right)-tan left(beta right)sin left(varepsilon right) over cos left(lambda right)};qquad {begin{cases}cos left(delta right)sin left(alpha right)=cos left(beta right)sin left(lambda right)cos left(varepsilon right)-sin left(beta right)sin left(varepsilon right);\cos left(delta right)cos left(alpha right)=cos left(beta right)cos left(lambda right).end{cases}}\[3pt]sin left(delta right)&=sin left(beta right)cos left(varepsilon right)+cos left(beta right)sin left(varepsilon right)sin left(lambda right).\[6pt]{begin{bmatrix}cos left(delta right)cos left(alpha right)\cos left(delta right)sin left(alpha right)\sin left(delta right)end{bmatrix}}&={begin{bmatrix}1&0&0\0&cos left(varepsilon right)&-sin left(varepsilon right)\0&sin left(varepsilon right)&cos left(varepsilon right)end{bmatrix}}{begin{bmatrix}cos left(beta right)cos left(lambda right)\cos left(beta right)sin left(lambda right)\sin left(beta right)end{bmatrix}}.end{aligned}}}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/32e64f7f6ef1f8a0eda9cf775fa41f0023c54d4d)
![{displaystyle {begin{aligned}tan left(Aright)&={sin left(hright) over cos left(hright)sin left(phi _{text{o}}right)-tan left(delta right)cos left(phi _{text{o}}right)};qquad {begin{cases}cos left(aright)sin left(Aright)=cos left(delta right)sin left(hright);\cos left(aright)cos left(Aright)=cos left(delta right)cos left(hright)sin left(phi _{text{o}}right)-sin left(delta right)cos left(phi _{text{o}}right)end{cases}}\[3pt]sin left(aright)&=sin left(phi _{text{o}}right)sin left(delta right)+cos left(phi _{text{o}}right)cos left(delta right)cos left(hright);end{aligned}}}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/24591754e1a4d05bbcb52fd2b752ad2fa281ad42)


![{displaystyle {begin{aligned}{begin{bmatrix}cos left(aright)cos left(Aright)\cos left(aright)sin left(Aright)\sin left(aright)end{bmatrix}}&={begin{bmatrix}sin left(phi _{text{o}}right)&0&-cos left(phi _{text{o}}right)\0&1&0\cos left(phi _{text{o}}right)&0&sin left(phi _{text{o}}right)end{bmatrix}}{begin{bmatrix}cos left(delta right)cos left(hright)\cos left(delta right)sin left(hright)\sin left(delta right)end{bmatrix}}\&={begin{bmatrix}sin left(phi _{text{o}}right)&0&-cos left(phi _{text{o}}right)\0&1&0\cos left(phi _{text{o}}right)&0&sin left(phi _{text{o}}right)end{bmatrix}}{begin{bmatrix}cos left(theta _{L}right)&sin left(theta _{L}right)&0\sin left(theta _{L}right)&-cos left(theta _{L}right)&0\0&0&1end{bmatrix}}{begin{bmatrix}cos left(delta right)cos left(alpha right)\cos left(delta right)sin left(alpha right)\sin left(delta right)end{bmatrix}};\[6pt]tan left(hright)&={sin left(Aright) over cos left(Aright)sin left(phi _{text{o}}right)+tan left(aright)cos left(phi _{text{o}}right)};qquad {begin{cases}cos left(delta right)sin left(hright)=cos left(aright)sin left(Aright);\cos left(delta right)cos left(hright)=sin left(aright)cos left(phi _{text{o}}right)+cos left(aright)cos left(Aright)sin left(phi _{text{o}}right)end{cases}}\[3pt]sin left(delta right)&=sin left(phi _{text{o}}right)sin left(aright)-cos left(phi _{text{o}}right)cos left(aright)cos left(Aright);end{aligned}}}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/d0b38b9e388153fa974a286f72be3bf6906a5fe3)

![{displaystyle {begin{aligned}x&=sin left(phi _{text{o}}right)cos left(aright)cos left(Aright)+cos left(phi _{text{o}}right)sin left(aright)\y&=cos left(aright)sin left(Aright)\[3pt]{begin{bmatrix}cos left(delta right)cos left(hright)\cos left(delta right)sin left(hright)\sin left(delta right)end{bmatrix}}&={begin{bmatrix}sin left(phi _{text{o}}right)&0&cos left(phi _{text{o}}right)\0&1&0\-cos left(phi _{text{o}}right)&0&sin left(phi _{text{o}}right)end{bmatrix}}{begin{bmatrix}cos left(aright)cos left(Aright)\cos left(aright)sin left(Aright)\sin left(aright)end{bmatrix}}\{begin{bmatrix}cos left(delta right)cos left(alpha right)\cos left(delta right)sin left(alpha right)\sin left(delta right)end{bmatrix}}&={begin{bmatrix}cos left(theta _{L}right)&sin left(theta _{L}right)&0\sin left(theta _{L}right)&-cos left(theta _{L}right)&0\0&0&1end{bmatrix}}{begin{bmatrix}sin left(phi _{text{o}}right)&0&cos left(phi _{text{o}}right)\0&1&0\-cos left(phi _{text{o}}right)&0&sin left(phi _{text{o}}right)end{bmatrix}}{begin{bmatrix}cos left(aright)cos left(Aright)\cos left(aright)sin left(Aright)\sin left(aright)end{bmatrix}}.end{aligned}}}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/e80cd665d08444dadd652d53b0f1bfd9bb35e9c5)


