How to get a process name from his pid ?
For example I execute cat file1.txt, but I want to figure out that cat command and its arguments since its pid in the system. Is there a struct to determine it or something similar? Any idea?
asked Mar 21, 2013 at 10:47
TheForbiddenTheForbidden
1,5334 gold badges22 silver badges30 bronze badges
1
There is not any general way to do this unix.
Each OS has different ways to handle it and some are very hard. You mention Linux though. With Linux, the info is in the /proc filesystem.
To get the command line for process id 9999, read the file /proc/9999/cmdline.
answered Mar 21, 2013 at 10:56
4
On linux, you can look in /proc/. Try typing man proc for more information. The contents of /proc/$PID/cmdline will give you the command line that process $PID was run with. There is also /proc/self for examining yourself 
An alternative (e.g. on Mac OS X) is to use libproc. See libproc.h.
answered Mar 21, 2013 at 11:00
robbie_crobbie_c
2,3981 gold badge18 silver badges28 bronze badges
2
POSIX C does NOT support give a standard API for getting the process name by PID.
In linux, you can get the name by LINUX Proc API: /proc/$PID/cmdline. And the code looks like these:
const char* get_process_name_by_pid(const int pid)
{
char* name = (char*)calloc(1024,sizeof(char));
if(name){
sprintf(name, "/proc/%d/cmdline",pid);
FILE* f = fopen(name,"r");
if(f){
size_t size;
size = fread(name, sizeof(char), 1024, f);
if(size>0){
if('n'==name[size-1])
name[size-1]='';
}
fclose(f);
}
}
return name;
}
answered Mar 6, 2014 at 3:32
QJGuiQJGui
9098 silver badges10 bronze badges
1
To get the process name of a process id say 9000 use this command:
ps -p 9000 -o comm=
answered Sep 8, 2014 at 6:00
ThunderThunder
2,9641 gold badge24 silver badges19 bronze badges
While this question has been answered, I’d like to add my 2 cents.
In my case, when process 1111 creates process 22222 via pipe (at least this is what I heard), /proc/2222/cmdline does not give correct process name, but instead gives something like 1111_1. I have to use /proc/2222/comm to get the correct process name.
hola
9181 gold badge17 silver badges35 bronze badges
answered Feb 17, 2016 at 15:13
toddwztoddwz
5114 silver badges8 bronze badges
Use the below command in Linux
ls -l /proc/[pid]/exe
It will give the name of the process/application name
Paul Roub
36.3k27 gold badges83 silver badges92 bronze badges
answered Apr 29, 2019 at 12:29
Vikram BVikram B
1171 silver badge6 bronze badges
ps --pid <pid> -o comm h :
This command gives executable file name. For example if you run a script name.sh, then the above command gives output as bash
ps --ppid <pid> -o comm h:
This command gives the output as name
answered Dec 11, 2019 at 6:11
If I have the PID number for a process (on a UNIX machine), how can I find out the name of its associated process?
What do I have to do?
slhck
221k70 gold badges600 silver badges590 bronze badges
asked Aug 17, 2013 at 7:12
AndreaNobiliAndreaNobili
6,90113 gold badges36 silver badges45 bronze badges
4
On all POSIX-compliant systems, and with Linux, you can use ps:
ps -p 1337 -o comm=
Here, the process is selected by its PID with -p. The -o option specifies the output format, comm meaning the command name.
For the full command, not just the name of the program, use:
ps -p 1337 -o command
See also: ps – The Open Group Base Specifications Issue 6
answered Aug 17, 2013 at 8:21
3
You can find the process name or the command used by the process-id or pid from
/proc/<pid>/cmdline
by doing
cat /proc/<pid>/cmdline
Here pid is the pid for which you want to find the name
For example:
# ps aux
................
................
user 2480 0.0 1.2 119100 12728 pts/0 Sl 22:42 0:01 gnome-terminal
................
................
To find the process name used by pid 2480 you use can
# cat /proc/2480/cmdline
gnome-terminal
Vishrant
2373 silver badges6 bronze badges
answered Aug 17, 2013 at 8:04
StormviruxStormvirux
1,0239 silver badges15 bronze badges
2
To get the path of of the program using a certain pid you can use:
ps ax|egrep "^ [PID]"
alternatively you can use:
ps -a [PID]
Or also:
readlink /proc/[PID]/exe
answered Apr 18, 2015 at 2:16
Pedro LobitoPedro Lobito
7841 gold badge9 silver badges19 bronze badges
2
You can use pmap.
I am searching for PID 6649. And cutting off the extra process details.
$ pmap 6649 | head -1
6649: /usr/lib64/firefox/firefox
answered May 27, 2017 at 4:28
1
# ls -la /proc/ID_GOES_HERE/exe
Example:
# ls -la /proc/1374/exe
lrwxrwxrwx 1 chmm chmm 0 Mai 5 20:46 /proc/1374/exe -> /usr/bin/telegram-desktop
answered May 6, 2016 at 0:14
4
You can Also use awk in combination with ps
ps aux | awk '$2 == PID number for a process { print $0 }'
example:
root@cprogrammer:~# ps aux | awk '$2 == 1 { print $0 }'
root 1 0.0 0.2 24476 2436 ? Ss 15:38 0:01 /sbin/init
to print HEAD LINE you can use
ps --headers aux |head -n 1 && ps aux | awk '$2 == 1 { print $0 }'
(or)
ps --headers aux |head -n 1; ps aux | awk '$2 == 1 { print $0 }'
root@cprogrammer:~# ps --headers aux |head -n 1 && ps aux | awk '$2 == 1 { print $0 }'
USER PID %CPU %MEM VSZ RSS TTY STAT START TIME COMMAND
root 1 0.0 0.2 24476 2436 ? Ss 15:38 0:01 /sbin/init
answered Aug 17, 2013 at 9:32
GangadharGangadhar
3911 silver badge6 bronze badges
3
Simmilar to slhck’s Answer, but relying on file operations instead of command invocations:
MYPID=1
cat "/proc/$MYPID/comm"
answered Aug 30, 2015 at 23:31
ThorSummonerThorSummoner
1,1001 gold badge15 silver badges25 bronze badges
1
Surprisingly, no one has mentioned the -f (full command) option for ps. I like to use it with -e (everything) and pipe the results to grep so I can narrow my search.
ps -ef | grep <PID>
This is also very useful for looking at full commands that someone is running that are taking a lot of resources on your system. This will show you the options and arguments passed to the command.
answered Feb 23, 2016 at 21:47
jdelaportejdelaporte
1461 silver badge7 bronze badges
1
I find the easiest method to be with the following command:
ps -awxs | grep pid
Gaff
18.5k15 gold badges57 silver badges68 bronze badges
answered Nov 21, 2016 at 9:48
1
If you want to see the path of the process by PID. You can use the pwdx command. The pwdx command reports the full path of the PID process.
$ pwdx 13896
13896: /home/user/python_program
Source: https://stackoverflow.com/a/63447358/6077264
answered Jun 27, 2022 at 23:58
You can also use this command:
cat /proc/PID/comm
It also works without root.
answered Jul 12, 2022 at 17:06
1
In this article, we will look at how to find a process name by its process identification number (PID). Before we dive into the actual solution, let us briefly talk about how processes are created and identified by Linux.
Every time a user or the system (Linux) launches a program, the kernel will create a process. A process holds execution details of the program in memory such as its input and output data, variables and so on.
Importantly, since Linux is a multitasking operating system, it executes several programs simultaneously, and this means each process process must be identified specifically.
The kernel identifies each process using a process ID (PID), a every instance of process must have a unique PID from other processes which is assigned when the process is invoked, to avoid any execution errors.
The /proc file system stores information about currently running processes on your system, it contains directories for each process.
Use the ls command to list its contents, however, the list may be long, so employ a pipeline and the less utility to view the /proc contents in a more convenient way as below:
$ ls /proc OR $ ls /proc | less
List /proc File System
1 168 2230 25 329 584 7386 83 driver schedstat 10 169 2234 2503 33 603 74 830 execdomains scsi 1070 17 2247 2507 34 610 7411 833 fb self 1081 1702 2256 2523 349 611 7423 836 filesystems slabinfo 109 1714 2258 253 35 612 745 839 fs softirqs 11 173 2266 2551 36 613 746 84 interrupts stat 110 1760 2273 26 362 62 75 844 iomem swaps 1188 1763 2278 2688 3642 63 7533 85 ioports sys 12 1769 2282 2694 3643 64 7589 86 irq sysrq-trigger 1204 177 2283 2695 37 6436 76 860 kallsyms sysvipc 1209 1773 2285 2698 38 65 7619 87 kcore thread-self 1254 18 2287 2699 39 66 7689 9 keys timer_list 13 1847 2295 27 3974 67 7690 94 key-users timer_stats 15 1914 23 2702 3976 68 77 977 kmsg tty 152 1917 2308 28 4273 6897 7725 981 kpagecgroup uptime 153 1918 2309 280 4374 69 7729 987 kpagecount version 154 1938 2310 2815 4392 6969 7733 997 kpageflags version_signature 155 1956 2311 2817 44 6980 78 acpi loadavg vmallocinfo 156 1981 2315 282 45 7 79 asound locks vmstat 1565 1986 2316 283 4543 70 790 buddyinfo mdstat zoneinfo 1567 1988 2317 29 46 71 8 bus meminfo 157 2 2324 2935 461 7102 80 cgroups misc 1579 20 2347 2944 4686 72 808 cmdline modules 158 2010 2354 3 47 73 81 consoles mounts 1584 2043 2436 30 4700 7304 810 cpuinfo mtrr 159 2044 2437 3016 5 7311 815 crypto net 1590 21 2442 31 515 7322 82 devices pagetypeinfo 16 2167 2443 318 5273 7347 820 diskstats partitions 160 22 2492 32 5274 7367 823 dma sched_debug
From the screenshot above, the numbered directories store information files about the processes in execution, where each number corresponds to a PID.
Below is the list of files for systemd process with PID 1:
$ ls /proc/1
Show SystemD Process PID
ls: cannot read symbolic link '/proc/1/cwd': Permission denied ls: cannot read symbolic link '/proc/1/root': Permission denied ls: cannot read symbolic link '/proc/1/exe': Permission denied attr coredump_filter gid_map mountinfo oom_score schedstat status autogroup cpuset io mounts oom_score_adj sessionid syscall auxv cwd limits mountstats pagemap setgroups task cgroup environ loginuid net personality smaps timers clear_refs exe map_files ns projid_map stack uid_map cmdline fd maps numa_maps root stat wchan comm fdinfo mem oom_adj sched statm
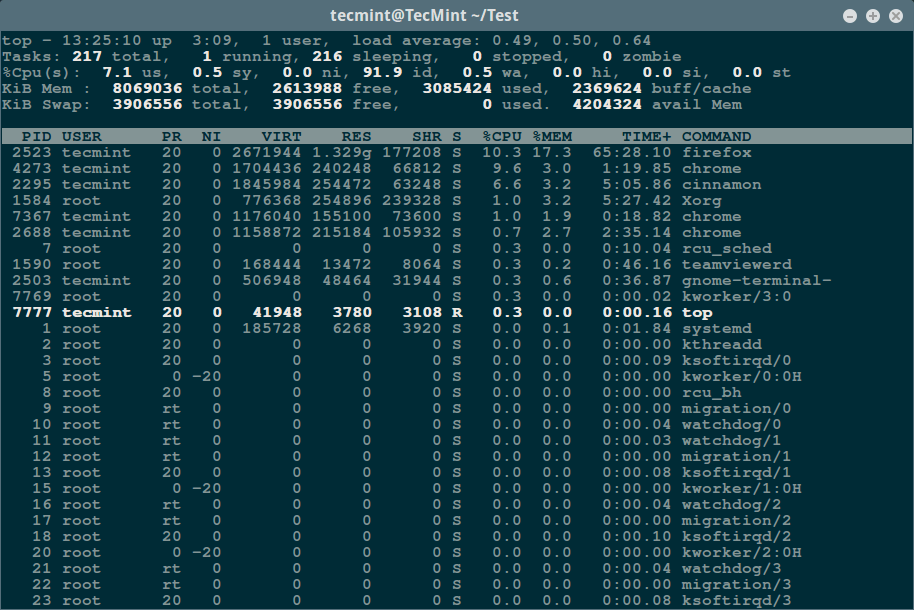
You can monitor processes and their PIDs using traditional Linux commands such as ps, top and relatively new glances command plus many more as in the examples below:
$ ps aux
Show Running Processes with PID
USER PID %CPU %MEM VSZ RSS TTY STAT START TIME COMMAND root 1 0.0 0.0 185728 6268 ? Ss 10:15 0:01 /sbin/init splash root 2 0.0 0.0 0 0 ? S 10:15 0:00 [kthreadd] root 3 0.0 0.0 0 0 ? S 10:15 0:00 [ksoftirqd/0] root 5 0.0 0.0 0 0 ? S< 10:15 0:00 [kworker/0:0H] root 7 0.0 0.0 0 0 ? S 10:15 0:09 [rcu_sched] root 8 0.0 0.0 0 0 ? S 10:15 0:00 [rcu_bh] root 9 0.0 0.0 0 0 ? S 10:15 0:00 [migration/0] root 10 0.0 0.0 0 0 ? S 10:15 0:00 [watchdog/0] root 11 0.0 0.0 0 0 ? S 10:15 0:00 [watchdog/1] root 12 0.0 0.0 0 0 ? S 10:15 0:00 [migration/1] root 13 0.0 0.0 0 0 ? S 10:15 0:00 [ksoftirqd/1] root 15 0.0 0.0 0 0 ? S< 10:15 0:00 [kworker/1:0H] root 16 0.0 0.0 0 0 ? S 10:15 0:00 [watchdog/2] root 17 0.0 0.0 0 0 ? S 10:15 0:00 [migration/2] root 18 0.0 0.0 0 0 ? S 10:15 0:00 [ksoftirqd/2] root 20 0.0 0.0 0 0 ? S< 10:15 0:00 [kworker/2:0H] root 21 0.0 0.0 0 0 ? S 10:15 0:00 [watchdog/3] root 22 0.0 0.0 0 0 ? S 10:15 0:00 [migration/3] root 23 0.0 0.0 0 0 ? S 10:15 0:00 [ksoftirqd/3] root 25 0.0 0.0 0 0 ? S< 10:15 0:00 [kworker/3:0H] root 26 0.0 0.0 0 0 ? S 10:15 0:00 [kdevtmpfs] root 27 0.0 0.0 0 0 ? S< 10:15 0:00 [netns] root 28 0.0 0.0 0 0 ? S< 10:15 0:00 [perf] ....
Monitor Linux processes using traditional top command.
$ top
Monitor Linux processes using glances, a new real-time process monitoring tool for Linux.
$ glances
Learn more about how to install Glances in Linux systems.
Find Out Process PID Number
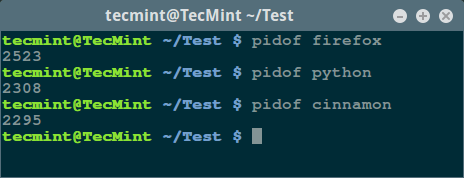
To find out the PID of a process, you can use pidof, a simple command to print out the PID of a process:
$ pidof firefox $ pidof python $ pidof cinnamon
Coming back to our point of focus, assuming you already know the PID of a process, you can print its name using the command form below:
$ ps -p PID -o format
Where:
-pspecifies the PID-oformat enables a user-defined format
Find Out Process Name Using PID Number
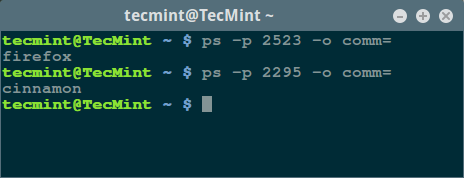
In this section, we will see how to find out a process name using its PID number with the help of user defined format i.e comm= which means command name, same as the process name.
$ ps -p 2523 -o comm= $ ps -p 2295 -o comm=
For additional usage information and options, look through the ps man page.
$ man ps
If you want to kill a process using its PID number, I suggest you to read Find and Kill Linux Processes Using its PID.
Thats it for the moment, if you know any other better way to find out a process name using PID, do share with us via our comment section below.
The process identifier (a.k.a. process ID or PID) is a number used to uniquely identify an active process.
In this short note i will show how to display information about the Windows process (incl. the process name and path to an executable file) by PID from the command-line prompt (CMD) or a Windows PowerShell.
Cool Tip: List processes in Windows from the CMD! Read more →
Execute the tasklist command to get the process name from PID:
C:> tasklist /FI "pid eq <pid>"
– or –
C:> tasklist /FI "pid eq <pid>" /V /FO List
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
/FI |
Displays a set of tasks that match a given criteria specified by the filter |
/V |
Displays verbose task information |
/FO |
Specifies the output format |
More information about the process by its PID (including the full path to an executable file) can be retrieved using the wmic command:
C:> wmic process where "ProcessID=<pid>" get /format:list
Cool Tip: Kill a hanging process in Windows from the CMD! Read more →
Was it useful? Share this post with the world!
I want to get the process name, given it’s pid in python.
Is there any direct method in python?
AndrewL64
15.7k8 gold badges46 silver badges79 bronze badges
asked Aug 30, 2015 at 10:09
2
The psutil package makes this very easy.
import psutil
process = psutil.Process(pid)
process_name = process.name()
answered Aug 30, 2015 at 10:25
CyphaseCyphase
11.4k2 gold badges30 silver badges32 bronze badges
3
If you want to see the running process, you can just use os module to execute the ps unix command
import os
os.system("ps")
This will list the processes.
But if you want to get process name by ID, you can try ps -o cmd= <pid>
So the python code will be
import os
def get_pname(id):
return os.system("ps -o cmd= {}".format(id))
print(get_pname(1))
The better method is using subprocess and pipes.
import subprocess
def get_pname(id):
p = subprocess.Popen(["ps -o cmd= {}".format(id)], stdout=subprocess.PIPE, shell=True)
return str(p.communicate()[0])
name = get_pname(1)
print(name)
answered Aug 30, 2015 at 10:31
nishparadoxnishparadox
7506 silver badges13 bronze badges
2
Command name (only the executable name):
from subprocess import PIPE, Popen
def get_cmd(pid)
with Popen(f"ps -q {pid} -o comm=", shell=True, stdout=PIPE) as p:
return p.communicate()[0]
Command with all its arguments as a string:
from subprocess import PIPE, Popen
def get_args(pid)
with Popen(f"ps -q {pid} -o cmd=", shell=True, stdout=PIPE) as p:
return p.communicate()[0]
answered Nov 4, 2021 at 11:15