If you don’t have Python 2.6 or higher, the alternative is to write an explicit for loop:
def set_list_intersection(set_list):
if not set_list:
return set()
result = set_list[0]
for s in set_list[1:]:
result &= s
return result
set_list = [set([1, 2]), set([1, 3]), set([1, 4])]
print set_list_intersection(set_list)
# Output: set([1])
You can also use reduce:
set_list = [set([1, 2]), set([1, 3]), set([1, 4])]
print reduce(lambda s1, s2: s1 & s2, set_list)
# Output: set([1])
However, many Python programmers dislike it, including Guido himself:
About 12 years ago, Python aquired lambda, reduce(), filter() and map(), courtesy of (I believe) a Lisp hacker who missed them and submitted working patches. But, despite of the PR value, I think these features should be cut from Python 3000.
So now reduce(). This is actually the one I’ve always hated most, because, apart from a few examples involving + or *, almost every time I see a reduce() call with a non-trivial function argument, I need to grab pen and paper to diagram what’s actually being fed into that function before I understand what the reduce() is supposed to do. So in my mind, the applicability of reduce() is pretty much limited to associative operators, and in all other cases it’s better to write out the accumulation loop explicitly.
In this article, a List of sets is given our task is to write a program to perform their intersection using Python.
Examples of finding the intersection of multiple sets
Input : test_list = [{5, 3, 6, 7}, {1, 3, 5, 2}, {7, 3, 8, 5}, {8, 4, 5, 3}]
Output : {3, 5}
Explanation : 3 and 5 is present in all the sets.
Method 1: Using a Logical operator
This is the simplest method to get the intersection of multiple sets using the Python logical operator
Python3
set_1 = {21, 10, 5, 11, 12}
set_2 = {5, 21, 3, 8, 9}
set_3 = {1, 21, 5, 3, 4, 5}
set4 = set1 & set2 & set3
print(set4)
Output:
{21, 5}
Method 2: Using intersection() + * operator
In this, we will perform tasks to get intersections using intersection() and the * operator is used to pack all the sets together.
Python3
test_list = [{5, 3, 6, 7}, {1, 3, 5, 2}, {7, 3, 8, 5}, {8, 4, 5, 3}]
print("The original list is : " + str(test_list))
res = set.intersection(*test_list)
print("Intersected Sets : " + str(res))
Output:
The original list is : [{3, 5, 6, 7}, {1, 2, 3, 5}, {8, 3, 5, 7}, {8, 3, 4, 5}]
Intersected Sets : {3, 5}
Method 3: Using reduce() + and_ operator
In this, we will perform intersection using and_ operator and Python reduce() does the task of getting all the sets packed together for the required operation.
Python3
from operator import and_
from functools import reduce
test_list = [{5, 3, 6, 7}, {1, 3, 5, 2}, {7, 3, 8, 5}, {8, 4, 5, 3}]
print("The original list is : " + str(test_list))
res = set(reduce(and_, test_list))
print("Intersected Sets : " + str(res))
Output:
The original list is : [{3, 5, 6, 7}, {1, 2, 3, 5}, {8, 3, 5, 7}, {8, 3, 4, 5}]
Intersected Sets : {3, 5}
Last Updated :
24 Mar, 2023
Like Article
Save Article
Метод intersection() возвращает новый набор с элементами, общими для всех наборов.
Пересечение двух или более наборов ‒ это набор элементов, общих для всех наборов. Например:
A = {1, 2, 3, 4}
B = {2, 3, 4, 9}
C = {2, 4, 9 10}
Then,
A∩B = B∩A ={2, 3, 4}
A∩C = C∩A ={2, 4}
B∩C = C∩B ={2, 4, 9}
A∩B∩C = {2, 4}
Синтаксис:
A.intersection(*other_sets)
Параметры
Метод intersection() в Python допускает произвольное количество аргументов (наборов).
Примечание: * не является частью синтаксиса. Он используется, чтобы указать, что метод допускает произвольное количество аргументов.
Возвращаемое значение из пересечения
Метод возвращает пересечение множества A со всеми наборами (переданными в качестве аргумента).
Если аргумент не передан в модуль, он возвращает мелкую копию набора(A).
Пример 1: Как работает?
A = {2, 3, 5, 4}
B = {2, 5, 100}
C = {2, 3, 8, 9, 10}
print(B.intersection(A))
print(B.intersection(C))
print(A.intersection(C))
print(C.intersection(A, B))
Выход
{2, 5}
{2}
{2, 3}
{2}
Дополнительные примеры
A = {100, 7, 8}
B = {200, 4, 5}
C = {300, 2, 3}
D = {100, 200, 300}
print(A.intersection(D))
print(B.intersection(D))
print(C.intersection(D))
print(A.intersection(B, C, D))
Выход
{100}
{200}
{300}
set()
Вы также можете найти пересечение множеств, используя & оператор.
Пример 3: Как установить пересечение с помощью оператора &?
A = {100, 7, 8}
B = {200, 4, 5}
C = {300, 2, 3, 7}
D = {100, 200, 300}
print(A C)
print(A D)
print(A C D)
print(A B C D)
Выход
{7}
{100}
set()
set()
72430cookie-checkРабота intersection() в Python
Прежде чем перейти к методу intersection(), мы должны знать, что такое пересечение. Оно относится к общим элементам двух заданных множеств. Это означает, что если есть два набора и у них есть некоторые общие элементы, то они известны как пересечение обоих множеств.
Set intersection() в Python — это встроенный метод, используемый для поиска пересечения между заданными множествами. Метод set.intersection() находит пересечение двух или более двух наборов. Он возвращает набор, содержащий сходство между двумя или более наборами.
Метод set.intersection() возвращает множество, которое содержит сходство между двумя или более наборами. Это означает, что возвращаемый набор содержит элементы только из обоих или всех наборов, если сравнение производится более чем с двумя наборами.
Итак, метод set.intersection() используется для нахождения пересечения между заданными множествами. Используя его, мы можем увидеть пересечение двух или более двух множеств.
Синтаксис
set1.intersection(set2,set3,set4...)
Здесь set1 — это набор, в котором мы хотим найти пересечения, а set2, set3, set4 и т. д. — другие наборы.
Возвращаемое значение
Метод set.intersection() возвращает пересечение набора 1 со всеми остальными наборами. Если в качестве параметра функции не передается ни один аргумент, она возвращает поверхностную копию набора set1.
Пример
См. следующий пример кода.
# app.py
# Declaring two sets
# Even nums between 2 and 10
set1 = {2, 4, 6, 8, 10}
# Multiple of 3 between 1 to 10
set2 = {3, 6, 9}
# priting both the sets
print("Set1 is: ", set1)
print("Set2 is : ", set2)
# Now we will find intersection of these two sets
print("intersection of set1 and set2 is: ", set1.intersection(set2))
Выход:
Set1 is: {2, 4, 6, 8, 10}
Set2 is : {9, 3, 6}
intersection of set1 and set2 is: {6}
Итак, здесь, в этом примере, мы видим, что мы объявили два набора четных чисел, кратных 3. Теперь мы нашли их пересечение. Как мы видим, пересечение должно быть 6, потому что только 6 является общим в обоих наборах; выход тоже 6.
Пересечение более чем двух множеств
См. следующий код.
# app.py
# Declaring two sets
# Even nums between 2 and 10
set1 = {2, 4, 6, 8, 10}
# Multiple of 3 between 1 to 10
set2 = {3, 6, 9}
# prime numbers between 1 to 10
set3 = {2, 3, 5, 7}
# odd numbers between 1 to 10
set4 = {1, 3, 5, 7, 9}
# Now we will find intersection of some sets
# intersection of set1 and set2
print("intersection of set1 and set2 is: ", set1.intersection(set2))
# intersection of set3 and set4
print("intersection of set3 and set4 is: ", set3.intersection(set4))
# intersection of set2 and set3
print("intersection of set2 and set3 is: ", set2.intersection(set3))
# intersection of set2 and set3,set4
print("intersection of set2 and set3,set4 is: ", set2.intersection(set3, set4))
# intersection of set1 and set2,set3,set4
print("intersection of set1 and set2,set3,set4 is: ",
set1.intersection(set2, set3, set4))
Выход:
intersection of set1 and set2 is: {6}
intersection of set3 and set4 is: {3, 5, 7}
intersection of set2 and set3 is: {3}
intersection of set2 and set3,set4 is: {3}
intersection of set1 and set2,set3,set4 is: set()
В этом примере мы видим, что нашли пересечение множества1 и множества2, множества3 и множества4, множества2 и множества3, поэтому в соответствии с этим выводятся все общие элементы. Точно так же пересечение set2 и set3, set4, равно 3, которые печатаются.
Кроме того, когда мы находим пересечение set2, set3 и set4 с set1, результатом будет None, потому что в них нет общего элемента.
In this post, you’ll learn how to find the intersection between two or more sets in Python. Sets in Python are a built-in data type, where items are unordered, unindexed, and unique. By finding the intersection between two or more sets, you’re finding the elements that are common between the sets.
By the end of this tutorial, you’ll have learned:
- How to use the Python
set.intersection()method to find intersections between sets, lists, and other iterables - How to use the
&operator to find the intersection between two or more sets - How to streamline finding the set intersection using the
*unpacking operator - How to handle errors when finding the intersection between iterables
Understanding Set Intersection in Python
Set intersection refers to finding the set of items that are common between two or more different sets, lists, tuples or other containers. This means that a set is returned that includes only items that exist in both sets (or in all of the sets if more than two sets are evaluated).
Because Python sets contain only unique items, each item will be represented only once. This is true even when you try to find the intersection between a set and a list (as you’ll learn later in this tutorial) – even if the list has the same item repeated multiple times. Looking to work only with lists? Check out my in-depth guide on finding the intersection between two Python lists.
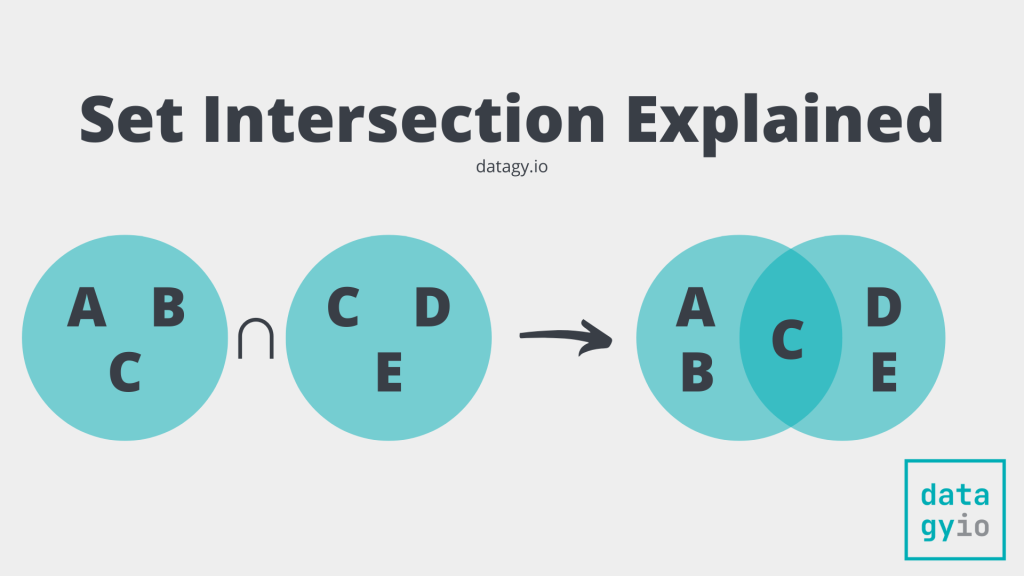
The intersection between two (or more) sets can be easily represented using a venn diagram, as shown below:
Now that you have an understanding of what is meant by intersection, let’s dive into understanding the set .intersection() method.
Understanding the Python Set intersection Method
Python sets have a method, .intersection(), available to them that allow you to easily identify the intersection between two sets (or a set and another container object). Let’s take a look at what this method looks like:
# Understanding the Python set.intersection() Method
set.intersection(set1, set2, ...)While the definition above identifies passing in sets, the .intersection() method actually allows you to pass in other container data types, such as lists and tuples. One important thing to note is that the method will always return a set.
Let’s see how we can use the .intersection() method to find the intersection between two sets:
# Finding the Intersection Between Two Sets
A = {1, 2, 3}
B = {2, 3, 4}
AnB = A.intersection(B)
print(AnB)
# Returns: {2, 3}In the following section, you’ll learn how to use the intersection method between a set and a list in Python.
How to Find the Intersection Between a Set and a List in Python
The Python set intersection method allows you to find the intersection between a set and a Python list. Because sets contain only unique items, the resulting set will contain each item only one time. This is true, even if it exists multiple times in a Python list.
Let’s see what happens when we use the .intersection() method to find the intersection between a Python set and a list.
# Finding the Intersection Between a Set and a List in Python
A = {1, 2, 3}
B = [2, 3, 4]
AnB = A.intersection(B)
print(AnB)
# Returns: {2, 3}We can see that by using the .intersection() method on a set and passing in a list, that the common items between the two objects are returned in a set.
How to Find the Intersection Between Multiple Sets in Python Using *
The Python set .intersection() method allows you to find the intersection between multiple sets. This can be done by passing in any number of sets into the method. Let’s see how we can find the intersection between three sets:
# Finding the Intersection Between Multiple Sets in Python
A = {1, 2, 3}
B = {2, 3, 4}
C = {3, 4, 5}
AnB = A.intersection(B, C)
print(AnB)
# Returns: {3}We can simplify this process as well if all the sets are contained in a single list. We can then use the * operator to unpack all the items in the list directly. Let’s see what this looks like:
# Finding the Intersection Between Multiple Sets in Python Using *
A = {1, 2, 3}
B = {2, 3, 4}
C = {3, 4, 5}
sets = [A, B, C]
AnBnC = A.intersection(*sets)
print(AnBnC)
# Returns: {3}In the following section, you’ll learn how to use the & operator to find the intersection between two or more sets in Python.
Using & to Find the Intersection Between Python Sets
A very elegant way to find the intersection between two or more sets in Python is to use the & operator. This allows us to write very Pythonic code that can be quite easy to understand. Let’s see what this looks like when we find the intersection between two sets:
# Finding the Intersection Between Two Sets Using &
A = {1, 2, 3}
B = {2, 3, 4}
print(AnB)
AnB = A & B
# Returns: {2, 3}We can see that this accomplishes the same thing as using the .intersection() method. We can also accomplish this with more than sets, simply by chaining the operator. Let’s take a look at what this looks like:
# Finding the Intersection Between Three Sets Using &
A = {1, 2, 3}
B = {2, 3, 4}
C = {3, 4, 5}
AnBnC = A & B & C
print(AnBnC)
# Returns: {3}In the following section, you’ll learn some of the quirks of the & operator.
Handling TypeError When Finding Set Intersection in Python
While the Python set.intersection() method works with a set and a different container data type, the & operator does not. The operator only works between sets, regardless of the number of sets. Let’s see what happens when we use the operator between a list and a set:
# Raising a Type Error When Finding the Intersection Between a List and a Set
A = {1, 2, 3}
B = [2, 3, 4]
AnB = A & B
# Raises: TypeError: unsupported operand type(s) for &: 'set' and 'list'We can resolve this error in two ways:
- We can convert the list to a set, by passing it into the
set()function - We can pass the list into the
.intersection()method
Let’s see what both of these methods look like:
# Resolving the TypeError
A = {1, 2, 3}
B = [2, 3, 4]
# Method 1: Converting to a set
AnB = A & set(B)
# Method 2: Using .intersection()
AnB2 = A.intersection(B)
print(AnB)
print(AnB2)
# Returns:
# {2, 3}
# {2, 3}In the following section, you’ll learn how to work with empty sets when attempting to find the intersection.
Working with Empty Sets When Finding Set Intersections
When you try to find the intersection between a set and an empty set, an empty set will always be returned. This happens, logically, because an empty set will have zero items in common with any other set.
Let’s see what this looks like:
# Finding the Intersection Between a Set and an Empty Set
A = {1, 2, 3}
B = set()
AnB = A.intersection(B)
print(AnB)
# Returns:
# set()Frequently Asked Questions
What is the best way to find the intersection between two sets in Python?
The best way to find the intersection between two or more sets is to use the .intersection() method. This method allows you to even find the intersection between a set and other data types.
How do you find the intersection between two lists or tuples in Python?
To find the intersection between between lists and tuples in Python, you can convert one of them to a set and pass the other into the .intersection() method. This process can look like this: set(list1).intersection(list2).
Conclusion
In this tutorial, you learned how to use Python to find the intersection between two or more sets. You first learned what is meant by finding the intersection between two sets. Then, you learned how to use the .intersection() method to find the intersection between two or more sets or between sets and other data types. Then, you learned how to use the & operator to find intersections.
Additional Resources
To learn more about related topics, check out the tutorials below:
- How to Remove Items from Python Sets
- Python frozenset: Overview and Examples
- How to Append to a Set in Python: Python Set Add() and Update()
- Python Sets: Official Documentation