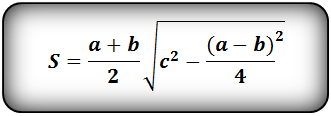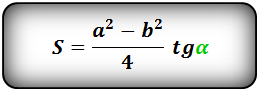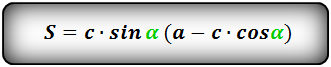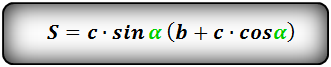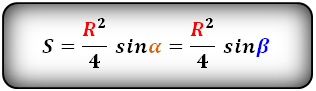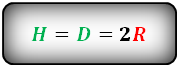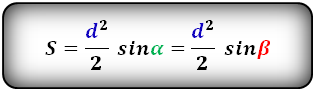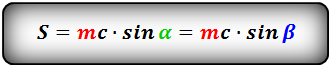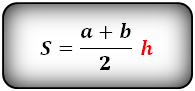Загрузить PDF
Загрузить PDF
Найти площадь фигуры (объекта) легко, если вы понимаете процесс и знаете необходимые формулы. В этом случае вы можете найти площадь и площадь поверхности той или иной фигуры.
-
1
Если вы столкнулись с фигурой непонятной (произвольной) формы, разбейте ее на несколько стандартных геометрических фигур, то есть разделите одну (большую) фигуру на ряд мелких фигур.
- Например, фигура разбивается на треугольник, трапецию, прямоугольник, квадрат и полукруг.
-
2
Запишите формулы для нахождения площади каждой из этих фигур. Эти формулы позволят вам найти площади фигур по данным или измеренным величинам.
- Площадь квадрата: S = a2, где а – сторона квадрата.
- Площадь прямоугольника: S = w x h, где w – длина прямоугольника, h – ширина прямоугольника.
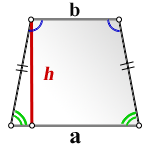
- Площадь трапеции: S = [(a + b) x h]/2, где a и b – основания трапеции, h – высота трапеции.
- Площадь треугольника: S = (b + h)/2, где b – сторона в основании треугольника, h – высота, опущенная на основание.
- Площадь полукруга: S = (π x r2)/2, где r – радиус полукруга.
-
3
Запишите данные вам значения, которые вы подставите в формулы.
- Квадрат: a = 2,5 см
- Прямоугольник = w = 4,5 см, h = 2,5 см
- Трапеция = a = 3 см, b = 5 см, h = 5 см
- Треугольник = b = 3 см, h = 2,5 см
- Полукруг = r = 1,5 см
-
4
Найдите площадь каждой фигуры по данным значениям и соответствующим формулам. После этого сложите значения площади каждой фигуры, и вы найдете площадь исходной фигуры. Не забудьте указать квадратные единицы измерения. Площадь исходной фигуры равна 44,78 см2. Вот как это вычисляется:
- Найдите площадь каждой фигуры:
- Площадь квадрата = 2,5 см2 = 6,25 см2
- Прямоугольник = 4,5 см x 2,5 см = 11,25 см2
- Трапеция = [(3 см + 5 см) x 5 см]/2 = 20 см2
- Треугольник = 3 см x 2,5 см x 1/2 = 3,75 см2
- Полукруг = 1,5 см2 x π x 1/2 = 3,53 см2
- Сложите найденные площади:
- Площадь исходной фигуры (объекта) = площадь квадрата + площадь прямоугольника + площадь трапеции + площадь треугольника + площадь полукруга.
- Площадь объекта = 6,25 см2 + 11,25 см2 + 20 см2 + 3,75 см2 + 3,53 см2
- Площадь объекта = 44,78 см2
Реклама
- Найдите площадь каждой фигуры:
-
1
Запишите формулы для нахождения площади поверхности различных фигур. Площадь поверхности – эти общая площадь, занимаемая поверхностью фигуры, будучи спроецированной на двумерную плоскость. Каждая трехмерная фигура имеет площадь поверхности. Вот формулы для нахождения площади поверхности различных объектов:
- Куб: S = 6s2, где s – сторона куба.
- Конус: S = π x r x s + πr2, где r – радиус, s – образующая.
- Шар (сфера): S = 4πr2, где r – радиус.
- Цилиндр: S = 2πr2 + 2πrh, где r – радиус, h – высота.
- Пирамида: = b2 + 2bh, где b – сторона основания, h – высота.
-
2
Запишите данные вам значения, которые вы подставите в формулы.
- Куб. s = 3,5 см
- Конус. r = 2 см, h = 4 см
- Шар. r = 3 см
- Цилиндр. r = 2 см, h = 3,5 см
- Квадратная пирамида. b = 2 см, h = 4 см
-
3
Найдите площадь поверхности каждой фигуры по данным значениям и соответствующим формулам.
- Площадь поверхности куба = 6 x 3,52 = 73,5 см2
- Конус = π(2 x 4) + π x 22 = 37,7 см2
- Шар = 4 x π x 32 = 113,09 см2
- Цилиндр = 2π x 22 + 2π(2 x 3,5) = 69,1 см2
- Квадратная пирамида = 22 + 2(2 x 4) = 20 см2
Реклама
Советы
- Измеряйте исходные объекты линейкой или штангенциркулем.
Реклама
Предупреждения
- Не путайте термины «площадь» и «площадь поверхности». Это родственные понятия, но используются они по-разному. Площадь употребляется в случае плоских объектов, а площадь поверхности — в случае трехмерных объектов.
Реклама
Об этой статье
Эту страницу просматривали 24 906 раз.
Была ли эта статья полезной?
Формулы площади геометрических фигур
Площадь геометрической фигуры — численная характеристика геометрической фигуры показывающая размер этой фигуры (части поверхности, ограниченной замкнутым контуром данной фигуры). Величина площади выражается числом заключающихся в нее квадратных единиц.
Формулы площади треугольника
-
Формула площади треугольника по стороне и высоте
Площадь треугольника равна половине произведения длины стороны треугольника на длину проведенной к этой стороне высоты -
Формула площади треугольника по трем сторонам
Формула Герона
S = √p(p — a)(p — b)(p — c)
-
Формула площади треугольника по двум сторонам и углу между ними
Площадь треугольника равна половине произведения двух его сторон умноженного на синус угла между ними. -
Формула площади треугольника по трем сторонам и радиусу описанной окружности
-
Формула площади треугольника по трем сторонам и радиусу вписанной окружности
Площадь треугольника равна произведения полупериметра треугольника на радиус вписанной окружности.где S — площадь треугольника,
a, b, c — длины сторон треугольника,
h — высота треугольника,
γ — угол между сторонами a и b,
r — радиус вписанной окружности,
R — радиус описанной окружности,p = a + b + c — полупериметр треугольника. 2
Формулы площади квадрата
-
Формула площади квадрата по длине стороны
Площадь квадрата равна квадрату длины его стороны.S = a2
-
Формула площади квадрата по длине диагонали
Площадь квадрата равна половине квадрата длины его диагонали.где S — площадь квадрата,
a — длина стороны квадрата,
d — длина диагонали квадрата.
Формула площади прямоугольника
Площадь прямоугольника равна произведению длин двух его смежных сторон
S = a · b
где S — Площадь прямоугольника,
a, b — длины сторон прямоугольника.
Формулы площади параллелограмма
-
Формула площади параллелограмма по длине стороны и высоте
Площадь параллелограмма равна произведению длины его стороны и длины опущенной на эту сторону высоты.S = a · h
-
Формула площади параллелограмма по двум сторонам и углу между ними
Площадь параллелограмма равна произведению длин его сторон умноженному на синус угла между ними.S = a · b · sin α
-
Формула площади параллелограмма по двум диагоналям и углу между ними
Площадь параллелограмма равна половине произведения длин его диагоналей умноженному на синус угла между ними.где S — Площадь параллелограмма,
a, b — длины сторон параллелограмма,
h — длина высоты параллелограмма,
d1, d2 — длины диагоналей параллелограмма,
α — угол между сторонами параллелограмма,
γ — угол между диагоналями параллелограмма.
Формулы площади ромба
-
Формула площади ромба по длине стороны и высоте
Площадь ромба равна произведению длины его стороны и длины опущенной на эту сторону высоты.S = a · h
-
Формула площади ромба по длине стороны и углу
Площадь ромба равна произведению квадрата длины его стороны и синуса угла между сторонами ромба.S = a2 · sin α
-
Формула площади ромба по длинам его диагоналей
Площадь ромба равна половине произведению длин его диагоналей.где S — Площадь ромба,
a — длина стороны ромба,
h — длина высоты ромба,
α — угол между сторонами ромба,
d1, d2 — длины диагоналей.
Формулы площади трапеции
-
Формула Герона для трапеции
S = a + b √(p-a)(p-b)(p-a-c)(p-a-d) |a — b| -
Формула площади трапеции по длине основ и высоте
Площадь трапеции равна произведению полусуммы ее оснований на высотугде S — площадь трапеции,
a, b — длины основ трапеции,
c, d — длины боковых сторон трапеции,p = a + b + c + d — полупериметр трапеции. 2
Формулы площади выпуклого четырехугольника
-
Формула площади четырехугольника по длине диагоналей и углу между ними
Площадь выпуклого четырехугольника равна половине произведения его диагоналей умноженному на синус угла между ними:
где S — площадь четырехугольника,
d1, d2 — длины диагоналей четырехугольника,
α — угол между диагоналями четырехугольника. -
Формула площади описанного четырехугольника (по длине периметра и радиусу вписанной окружности)
Площадь выпуклого четырехугольника равна произведению полупериметра на радиус вписанной окружности
S = p · r
-
Формула площади четырехугольника по длине сторон и значению противоположных углов
S = √(p — a)(p — b)(p — c)(p — d) — abcd cos2θ
где S — площадь четырехугольника,
a, b, c, d — длины сторон четырехугольника,
p = a + b + c + d2 — полупериметр четырехугольника,
θ = α + β2 — полусумма двух противоположных углов четырехугольника.
-
Формула площади четырехугольника, вокруг которого можно описать окружность
S = √(p — a)(p — b)(p — c)(p — d)
Формулы площади круга
-
Формула площади круга через радиус
Площадь круга равна произведению квадрата радиуса на число пи.S = π r2
-
Формула площади круга через диаметр
Площадь круга равна четверти произведения квадрата диаметра на число пи.где S — Площадь круга,
r — длина радиуса круга,
d — длина диаметра круга.
Формулы площади эллипса
Площадь эллипса равна произведению длин большой и малой полуосей эллипса на число пи.
S = π · a · b
где S — Площадь эллипса,
a — длина большей полуоси эллипса,
b — длина меньшей полуоси эллипса.
Почему бы просто не считать клеточки?
Возможно, вы читаете всё это и думаете: зачем все эти сложности? Формулы запоминать. Дорисовывать. Тут ведь сразу видно, сколько клеточек в фигуре.
Вот, например, трапеция:
Посчитаем клеточки: их всего 46, верно?
Но стоп, там же некоторые из них только наполовину внутри фигуры. Отметим их – всего таких 10. Итого, 36 полных (красные точки) и 10 половинчатых, вместе ( 36+frac{10}{2} = 41)
Вроде бы всё верно. Но, если присмотреться, можно заметить ещё маленькие треугольнички, которые попали внутрь. А также, что «синие» клеточки слева на самом деле разрезаны не ровно пополам – какие-то чуть больше, какие-то меньше…
Как всё это учитывать?
Попробуем рассуждать так: заметно, что тот маленький розовый треугольник дополняет серый кусок клетки.
А жёлтые сколько занимают? Постарайтесь ответить сами.
Если всё сделать правильно, то увидите, что жёлтые кусочки можно сложить вместе в одну целую клетку.
Итак, 2 жёлтых куска = 1 клетка.
Розовый треугольник + серый кусок = 1 клетка. Всего у нас две таких пары (розовый+серый) – это 2 полных клетки.
Всё остальное как было: 36 полных клеток и 6 половинок у правой стороны – это ( 36+frac{6}{2}=39) клетки.
Итого клеток: ( 1 + 2 + 39 = 42).
Проверим результат по формуле площади трапеции: нижнее основание 11, верхнее основание 3, высота 6. Полусумма оснований равна 7, умножаем на высоту – получилось 42. Всё совпало.
Но! Настолько ли проще был наш способ подсчёта клеточек? Не сказал бы. А если там будет несколько косых линий, то вообще можно замучиться собирать этот паззл (искать, какие кусочки друг друга дополняют).
Вычислите площадь простых фигур тремя способами
Стороны клеток равны 1. Вычислите самостоятельно площадь фигуры всеми тремя способами. Сравните результаты.
Вычислите площадь произвольных фигур по формуле Пика
Вычислите самостоятельно площади фигур с помощью формулы Пика:
Посчитайте площадь корабля и котика по формуле Пика
Посчитайте самостоятельно для тренировки и чтобы запомнить формулу Пика!
Фигуры с отверстиями — посчитайте площади двумя способами
Ну и напоследок фигуры с «дырками». Как думаешь, здесь придётся вычислять сначала площадь целой фигуры, а потом площадь дырки?
Или достаточно просто посчитать точки внутри закрашенной области и на её границах (в том числе, на границе с дыркой)?
Проверим на простом примере: это квадрат ( 4times 4), и в нём вырезан прямоугольник ( 1times 2), значит, его площадь ( 16-2=14).
А теперь по точкам. На границах (включая внутренние) ( Г = 22). Внутри ( В = 3). Тогда площадь по формуле Пика
( S = frac{22}{2} + 3 -1 = 13.)
Хм, близко, но не совпало. Может, я где-то ошибся? Давай ещё одну фигуру, для верности.
Сосчитай сам и проверь.
Что получилось?
У меня снова на 1 меньше.
Так может быть просто формулу немного «подкрутить»? Нет!
Очень и очень не рекомендую вам запоминать несколько похожих формул для похожих случаев, потому что придёт время, и вы обязательно перепутаете формулу.
Даже если вы уверены, что не перепутаете, оно всё равно того не стоит. В общем, наилучший вариант – это запомнить одну формулу. А если попалась фигура с дыркой, вычислить всю фигуру, а потом дырку. И вычесть.
Площадь поверхности пирамиды
Для пирамиды тоже действует общее правило:
Площадь полной поверхности пирамиды – это сумма площадей всех граней.( displaystyle {{S}_{полн. пов. }}={{S}_{боков.пов. }}+{{S}_{основания }})
Теперь давай посчитаем площадь поверхности самых популярных пирамид.
Площадь поверхности правильной треугольной пирамиды
Пусть сторона основания равна ( displaystyle a), а боковое ребро равно ( displaystyle b). Нужно найти ( displaystyle {{S}_{осн}}) и ( displaystyle {{S}_{ASB}}).
И тогда
( displaystyle {{S}_{полн. пов. }}=3{{text{S}}_{ASB}}+{{text{S}}_{text{осн}.}})
Вспомним теперь, что
( displaystyle {{S}_{осн}}) — это площадь правильного треугольника ( displaystyle ABC).
И еще вспомним, как искать эту площадь.
Используем формулу площади:
( displaystyle S=frac{1}{2}abcdot sin gamma ).
У нас «( displaystyle a)» — это ( displaystyle a), а «( displaystyle b)» — это тоже ( displaystyle a), а ( displaystyle sin gamma =sin 60{}^circ =frac{sqrt{3}}{2}).
Значит, ( displaystyle {{S}_{ABC}}=frac{1}{2}{{a}^{2}}frac{sqrt{3}}{2}=frac{{{a}^{2}}sqrt{3}}{4}).
Теперь найдем ( displaystyle {{S}_{Delta ASB}}).
Пользуясь основной формулой площади и теоремой Пифагора, находим
( displaystyle {{S}_{Delta ASB}} = frac{1}{2}asqrt{b^2-frac{a^2}{4}})
Внимание: если у тебя правильный тетраэдр (т.е. ( displaystyle b=a)), то формула получается такой:
( displaystyle S={{a}^{2}}sqrt{3}).
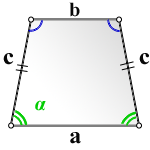
1. Формула площади равнобедренной трапеции через стороны и угол
b — верхнее основание
a — нижнее основание
c — равные боковые стороны
α — угол при нижнем основании
Формула площади равнобедренной трапеции через стороны, (S):
Формула площади равнобедренной трапеции через стороны и угол, (S):
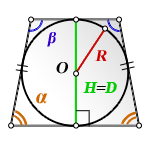
2. Формула площади равнобокой трапеции через радиус вписанной окружности
R — радиус вписанной окружности
D — диаметр вписанной окружности
O — центр вписанной окружности
H — высота трапеции
α, β — углы трапеции
Формула площади равнобокой трапеции через радиус вписанной окружности, (S):
СПРАВЕДЛИВО, для вписанной окружности в равнобокую трапецию:
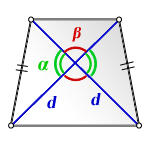
3. Формула площади равнобедренной трапеции через диагонали и угол между ними
d — диагональ трапеции
α, β — углы между диагоналями
Формула площади равнобедренной трапеции через диагонали и угол между ними, (S):
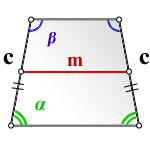
4. Формула площади равнобедренной трапеции через среднюю линию, боковую сторону и угол при основании
m — средняя линия трапеции
c — боковая сторона
α, β — углы при основании
Формула площади равнобедренной трапеции через среднюю линию, боковую сторону и угол при основании, (S ):
5. Формула площади равнобедренной трапеции через основания и высоту
b — верхнее основание
a — нижнее основание
h — высота трапеции
Формула площади равнобедренной трапеции через основания и высоту, (S):
Download Article
Download Article
Surface area is the total amount of space that all of the surfaces of an object take up. It is the sum of the area of all the surfaces of that object.[1]
Finding the surface area of a three-dimensional shape is moderately easy as long as you know the correct formula. Each shape has its own separate formula, so you’ll first need to identify the shape you’re working with. Memorizing the surface area formula for various objects can make calculations easier in the future. Here are a few of the most common shapes you might encounter.
-
1
Define the formula for surface area of a cube. A cube has six identical square sides. Because both the length and width of a square are equal, the area of a square is a2, where a is the length of a side. Since there are 6 identical sides of a cube, to find the surface area, simply multiply the area of one side times 6. The formula for surface area (SA) of a cube is SA = 6a2, where a is the length of one side.[2]
- The units of surface area will be some unit of length squared: in2, cm2, m2, etc.
-
2
Measure the length of one side. Each side or edge of a cube should, by definition, be equal in length to the others, so you only need to measure one side. Using a ruler, measure the length of the side. Pay attention to the units you are using.
- Mark this measurement down as a.
- Example: a = 2 cm
Advertisement
-
3
Square your measurement for a. Square the measurement taken for the length of the edge. To square a measurement means to multiply it by itself. When you are first learning these formulas, it might be helpful to write it as SA= 6*a*a.
- Note that this step calculates the area of one side of the cube.
- Example: a = 2 cm
- a2 = 2 x 2 = 4 cm2
-
4
Multiply this product by six. Remember, a cube has six identical sides. Now that you have the area of one side, you need to multiply it by six to account for all six sides.
- This step completes the calculation for the cube’s surface area.
- Example: a2 = 4 cm2
- Surface Area = 6 x a2 = 6 x 4 = 24 cm2
Advertisement
-
1
Define the formula for surface are of a rectangular prism. Like a cube, a rectangular prism has six sides, but unlike a cube, the sides are not identical. In a rectangular prism, only opposite sides are equal.[3]
Because of this, the surface of a rectangular prism must take into account the various side lengths making the formula SA = 2ab + 2bc + 2ac.- For this formula, a equals the width of the prism, b equals the height, and c equals the length.
- Breaking down the formula, you can see that you are simply adding up all of the areas of each face of the object.
- The units of surface area will be some unit of length squared: in2, cm2, m2, etc.
-
2
Measure the length, height, and width of each side. All three measurements can vary, so all three need to be taken separately. Using a ruler, measure each side and write it down. Use the same units for each measurement.
- Measure the length of the base to determine the length of the prism, and assign this to c.
- Example: c = 5 cm
- Measure the width of the base to determine the width of the prism, and assign this to a.
- Example: a = 2 cm
- Measure the height of the side to determine the height of the prism, and assign this to b.
- Example: b = 3 cm
-
3
Calculate the area of one of the sides of the prism, then multiply by two. Remember, there are 6 faces of a rectangular prism, but opposite sides are identical. Multiply the length and height, or c and a to find the area of one face. Take this measurement and multiply it by two to account for the opposite identical side.[4]
- Example: 2 x (a x c) = 2 x (2 x 5) = 2 x 10 = 20 cm2
-
4
Find the area of the other side of the prism and multiply by two. Like with the first pair of faces, multiply the width and height, or a and b to find the area of another face of the prism. Multiply this measurement by two to account for the opposite identical sides.[5]
- Example: 2 x (a x b) = 2 x (2 x 3) = 2 x 6 = 12 cm2
-
5
Calculate the area of the ends of the prism and multiply by two. The final two faces of the prism will be the ends. Multiply the length and width, or c and b to find their area. Multiply this measurement by two to account for both sides.[6]
- Example: 2 x (b x c) = 2 x (3 x 5) = 2 x 15 = 30 cm2
-
6
Add the three separate measurements together. Because surface area is the total area of all of the faces of an object, the final step is to add all of the individually calculated areas together. Add the area measurements for all the sides together to find the total surface area.[7]
- Example: Surface Area = 2ab + 2bc + 2ac = 12 + 30 + 20 = 62 cm2.
Advertisement
-
1
Define the surface area formula for a triangular prism. A triangular prism has two identical triangular sides and three rectangular faces. To find the surface area, you must calculate the area of all of the sides and add them together. The surface area of a triangular prism is SA = 2A + PH, where A is the area of the triangular base, P is the perimeter of the triangular base, and h is the height of the prism.
- For this formula, A is the area of a triangle which is A = 1/2bh where b is the base of the triangle and h is the height.
- P is simply the perimeter of the triangle which is calculated by adding all three sides of the triangle together.
- The units of surface area will be some unit of length squared: in2, cm2, m2, etc.
-
2
Calculate the area of the triangular face and multiply by two. The area of a triangle is 1/2b*h where b is the base of the triangle and h is the height. Because there are two identical triangle faces we can multiply the formula by two. This makes the calculation for both faces simply, b*h.
- The base, b, equals the length of the bottom of the triangle.
- Example: b = 4 cm
- The height, h, of the triangular base equals the distance between the bottom edge and the top peak.
- Example: h = 3 cm
- Area of the one triangle multiplied by 2= 2(1/2)b*h = b*h = 4*3 =12 cm
-
3
Measure each side of the triangle and the height of the prism. To finish the surface area calculation, you need to know the length of each side of the triangle and the height of the prism. The height is the distance between the two triangular faces.
- Example: H = 5 cm
- The three sides refer to the three sides of the triangular base.
- Example: S1 = 2 cm, S2 = 4 cm, S3 = 6 cm
-
4
Determine the perimeter of the triangle. The perimeter of the triangle can be calculated simply by adding up all of the measured sides: S1 + S2 + S3.
- Example: P = S1 + S2 + S3 = 2 + 4 + 6 = 12 cm
-
5
Multiply the perimeter of the base by the height of the prism. Remember, the height of the prism is distance between the two triangular bases. In other words, multiply P by H.
- Example: P x H = 12 x 5 = 60 cm2
-
6
Add the two separate measurements together. You will need to add the two measurements from the previous two steps together to calculate the triangular prism’s surface area.
- Example: 2A + PH = 12 + 60 = 72 cm2.
Advertisement
-
1
Define the surface area formula for a sphere. A sphere has a curved surface and therefore the surface area must use the mathematical constant, pi. The surface area of a sphere is given by the equation SA = 4π*r2.[8]
- For this formula, r equals the radius of the sphere. Pi, or π, should be approximated to 3.14.
- The units of surface area will be some unit of length squared: in2, cm2, m2, etc.
-
2
Measure the radius of the sphere. The radius of the sphere is half the diameter, or half the distance from one side of the center of the sphere to the other.[9]
- Example: r = 3 cm
-
3
Square the radius. To square a number, simply multiply it by itself. Multiply the measurement for r by itself. Remember, this formula can be rewritten as SA = 4π*r*r.[10]
- Example: r2 = r x r = 3 x 3 = 9 cm2
-
4
Multiply the squared radius by an approximation of pi. Pi is a constant that represents the ratio of a circle’s circumference to its diameter.[11]
It is an irrational number that has many decimal digits. It is frequently approximated as 3.14. Multiply the squared radius by π, or 3.14, to find the area of one circular section of the sphere.[12]
- Example: π*r2 = 3.14 x 9 = 28.26 cm2
-
5
Multiply this product by four. To complete the calculation, multiply by 4. Find the surface area of the sphere by multiplying the flat circular area by four.[13]
- Example: 4π*r2 = 4 x 28.26 = 113.04 cm2
Advertisement
-
1
Define the surface area formula for a cylinder. A cylinder has two circular ends enclosing a rounded surface. The formula for surface area of a cylinder is SA = 2π*r2 + 2π*rh, where r equals the radius of the circular base and h equals the height of the cylinder. Round pi or π off to 3.14.[14]
- 2π*r2 represents the surface area of the two circular ends while 2πrh is the surface area of the column connecting the two ends.
- The units of surface area will be some unit of length squared: in2, cm2, m2, etc.
-
2
Measure the radius and height of the cylinder. The radius of a circle is half of the diameter, or half the distance from one side of the center of the circle to the other.[15]
The height is the total distance of the cylinder from end to end. Using a ruler, take these measurements and write them down.- Example: r = 3 cm
- Example: h = 5 cm
-
3
Find the area of the base and multiply by two. To find the area of the base, you simply use the formula for area of circle, or π*r2. To complete the calculation, square the radius and multiply by pi. Multiply by two to take into account the second identical circle on the other end of the cylinder.[16]
- Example: Area of base = π*r2 = 3.14 x 3 x 3 = 28.26 cm2
- Example: 2π*r2 = 2 x 28.26 = 56.52 cm2
-
4
Calculate the surface area of the cylinder itself, using 2π*rh. This is the formula to calculate the surface area of a tube. The tube is the space between the two circular ends of the cylinder. Multiply the radius by two, pi, and the height.[17]
- Example: 2π*rh = 2 x 3.14 x 3 x 5 = 94.2 cm2
-
5
Add the two separate measurements together. Add the surface area of the two circles to the surface area of the space between the two circles to calculate the total surface area of the cylinder. Note, adding these two pieces together allows you to recognize the original formula: SA =2π*r2 + 2π*rh.[18]
- Example: 2π*r2 + 2π*rh = 56.52 + 94.2 = 150.72 cm2
Advertisement
-
1
Define the surface area formula for a square pyramid. A square pyramid has a square base and four triangular sides. It is defined as the total lateral area of the base. Remember, the area of the square is the length of one side squared. The area of a triangle is 1/2sl (side of the triangle times the length or height of the triangle). Because there are four triangles, to find the total surface area, you must multiply by four. Adding all of these faces together yields the equation of surface area for a square pyramid: SA = s2 + 2sl.[19]
- For this equation, s refers to the length of each side of the square base and l refers to the slant height of each triangular side.
- The units of surface area will be some unit of length squared: in2, cm2, m2, etc.
-
2
Measure the slant height and base side. The slant height, l, is the height of one of the triangular sides. It is the distance between the base to the peak of the pyramid as measured along one flat side. The base side, s, is the length of one side of the square base. Because the base is square, this measurement is the same for all sides. Use a ruler to make each measurement.[20]
- Example: l = 3 cm
- Example: s = 1 cm
-
3
Find the area of the square base. The area of a square base can be calculated by squaring the length of one side, or multiplying s by itself.[21]
- Example: s2 = s x s = 1 x 1 = 1 cm2
-
4
Calculate the total area of the four triangular faces. The second part of the equation involves the surface area of the remaining four triangular sides. Using the formula 2ls, multiply s by l and two. Doing so will allow you to find the area of each side.[22]
- Example: 2 x s x l = 2 x 1 x 3 = 6 cm2
-
5
Add the two separate areas together. Add the total area of the sides to the area of the base to calculate the total surface area.[23]
- Example: s2 + 2sl = 1 + 6 = 7 cm2
Advertisement
-
1
Define the surface area formula for a cone. A cone has a circular base and a rounded surface that tapers into a point. To find the surface area, you need to calculate the area of the circular base and the surface of the cone and add these two together. The formula for surface area of a cone is: SA = π*r2 + π*rl, where r is the radius of the circular base, l is the slant height of the cone, and π is the mathematical constant pi (3.14).[24]
- The units of surface area will be some unit of length squared: in2, cm2, m2, etc.
-
2
Measure the radius and height of the cone. The radius is the distance from the center of the circular base to the side of the base. The height is the distance from the center of the base to the top peak of the cone, as measured through the center of the cone.[25]
- Example: r = 2 cm
- Example: h = 4 cm
-
3
Calculate the slant height (l) of the cone. Because the slant height is actually the hypotenuse of a triangle, you must use the Pythagorean Theorem to calculate it. Use the rearranged form, l = √ (r2 + h2), where r is the radius and h is the height of the cone. [26]
- Example: l = √ (r2 + h2) = √ (2 x 2 + 4 x 4) = √ (4 + 16) = √ (20) = 4.47 cm
-
4
Determine the area of the circular base. The area of the base is calculated with the formula π*r2. After measuring the radius, square it (multiply it by itself) and then multiply that product by pi.[27]
- Example: π*r2 = 3.14 x 2 x 2 = 12.56 cm2
-
5
Calculate the surface area of the top of the cone. Using the formula π*rl, where r is the radius of the circle and l is the slant height previously calculated, you can find the surface area of the top part of the cone.[28]
- Example: π*rl = 3.14 x 2 x 4.47 = 28.07 cm
-
6
Add two areas together to find total surface area. Calculate the final surface area of your cone by adding the area of the circular base to the calculation from the previous step.[29]
- Example: π*r2 + π*rl = 12.56 + 28.07 = 40.63 cm2
Advertisement
Add New Question
-
Question
How do I find the surface area for something that is «L»-shaped? Is there a formula?
Let’s assume we’re considering a three-dimensional, rectilinear object in the shape of an «L» and that we know the dimensions of all ten sides. There is no formula other than to add together the areas of all the sides. All sides are rectangles or squares, so in each case the area of a side is simply length multiplied by width.
-
Question
How do I solve problems involving capacity?
Volume («capacity») always involves three dimensions, typically length, width, and height (or depth). To calculate volume, multiply the three dimensions together.
-
Question
How do I find it as an irregular shape?
In general, it is not possible to calculate the surface area of an irregular shape unless all of its surface dimensions are known.
See more answers
Ask a Question
200 characters left
Include your email address to get a message when this question is answered.
Submit
Advertisement
Things You’ll Need
- Ruler
- Writing utensil
- Paper
References
About This Article
Article SummaryX
To find surface area for a rectangular prism, use the formula SA = 2ab + 2bc + 2ac, where a is the width, b is the height, and c is the length. If you’re trying to find the surface area of a triangular prism, use the formula SA = 2a + ph, where a is the area of the triangle, p is the perimeter, and h is the height. To find the surface area of a cube, use the formula SA = 6a^2, where a is the length. If you need to learn how to find the surface area of a sphere or pyramid, keep reading the article!
Did this summary help you?
Thanks to all authors for creating a page that has been read 306,915 times.
Reader Success Stories
-
Christine Meleg
Jul 3, 2017
«I am sewing a Quilt of Valor for my great nephew, an active member of the U.S. Marine Corps. I need to calculate…» more