This SQL tutorial explains how to use the SQL MAX function with syntax and examples.
Description
The SQL MAX function is used to return the maximum value of an expression in a SELECT statement.
Syntax
The syntax for the MAX function in SQL is:
SELECT MAX(aggregate_expression) FROM tables [WHERE conditions];
OR the syntax for the MAX function when grouping the results by one or more columns is:
SELECT expression1, expression2, ... expression_n,
MAX(aggregate_expression)
FROM tables
[WHERE conditions]
GROUP BY expression1, expression2, ... expression_n;
Parameters or Arguments
- expression1, expression2, … expression_n
- Expressions that are not encapsulated within the MAX function and must be included in the GROUP BY clause at the end of the SQL statement.
- aggregate_expression
- This is the column or expression from which the maximum value will be returned.
- tables
- The tables that you wish to retrieve records from. There must be at least one table listed in the FROM clause.
- WHERE conditions
- Optional. These are conditions that must be met for the records to be selected.
Example — With Single Expression
The simplest way to use the SQL MAX function would be to return a single field that calculates the MAX value.
For example, you might wish to know the maximum salary of all employees.
SELECT MAX(salary) AS "Highest salary" FROM employees;
In this SQL MAX function example, we’ve aliased the MAX(salary) field as «Highest salary». As a result, «Highest salary» will display as the field name when the result set is returned.
Example — Using SQL GROUP BY Clause
In some cases, you will be required to use the SQL GROUP BY clause with the SQL MAX function.
For example, you could also use the SQL MAX function to return the name of each department and the maximum salary in the department.
SELECT department, MAX(salary) AS "Highest salary" FROM employees GROUP BY department;
Because you have listed one column in your SQL SELECT statement that is not encapsulated in the MAX function, you must use the SQL GROUP BY clause. The department field must, therefore, be listed in the GROUP BY section.
Frequently Asked Questions
Question: I’m trying to pull some info out of a table. To simplify, let’s say the table (report_history) has 4 columns: user_name, report_job_id, report_name, and report_run_date.
Each time a report is run in Oracle, a record is written to this table noting the above info. What I am trying to do is pull from this table when the last time each distinct report was run and who ran it last.
My initial query:
SELECT report_name, MAX(report_run_date) FROM report_history GROUP BY report_name
runs fine. However, it does not provide the name of the user who ran the report.
Adding user_name to both the select list and to the group by clause returns multiple lines for each report; the results show the last time each person ran each report in question. (i.e. User1 ran Report 1 on 01-JUL-03, User2 ran Report1 on 01-AUG-03). I don’t want that….I just want to know who ran a particular report the last time it was run.
Any suggestions?
Answer: This is where things get a bit complicated. The SQL SELECT statement below will return the results that you want:
SELECT rh.user_name, rh.report_name, rh.report_run_date FROM report_history rh, (SELECT MAX(report_run_date) AS maxdate, report_name FROM report_history GROUP BY report_name) maxresults WHERE rh.report_name = maxresults.report_name AND rh.report_run_date= maxresults.maxdate;
Let’s take a few moments to explain what we’ve done.
First, we’ve aliased the first instance of the report_history table as rh.
Second, we’ve included two components in our FROM clause. The first is the table called report_history (aliased as rh). The second is a select statement:
(SELECT MAX(report_run_date) AS maxdate, report_name FROM report_history GROUP BY report_name) maxresults
We’ve aliased the max(report_run_date) as maxdate and we’ve aliased the entire result set as maxresults.
Now, that we’ve created this select statement within our FROM clause, Oracle will let us join these results against our original report_history table. So we’ve joined the report_name and report_run_date fields between the tables called rh and maxresults. This allows us to retrieve the report_name, max(report_run_date) as well as the user_name.
Question: I need help with a SQL query. I have a table in Oracle called orders which has the following fields: order_no, customer, and amount.
I need a query that will return the customer who has ordered the highest total amount.
Answer: The following SQL should return the customer with the highest total amount in the orders table.
SELECT query1.*
FROM (SELECT customer, SUM(orders.amount) AS total_amt
FROM orders
GROUP BY orders.customer) query1,
(SELECT MAX(query2.total_amt) AS highest_amt
FROM (SELECT customer, SUM(orders.amount) AS total_amt
FROM orders
GROUP BY orders.customer) query2) query3
WHERE query1.total_amt = query3.highest_amt;
This SQL SELECT statement will summarize the total orders for each customer and then return the customer with the highest total orders. This syntax is optimized for Oracle and may not work for other database technologies.
Question: I’m trying to retrieve some info from an Oracle database. I’ve got a table named Scoring with two fields — Name and Score. What I want to get is the highest score from the table and the name of the player.
Answer: The following SQL SELECT statement should work:
SELECT Name, Score FROM Scoring WHERE Score = (SELECT MAX(Score) FROM Scoring);
Question: I need help in a SQL query. I have a table in Oracle called cust_order which has the following fields: OrderNo, Customer_id, Order_Date, and Amount.
I would like to find the customer_id, who has Highest order count.
I tried with following query.
SELECT MAX(COUNT(*)) FROM CUST_ORDER GROUP BY CUSTOMER_ID;
This gives me the max Count, But, I can’t get the CUSTOMER_ID. Can you help me please?
Answer: The following SQL SELECT statement should return the customer with the highest order count in the cust_order table.
SELECT query1.*
FROM (SELECT Customer_id, Count(*) AS order_count
FROM cust_order
GROUP BY cust_order.Customer_id) query1,
(SELECT max(query2.order_count) AS highest_count
FROM (SELECT Customer_id, Count(*) AS order_count
FROM cust_order
GROUP BY cust_order.Customer_id) query2) query3
WHERE query1.order_count = query3.highest_count;
This SQL SELECT statement will summarize the total orders for each customer and then return the customer with the highest order count. This syntax is optimized for Oracle and may not work for other database technologies.
Question: I’m trying to get the employee with the maximum salary from department 30, but I need to display the employee’s full information. I’ve tried the following query, but it returns the result from both department 30 and 80:
SELECT *
FROM employees
WHERE salary = (SELECT MAX(salary)
FROM employees
WHERE department_id=30);
Answer: The SQL SELECT statement that you have written will first determine the maximum salary for department 30, but then you select all employees that have this salary. In your case, you must have 2 employees (one in department 30 and another in department 80) that have this same salary. You need to make sure that you are refining your query results to only return employees from department 30.
Try using this SQL SELECT statement:
SELECT *
FROM employees
WHERE department_id=30
AND salary = (SELECT MAX(salary)
FROM employees
WHERE department_id=30);
This will return the employee information for only the employee in department 30 that has the highest salary.
Let’s say I have the following data in the Customers table: (nothing more)
ID FirstName LastName
-------------------------------
20 John Mackenzie
21 Ted Green
22 Marcy Nate
What sort of SELECT statement can get me the number 22, in the ID column?
I need to do something like this to generate a unique ID. Sure I can let the system do this via auto-increment, but then how would I get the auto generated ID?
I thought of SELECT ID FROM Customers and counting the rows returned but this seems horribly inefficient, and in this case, it will incorrectly return «3», though I need a unique ID of 23.
Kevin
16.2k8 gold badges56 silver badges74 bronze badges
asked Oct 10, 2009 at 5:14
Robin RodricksRobin Rodricks
110k141 gold badges396 silver badges606 bronze badges
10
You can do
SELECT MAX(ID) FROM Customers;
answered Oct 10, 2009 at 5:15
If you’ve just inserted a record into the Customers table and you need the value of the recently populated ID field, you can use the SCOPE_IDENTITY function. This is only useful when the INSERT has occurred within the same scope as the call to SCOPE_IDENTITY.
INSERT INTO Customers(ID, FirstName, LastName)
Values
(23, 'Bob', 'Smith')
SET @mostRecentId = SCOPE_IDENTITY()
This may or may not be useful for you, but it’s a good technique to be aware of. It will also work with auto-generated columns.
Kevin
16.2k8 gold badges56 silver badges74 bronze badges
answered Oct 10, 2009 at 5:21
David AndresDavid Andres
31.3k7 gold badges45 silver badges36 bronze badges
0
SELECT * FROM Customers ORDER BY ID DESC LIMIT 1
Then get the ID.
McGarnagle
101k31 gold badges228 silver badges260 bronze badges
answered Oct 17, 2012 at 3:37
select max(id) from customers
warren
32.3k21 gold badges85 silver badges122 bronze badges
answered Oct 10, 2009 at 5:15
deostrolldeostroll
11.6k21 gold badges87 silver badges158 bronze badges
To get it at any time, you can do SELECT MAX(Id) FROM Customers .
In the procedure you add it in, however, you can also make use of SCOPE_IDENTITY — to get the id last added by that procedure.
This is safer, because it will guarantee you get your Id—just in case others are being added to the database at the same time.
Pritesh Jain
9,1064 gold badges37 silver badges51 bronze badges
answered Oct 10, 2009 at 5:19
BrisbeBrisbe
1,5782 gold badges20 silver badges42 bronze badges
If you’re talking MS SQL, here’s the most efficient way. This retrieves the current identity seed from a table based on whatever column is the identity.
select IDENT_CURRENT('TableName') as LastIdentity
Using MAX(id) is more generic, but for example I have an table with 400 million rows that takes 2 minutes to get the MAX(id). IDENT_CURRENT is nearly instantaneous…
answered Oct 10, 2009 at 17:34
DamonDamon
6873 silver badges17 bronze badges
3
select max(id) from Customers
warren
32.3k21 gold badges85 silver badges122 bronze badges
answered Oct 10, 2009 at 5:16
monksymonksy
14.1k17 gold badges75 silver badges123 bronze badges
If you are using AUTOINCREMENT, use:
SELECT LAST_INSERT_ID();
Assumming that you are using Mysql:
http://dev.mysql.com/doc/refman/5.0/en/example-auto-increment.html
Postgres handles this similarly via the currval(sequence_name) function.
Note that using MAX(ID) is not safe, unless you lock the table, since it’s possible (in a simplified case) to have another insert that occurs before you call MAX(ID) and you lose the id of the first insert. The functions above are session based so if another session inserts you still get the ID that you inserted.
ItsJ0el
551 silver badge5 bronze badges
answered Oct 10, 2009 at 5:33
1
If you’re not using auto-incrementing fields, you can achieve a similar result with something like the following:
insert into Customers (ID, FirstName, LastName)
select max(ID)+1, 'Barack', 'Obama' from Customers;
This will ensure there’s no chance of a race condition which could be caused by someone else inserting into the table between your extraction of the maximum ID and your insertion of the new record.
This is using standard SQL, there are no doubt better ways to achieve it with specific DBMS’ but they’re not necessarily portable (something we take very seriously in our shop).
answered Oct 10, 2009 at 6:53
paxdiablopaxdiablo
847k233 gold badges1568 silver badges1943 bronze badges
You can also use relational algebra. A bit lengthy procedure, but here it is just to understand how MAX() works:
E := πID (Table_Name)
E1 := πID (σID >= ID’ ((ρID’ E) ⋈ E)) – πID (σID < ID’ ((ρID’ E) ⋈ E))
Your answer:
Table_Name ⋈ E1
Basically what you do is subtract set of ordered relation(a,b) in which a<b from A where a, b ∈ A.
For relation algebra symbols see:
Relational algebra
From Wikipedia
answered Jan 24, 2013 at 17:33
ArnabArnab
5551 gold badge7 silver badges12 bronze badges
1
Here’s how I would make the next ID:
INSERT INTO table_name (
ID,
FIRSTNAME,
SURNAME)
VALUES (((
SELECT COALESCE(MAX(B.ID)+1,1) AS NEXTID
FROM table_name B
)), John2, Smith2);
With this you can make sure that even if the table ID is NULL, it will still work perfectly.
answered Jan 12, 2021 at 21:20
Depends on what SQL implementation you are using. Both MySQL and SQLite, for example, have ways to get last insert id. In fact, if you’re using PHP, there’s even a nifty function for exactly that mysql_insert_id().
You should probably look to use this MySQL feature instead of looking at all the rows just to get the biggest insert ID. If your table gets big, that could become very inefficient.
answered Oct 10, 2009 at 6:26
sohumsohum
3,2072 gold badges39 silver badges62 bronze badges
If you want to just select the id use select max(id) from customer.
If you want to select the entire row then use a query like this:
select c1.*
from customer c1, (select max(id) as max_id from customer )c2
where c1.id=c2.max_id
c2 is an alias for the new temporary table which contains max id. Then its cross product is taken with customer table to get the entire row.
Here we are writing a query in the from clause, which can often be quite useful.
answered Jul 7, 2018 at 19:48
To find the next (still not used) auto-increment, I am using this function for somewhat years now.
public function getNewAI($table)
{
$newAI = false;
$mysqli = new mysqli(DB_HOST, DB_USER, DB_PASSWORD, DB_NAME);
if(mysqli_connect_errno()) {
echo "Failed to connect to MySQL: " . mysqli_connect_error();
}
$sql = "SHOW TABLE STATUS LIKE '".$table."'";
$result = $mysqli->query($sql);
if($result) {
$row = $result->fetch_assoc();
$newAI = $row['Auto_increment'];
}
$mysqli->close();
return $newAI;
}
answered Dec 4, 2019 at 14:55
select * from tablename order by ID DESC
that will give you row with id 22
Ben
51.5k36 gold badges127 silver badges148 bronze badges
answered Aug 23, 2012 at 6:02
1
In PHP:
$sql = mysql_query("select id from customers order by id desc");
$rs = mysql_fetch_array($sql);
if ( !$rs ) { $newid = 1; } else { $newid = $rs[newid]+1; }
thus $newid = 23 if last record in column id was 22.
skuntsel
11.6k11 gold badges44 silver badges67 bronze badges
answered Feb 13, 2015 at 13:27
1
I have the following table
Table structure:
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS `people` (
`name` varchar(10) NOT NULL,
`age` smallint(5) unsigned NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`name`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=latin1;
Insert some values:
INSERT INTO `people` (`name`, `age`) VALUES
('bob', 13),
('john', 25),
('steve', 8),
('sue', 13);
Executed Query:
SELECT MAX( `age` ) , `name` FROM `people` WHERE 1
Expected Result:
25, John
Generated Result
25, bob
We can achieve this by using this query
SELECT `age`, `name` FROM `people` ORDER BY age DESC LIMIT 1
Question 1 : What I made mistake here and why this MAX function is not return the relevant row information?
Question 2: Which one is good to use, to increase performance MAX function or ORDER BY clause?
Here are three examples that use SQL to find and select the row with the maximum value in a given column.
The examples work in most major RDBMSs, including MySQL, MariaDB, PostgreSQL, SQLite, Oracle, and SQL Server.
Sample Data
We’ll start with the following data:
SELECT * FROM PetShow;Result:
+---------+-----------+---------+ | PetId | PetName | Score | |---------+-----------+---------| | 1 | Wag | 85 | | 2 | Scratch | 3 | | 3 | Tweet | 65 | | 4 | Bark | 8 | | 5 | Ruff | 15 | | 6 | Woof | 20 | | 7 | Punch | 3 | +---------+-----------+---------+
Option 1
Here’s an example of selecting the row with the maximum value from the Score column in the above table:
SELECT
PetId,
PetName,
Score
FROM PetShow
WHERE Score = ( SELECT MAX(Score) FROM PetShow );Result:
+---------+-----------+---------+ | PetId | PetName | Score | |---------+-----------+---------| | 1 | Wag | 85 | +---------+-----------+---------+
We used the MAX() function within a subquery to find the maximum value, and returned the whole row with the outer query.
When there are Multiple Rows with the Max Value
Using this method, if there’s more than one row with the max value, all of them are returned.
Suppose we insert another row into our table with the same score as the existing max score:
INSERT INTO PetShow VALUES (8, 'Purr', 85);
SELECT * FROM PetShow;Our table now looks like this:
+---------+-----------+---------+ | PetId | PetName | Score | |---------+-----------+---------| | 1 | Wag | 85 | | 2 | Scratch | 3 | | 3 | Tweet | 65 | | 4 | Bark | 8 | | 5 | Ruff | 15 | | 6 | Woof | 20 | | 7 | Punch | 3 | | 8 | Purr | 85 | +---------+-----------+---------+
We can see that both Wag and Purr have got the highest score of 85.
Let’s run the previous query again to return the maximum value from that column:
SELECT
PetId,
PetName,
Score
FROM PetShow
WHERE Score = ( SELECT MAX(Score) FROM PetShow );Result:
+---------+-----------+---------+ | PetId | PetName | Score | |---------+-----------+---------| | 1 | Wag | 85 | | 8 | Purr | 85 | +---------+-----------+---------+
Both rows with the max values are returned as expected.
We can limit the result set to just one row if required. The exact code will depend on the RDBMS being used.
The LIMIT clause can be used with RDBSs such as PostgreSQL, MariaDB, MySQL, and SQLite:
SELECT
PetId,
PetName,
Score
FROM PetShow
WHERE Score = ( SELECT MAX(Score) FROM PetShow )
ORDER BY PetId ASC
LIMIT 1;Result:
+-------+---------+-------+ | PetId | PetName | Score | +-------+---------+-------+ | 1 | Wag | 85 | +-------+---------+-------+
In SQL Server, we can use the TOP clause:
SELECT TOP 1
PetId,
PetName,
Score
FROM PetShow
WHERE Score = ( SELECT MAX(Score) FROM PetShow )
ORDER BY PetId ASC;Result:
+-------+---------+-------+ | PetId | PetName | Score | +-------+---------+-------+ | 1 | Wag | 85 | +-------+---------+-------+
And in Oracle Database:
SELECT
PetId,
PetName,
Score
FROM PetShow
WHERE Score = ( SELECT MAX(Score) FROM PetShow )
ORDER BY PetId ASC
FETCH FIRST 1 ROW ONLY;Result:
+-------+---------+-------+ | PetId | PetName | Score | +-------+---------+-------+ | 1 | Wag | 85 | +-------+---------+-------+
Option 2
If we only want one row returned, we can actually do away with most of the other code and just get the first row out of the ordered results:
SELECT
PetId,
PetName,
Score
FROM PetShow
ORDER BY Score DESC
LIMIT 1;Result:
+---------+-----------+---------+ | PetId | PetName | Score | |---------+-----------+---------| | 1 | Wag | 85 | +---------+-----------+---------+
In SQL Server:
SELECT TOP 1
PetId,
PetName,
Score
FROM PetShow
ORDER BY Score DESC;Result:
+---------+-----------+---------+ | PetId | PetName | Score | |---------+-----------+---------| | 1 | Wag | 85 | +---------+-----------+---------+
And in Oracle Database:
SELECT
PetId,
PetName,
Score
FROM PetShow
ORDER BY Score DESC
FETCH FIRST 1 ROW ONLY;Result:
+---------+-----------+---------+ | PetId | PetName | Score | |---------+-----------+---------| | 1 | Wag | 85 | +---------+-----------+---------+
Option 3
Another way to select the row with the maximum value is to join the table on itself, like this:
SELECT
p1.PetId,
p1.PetName,
p1.Score
FROM PetShow p1
LEFT JOIN PetShow p2 ON p1.Score < p2.Score
WHERE p2.PetId IS NULL;Result:
+---------+-----------+---------+ | PetId | PetName | Score | |---------+-----------+---------| | 1 | Wag | 85 | | 8 | Purr | 85 | +---------+-----------+---------+
As with the earlier example, we can limit the results to one row (or some other number) if required.
Introduction to SQL MAX()
SQL MAX() is one of the aggregate functions available in SQL that helps us fetch the greatest value among multiple values specified in the column values of records, the expression consisting of the column that is mentioned. When a query is used to retrieve the data that report related and contains a group by a statement, the MAX() function is used to get the greatest value of a particular column or columns based on the grouping function.
Syntax and Usage
The syntax of the MAX function in SQL is given below:
SELECT MAX(expression)
FROM table_name
[WHERE restriction];Where expression can be any name of the column of the table or a formula built up using column names and static literal values or variables, the table_name is the name of the table from which you want to retrieve the records and calculate the greatest value from one of their columns. The use of the FROM table name clause is required. One optional thing is the use of a where clause to mention the conditions and restrictions that the records of the table should fulfil to consider that record’s column value for fetching the greatest value.
When where clause is used, only filtered out data is considered for the greatest calculation by MAX() function. The MAX() function collects all the values of the expression mentioned in it and adds them up, which is further divided by the number of values or expressions that were added to find out the final greatest value. For example, consider that we have to find out a greatest of 50, 100, 150, and 200. Then the max function will internally compare each of their values and finally derive 200 as the greatest maximum value.
Examples of SQL MAX()
Given below are the examples of SQL MAX():
Example #1 – Using a single column.
Let us firstly consider a simple example that we used above. We will calculate the greatest value of SQL numbers using the MAX() function. Let us create one simple table named numbers and store the num column value in it.
We will use the following query statement to create our table.
Code:
CREATE TABLE numbers (num INT) ;Now, we will insert the above records in the table.
Code:
INSERT INTO numbers(num) VALUES (50), (100), (150), (200);Let us now retrieve the records once.
Code:
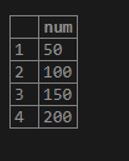
SELECT * FROM numbers ;Output:
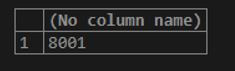
Now, we will calculate the greatest of num column of numbers table using MAX() function using the following query statement.
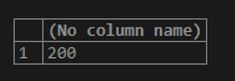
Code:
SELECT MAX(num) FROM numbers ;Output:
Example #2 – Using the distinct function.
We can use the distinct function in MAX() function to consider the column’s repetitive values only once while fetching the greatest value. Suppose that we insert some more records in the numbers table using the following query statement.
Code:
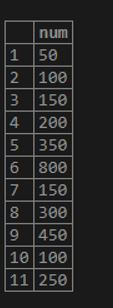
INSERT INTO numbers(num) VALUES (350), (800), (150), (300),(450), (100), (250);
select * from numbers;Output:
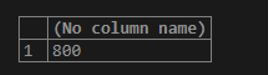
If we use SELECT MAX(num) FROM numbers; statement to calculate the greatest value of num column, then each of the values will be considered while fetching the greatest value.
Code:
SELECT MAX(DISTINCT(num)) FROM numbers ;The output will be the same as that of the first query without a distinct function but internally the calculation of greatest value by MAX() function will only consider the column values that are repeated such as 100 and 150 only once.
The output of both of the above queries is as shown below.
Output:
Example #3 – Using formula.
We can use the MAX() function expressions to consider the value evaluated by fetching each of the formula or expression values containing column value to calculate the greatest value.
Let us consider one example; we will calculate the greatest of all the columns after they are multiplied by 10 and added by 1.
Code:
SELECT MAX((num * 10) + 1) FROM numbers ;Output:
We can even use the existing functions such as SUM() and COUNT() inside the MAX() function.
Example #4 – Using group by.
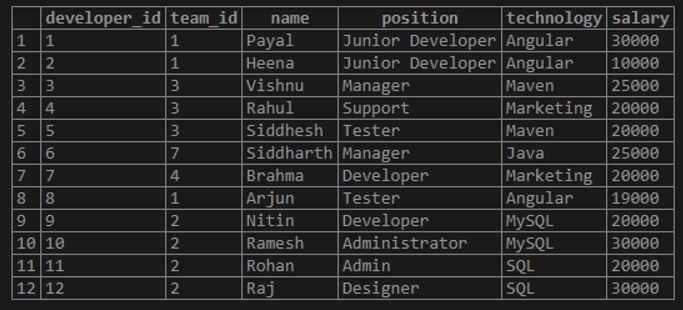
When we have complex tables and relations between multiple tables, we have to query those tables using joins to retrieve data, usually for reporting purposes that consist of summarized data. Even in some scenarios, the data from a single table need to be manipulated to get summarized data. Suppose that we have one table named workers consisting of the following records in it that are retrieved by executing a simple select query on that table.
Code:
SELECT * FROM workers;Output:
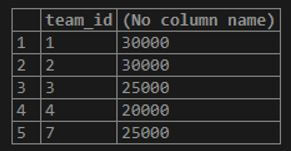
Now, the situation is such that we have to calculate the greatest salary of the workers per team. The output should consist of the team id and the greatest salary of that team. For this, we will have to use the group by statement and group the records based on team id and calculate the greatest salary by using MAX() function.
Code:
SELECT
team_id,
MAX(salary)
FROM
workers
GROUP BY team_id ;The execution of the above query statement will give the following output along with team ids and their respective greatest salaries.
Output:
Conclusion
We can use the MAX() function in SQL to fetch the greatest value of the columns of the tables or greatest of expressions that involve column values and even calculate the greatest value of columns in the grouped manner using the GROUP BY statement.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “SQL MAX()” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.
- SQL ORDER BY Ascending
- SQL ORDER BY Alphabetical
- SQL NOT Operator
- SQL Temporary Table