Задача — построить график функции sin(2*3.14*i/50)/cos(2*3.14*i/50) на Python
while i<=50:
y=math.sin(2*3.14*i/50)/math.cos(2*3.14*i/50)
if(y>max):
max=y
elif(y<min):
min=y
i+=1
print('n')
j=1
while j<=50:
y= math.ceil(((math.sin(2*3.14*i/50)/math.cos(2*3.14*i/50))-min)*50/(max-min))
if y==50-j:
print('*')
else:
print (' ')
j+=1
print(max)
print(min)
При запуске выходит ошибка:
ZeroDivisionError: float division by zero.
Проверял — значения максимума и минимума присваиваются верно, значит беда во внутреннем цикле. Зафэйлил с пробелами, или же в Python так вообще делать нельзя?
Обновление
Изначально:
import math
min=max=math.sin(2*3.14/50)/math.cos(2*3.14/50)
i=1
Значения max = 15.7029740933..., min = -16.53312943.... Отсчет i начинается с 1, изначально max = min, а затем присваиваем значения.
Вывел min и max перед ошибкой. Оба значения 0.126264… Хотя если убрать внутренний цикл — все нормально. По идее должно 50 раз вывести на экран значения max и min (15.703… и -16.533).
задан 25 окт 2015 в 16:19
10
Если min=max хотя бы на одной (первой) итерации цикла, то это достаточно чтобы ошибка деления на ноль (ZeroDivisionError) возникла, что прерывает нормальное исполнение кода.
Чтобы лучше понять что происходит, попробуйте выбросить весь код и оставьте только min:
min = 0
while True:
1 / min # выбрасывается ошибка на первой итерации
min += 1
В этом коде min=0 только на одной (первой) итерации цикла, но этого достаточно чтобы ошибка деления на ноль завершила программу (дальнейшие итерации не состоятся). Eсли min=1 в начале поставить вместо min=0, то это создаст бесконечный цикл с разными значениями min на каждой итерации.
ответ дан 26 окт 2015 в 12:59
jfsjfs
51.8k11 золотых знаков107 серебряных знаков306 бронзовых знаков
Для подобной задачи обычно используют такой подход:
- Первым делом считаются точки по которым строится график (тут же можно посчитать максимум и минимум)
- По точкам строим график
А для циклов в питоне лучше использовать for. Так код легче читается и в таком цикле сложнее сделать ошибку. while в питоне достаточно редкий гость.
Если сложить все вместе, то получится примерно такой код:
import math
max_y=min_y=None
ys=[]
for i in range(1,51):
y=math.sin(2*3.14*i/50)/math.cos(2*3.14*i/50)
max_y = max(y, max_y) if max_y is not None else y
min_y = min(y, max_y) if min_y is not None else y
ys.append(y)
spaces = ' '*50
for y in ys:
i = math.ceil((max_y - y)*50/(max_y - min_y))
print(i)
print(spaces[:i] + '*' + spaces[i+1:])
ответ дан 2 ноя 2015 в 19:36
Если задача нарисовать звездочками график,
у меня получился такой код:
import math
min=max=math.sin(2*3.14/50)/math.cos(2*3.14/50)
i=1
while i<=50:
y=math.sin(2*3.14*i/50)/math.cos(2*3.14*i/50)
if(y>max):
max=y
elif(y<min):
min=y
i+=1
print(max)
print(min)
j=1
while j<=50:
y= math.ceil(((math.sin(2*3.14*j/50)/math.cos(2*3.14*j/50))-min)*50/(max-min))
for pr in range(int(y)):
print (" ",end='');
print ("*")
j+=1
ответ дан 29 окт 2015 в 8:19
In Python, a ZeroDivisionError is raised when a division or modulo operation is attempted with a denominator or divisor of 0.
What Causes ZeroDivisionError
A ZeroDivisionError occurs in Python when a number is attempted to be divided by zero. Since division by zero is not allowed in mathematics, attempting this in Python code raises a ZeroDivisionError.
Python ZeroDivisionError Example
Here’s an example of a Python ZeroDivisionError thrown due to division by zero:
a = 10
b = 0
print(a/b)
In this example, a number a is attempted to be divided by another number b, whose value is zero, leading to a ZeroDivisionError:
File "test.py", line 3, in <module>
print(a/b)
ZeroDivisionError: division by zero
How to Fix ZeroDivisionError in Python
The ZeroDivisionError can be avoided using a conditional statement to check for a denominator or divisor of 0 before performing the operation.
The code in the earlier example can be updated to use an if statement to check if the denominator is 0:
a = 10
b = 0
if b == 0:
print("Cannot divide by zero")
else:
print(a/b)
Running the above code produces the correct output as expected:
Cannot divide by zero
A try-except block can also be used to catch and handle this error if the value of the denominator is not known beforehand:
try:
a = 10
b = 0
print(a/b)
except ZeroDivisionError as e:
print("Error: Cannot divide by zero")
Surrounding the code in try-except blocks like the above allows the program to continue execution after the exception is encountered:
Error: Cannot divide by zero
Track, Analyze and Manage Errors With Rollbar
Managing errors and exceptions in your code is challenging. It can make deploying production code an unnerving experience. Being able to track, analyze, and manage errors in real-time can help you to proceed with more confidence. Rollbar automates error monitoring and triaging, making fixing Python errors easier than ever. Try it today!
If the number (positive or negative) is divided by zero in mathematics, the output will be undefined or of no value. Similarly, if the number (integer or float) is divided by zero in Python, the interpreter will throw a “ZeroDivisionError”. To resolve this error, various solutions are used in Python, such as the “if” statement and the “try-except” block.
This blog provides the reason for the error “float division by zero” with their solutions and examples. The following aspects are followed in this article:
- Reason: Dividing Floating Point Number By “0”
- Solution 1: Use if-Statement
- Solution 2: Use try-except Block
So, let’s get started!
Reason: Dividing Floating Point Number By “0”
The prominent reason which causes this error in Python is when a user tries to divide the floating point number by “0” in a program. The error snippet is shown below:
The above snippet shows “ZeroDivisionError” because the floating point number is divided by “0”.
Solution 1: Use if-Statement
To resolve this error, you can use the “if” statement to check if the divisor is equal to “0” or not. Here is a code example:
Code:
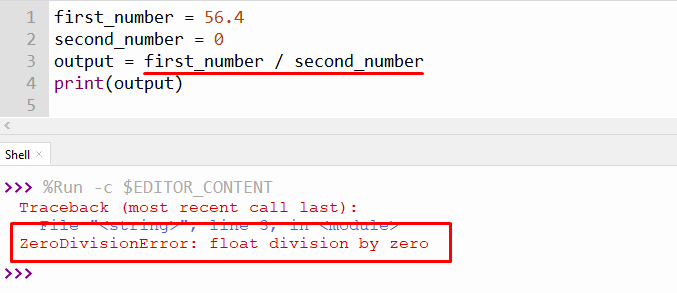
first_number = 56.4
second_number = 0
if second_number!=0:
output = first_number / second_number
else:
output = 0
print(output)
In the above code:
- The “if” statement is utilized to check whether the divisor or the number which we are dividing by is equal to zero or not.
- If the number is not equal to zero, then the “if” block statement is executed and shows the division result.
- The else block is executed when the divisor is equal to zero.
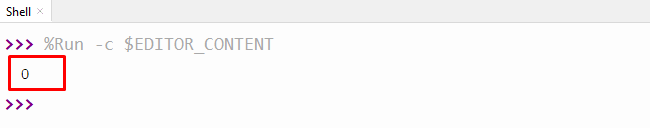
The above output shows the value “0” because the divisor number is equal to “0”.
Solution 2: Use try-except Block
Another solution to handle this particular error is using the “try-except” block in the program. Let’s understand this concept via the below-given Python program.
Code:
first_number = 56.4
second_number = 0
try:
output = first_number / second_number
except ZeroDivisionError:
output = 0
print(output)
In the above code:
- The “try” block executes when the divisor is not equal to zero.
- If the dividing number/divisor is equal to zero, then the “except” block handles the “ZeroDivisionError” and assigns a “0” value to the output variable.
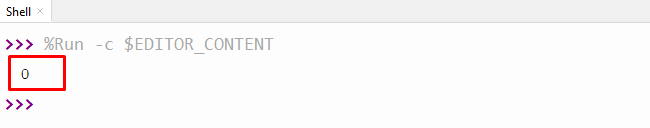
The output shows that the try-except block successfully resolves the stated error.
That’s it from this guide!
Conclusion
The “ZeroDivisionError: float division by zero” occurs when a user tries to divide a floating point number by the value “0” in Python. To resolve this error, you can use the “if-else” statement to check whether the input number is equal to zero or not before performing the calculation. The “try-except” block is also used to handle the “ZeroDivisionError” in Python programs. This blog explained how to resolve the “float division by zero” error in Python using appropriate examples.

We will introduce why ZeroDivisionError occurs and how we can easily resolve it with examples in Python.
ZeroDivisionError: Float Division by Zero in Python
While working on mathematical equations or code that includes mathematical expressions based on results, it is a common error. In Python, a ZeroDivisionError occurs when attempting to divide a number by zero.
In mathematics, it is impossible to divide any number by zero. Whenever there is a situation through our code, dividing a number by zero will throw an exception.
Let’s write a program to throw this exception using Python, as shown below.
firstNum = 10
secondNum = 5
thirdNum = 7
forthNum = 5
print((firstNum + thirdNum)/(secondNum - forthNum))
Output:
As we can see from the above example, the subtraction of the denominators resulted in 0, which we got the error ZeroDivisionError. Let’s test another example with float numbers instead, as shown below.
firstNum = 10.0
secondNum = 5.0
thirdNum = 7.0
forthNum = 5.0
print((firstNum + thirdNum)/(secondNum - forthNum))
We will get the following error message now.
As we can see from the above examples, whenever our result in the denominator is zero, it will crash our application and could also lose important data during an important program run.
It is important to deal with this kind of error properly, to protect our program from crashing and losing any important information.
There are two ways to resolve this issue, which we will discuss in detail. The first solution is to use an if-else statement.
We will always ensure that to execute division, the difference of denominators is always bigger than zero. If the difference between both denominators equals zero, it will just output the message saying that we cannot divide by zero.
The code of the solution is shown below.
firstNum = 10.0
secondNum = 5.0
thirdNum = 7.0
forthNum = 5.0
nominators = firstNum + thirdNum
denominators = secondNum - forthNum
if denominators != 0:
print((firstNum + thirdNum)/(secondNum - forthNum))
else:
print("Cannot divide by zero.")
When we run this code, it will give the following output.
As we can see from the above example, instead of throwing an error, our code outputs the phrase we wanted it to output if the result of denominators results in 0. Our second solution uses the try and except methods, as shown below.
firstNum = 10.0
secondNum = 5.0
thirdNum = 7.0
forthNum = 5.0
try:
print((firstNum + thirdNum)/(secondNum - forthNum))
except:
print("Cannot divide by zero.")
The code will try to run the expression; if it runs successfully, it will display the result; otherwise, it will display the phrase saying that we cannot divide by zero. The output of the following code is shown below.
It is very important to note that these solutions only handle the error when we know the source of the error is because the denominator is zero, but if you are not sure if the denominator could be zero, it is better to check it before doing the operation.
In conclusion, the ZeroDivisionError: float division by zero is a common exception in Python that occurs when attempting to divide a float by zero.
This exception can be handled using an if statement and a try-except block. To avoid crashing or producing incorrect results, we must handle this exception in our code.
The super class of ZeroDivisionError is ArithmeticError. This exception raised when the second argument of a division or modulo operation is zero. The associated value is a string indicating the type of the operands and the operation.
In simple term in any arithmetic operation when value divided by zero then in Python throw ZeroDivisionError.
You can see complete Python exception hierarchy through this link : Python: Built-in Exceptions Hierarchy.
Example :
In the Python program will throw ZeroDivisionError in case of num_list is not having any element then it’s length become 0 and while executing this program will through ZeroDivisionError.
num_list=[]
total=0
avg=total/len(num_list)
print("Average:"+avg)
Output
ZeroDivisionError : Division by Zero
Solution
While implementing any program logic and there is division operation make sure always handle ArithmeticError or ZeroDivisionError so that program will not terminate. To solve above problem follow this example:
num_list=[]
total=0
try:
avg=total/len(num_list)
print("Average:"+avg)
except ZeroDivisionError:
print ("Zero Division Error occurred")
Output
Zero Division Error occurred.
In this above modified code applied exception handling for particular code section so that program will not terminate.
Learn Python exception handling in more detain in topic Python: Exception Handling
Let me know your thought on it.
Happy Learning !!!